Ionic Compounds
This lesson covers:
- The structure of ionic compounds
- The properties of ionic compounds
- How to work out the formula of an ionic compound
positive / negative / electrostatic / ionic / covalent
Metals normally form ions which have a charge, while non-metals form ions with a charge.
Ions are attracted to other ions with the opposite charge, due to forces.
|
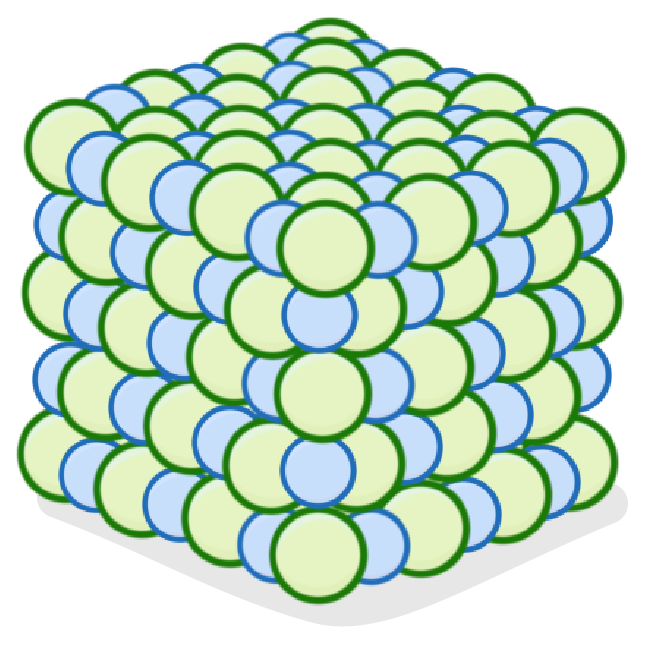
Ionic structures involve many ions bonded together via bonds.
The solid arranges itself into a regular 3D structure known as a la.
|
Select three properties that ionic compounds have:
Conduct electricity when solid
Conduct electricity when liquid
Low melting and boiling points
High melting and boiling points
High strength bonds
Weak strength bonds
|
Why can ionic compounds only conduct electricity when in liquid/molten, or aqueous form?
Water is required to conduct electricity
Solid ionic compounds do not contain charged particles
The negative ions can approach other negative ions
The ions are free to move and carry charge
|
strong / weak / high / low / energy / water
Ionic compounds have relatively melting and boiling points.
This is because ionic bonds are very , and a high amount of is required to break the bonds.
|

Select the correct formula for the ionic compound potassium chloride:
K2Cl
KCl
NaCl
KCl2
|

Remember that ionic compounds arrange their ions in a way that creates a neutral overall charge.
For example, magnesium ions have a 2+ charge, while chloride ions have a 1- charge.
Therefore, for every magnesium ion, two chloride ions will be attracted to it, resulting in an overall neutral charge.
Select the correct formula for a nitrate ion:
NO3+
N3-
NO3-
NO3
|
Potassium ions and carbonate ions can form an ionic compound.
Potassium ions have a + charge, while carbonate ions have a - charge.
This means every carbonate ion will ionically bond with potassium ions.
|
What is the chemical formula for the compound calcium sulfate?
Ca2SO4
CaSO4
CaSO42+
Ca(SO4)2
|
Make sure you learn the formulae for the following ions:
- Hydroxide: OH-
- Sulphate: SO42-
- Nitrate: NO3-
- Carbonate: CO32-
- Ammonium: NH4+