Covalent Bonding
This lesson covers:
- The structure and formation of covalent bonds
- The different ways we can represent covalent bonds
- The different types of covalent structures
In covalent bonding, are electrons transferred between atoms, or shared between atoms?
Transferred
Shared
|
Covalent bonds form between ________ atoms.
non-metallic
metallic
|
In a water molecule, the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are held together by bonds.
Before bonding, each hydrogen atom requires extra electron to complete its outer shell, and so wants to form covalent bond. Meanwhile, each oxygen atom requires more electrons, and so wants to form covalent bonds.
This means that water molecules will be made from hydrogen atoms and oxygen atom, so that all the atoms obtain full outer shells.
|
Which of the following is an example of a simple molecule?
Neon
Graphite
Ammonia
Sodium chloride
|
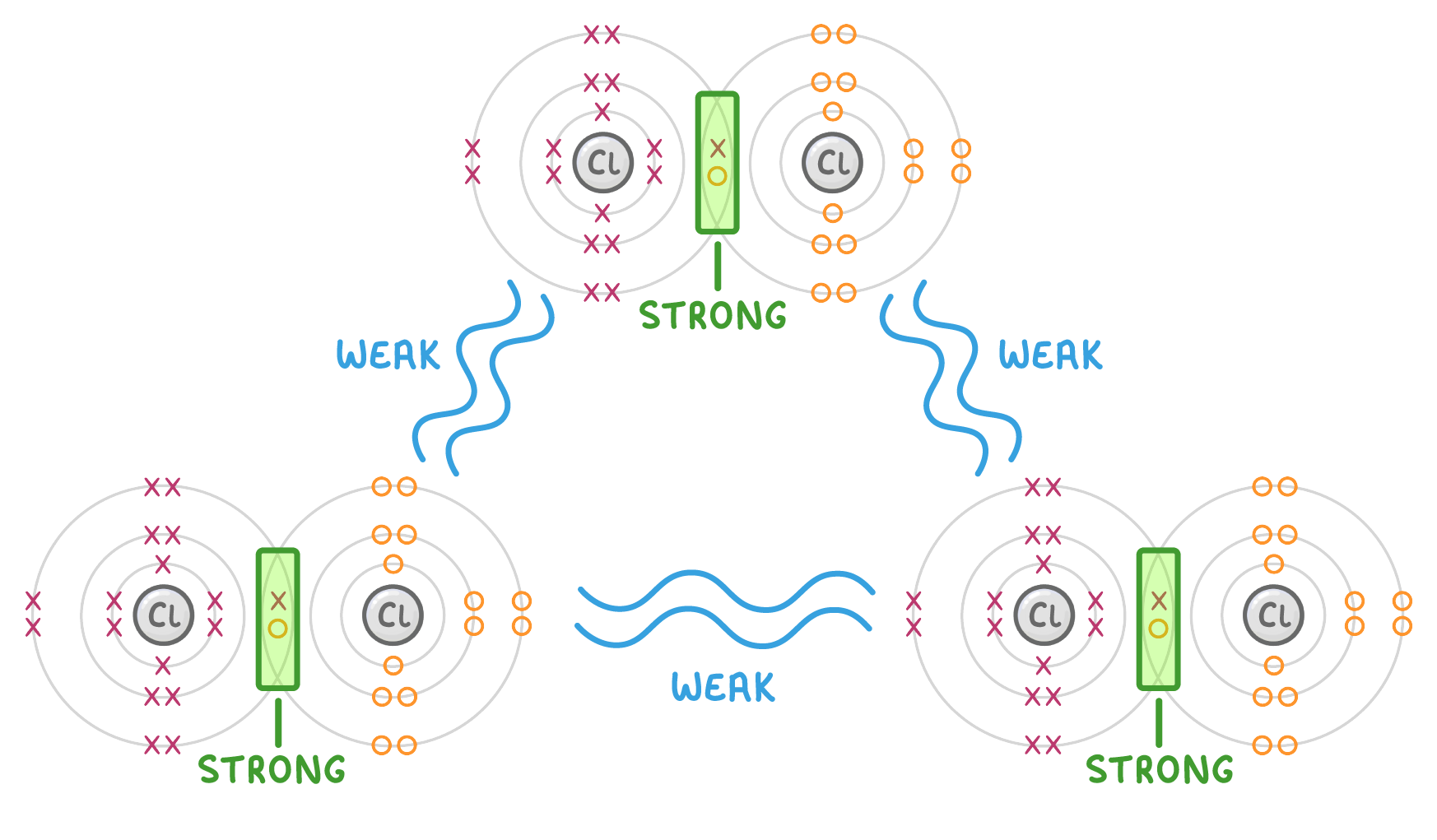
A simple molecule has multiple atoms covalently bonded together. These covalent bonds between atoms are very strong.
However, the forces of attraction between separate molecules are weak, and so simple molecules are easily separated from each other.
This is why many simple molecules have low melting and boiling points - the intermolecular forces (forces between molecules) only require a small amount of energy to break, which means they'll break at low temperatures.
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show covalent bonding in an ammonia molecule, NH3 (only include the outer shell of electrons). (You may need a periodic table) When you're ready to check your answer, click the 'Continue' button. |
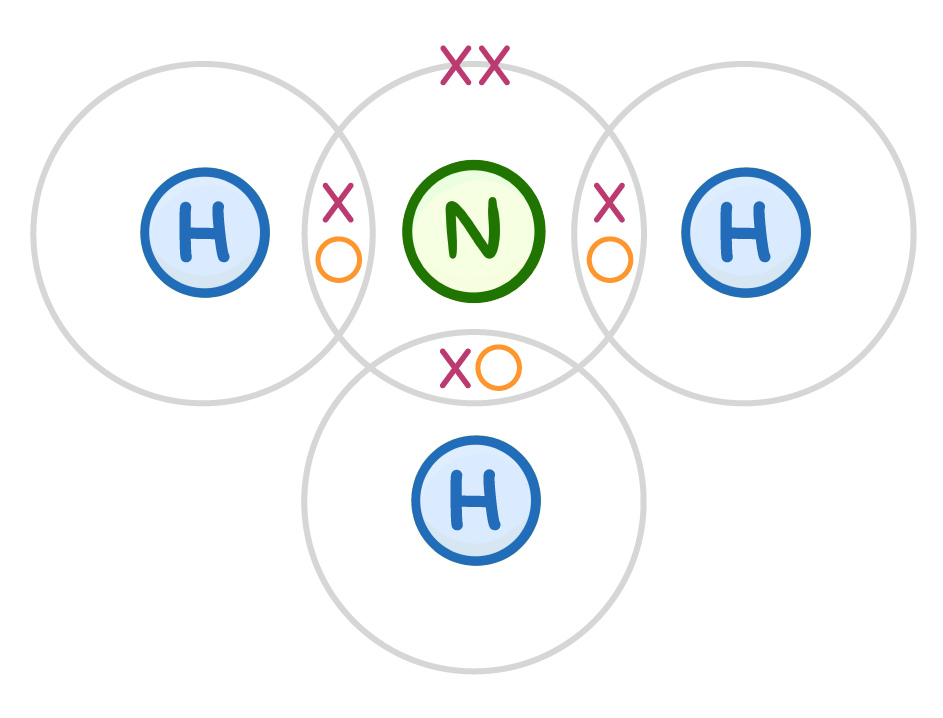 |
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show covalent bonding in a chlorine molecule, Cl2 (only include the outer shell of electrons). (You may need a periodic table) When you're ready to check your answer, click the 'Continue' button. |
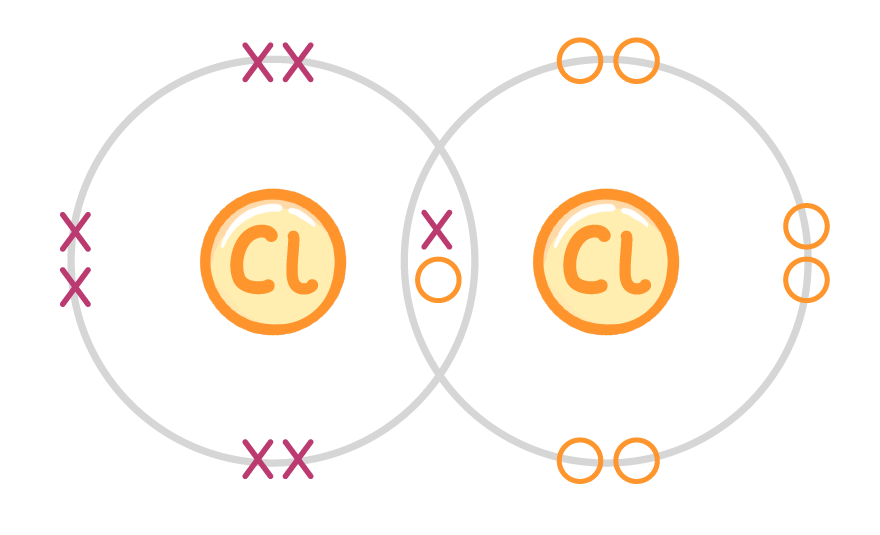 |