Naturally Occurring Polymers
This lesson covers:
- How amino acids combine to form 'polypeptides' (and proteins)
- How nucleotides combine to form 'nucleic acids' (and DNA)
- How sugars combine to form carbohydrates
Which monomers combine to form a polypeptide?
Sugars
Nucleotides
Amino acids
Dicarboxylic acids and diols
|
What do polypeptides form once they fold up?
A protein
A fat molecule
A starch molecule
|
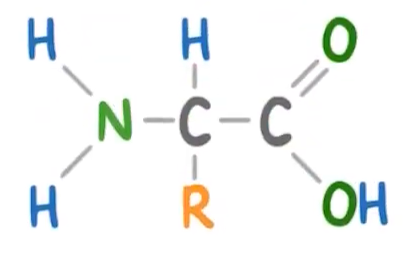
The above molecule is an amino acid.
Which functional groups does an amino acid have?
(Select all that apply)
A carboxylic acid group
An ester group
An amino group
An 'R' group
|
What type of reaction takes place when amino acids combine to form a polypeptide?
Addition reaction
Condensation reaction
Combustion reaction
|
Which of the following names can be used to refer to the bond formed in a condensation reaction between amino acids?
(Select all that apply)
Peptide bond
Amide link
Amino bond
Amide bond
|
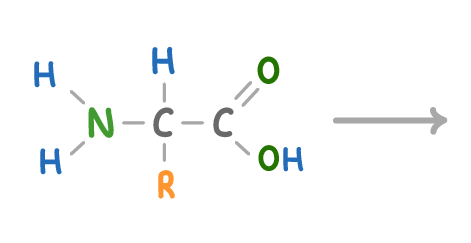
Using pen and paper, complete the equation for the condensation reaction between amino acids.
(Click 'Continue' when you're ready to check your answer)
|
Which monomers combine to form DNA?
Dicarboxylic acids and diols
Amino acids
Nucleotides
Sugars
|
Which letters do we use to represent the four nucleotides that make up DNA?
(Select all that apply)
A
C
T
P
G
|
one / two / three / helix / damage / pathogens
DNA molecules consist of polymer chains that coil around each other in a double . This helps to protect the DNA from .
|
What are the three elements that make up carbohydrates?
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Carbon
Hydrogen
|
Which of the following are examples of carbohydrate polymers?
(Select all that apply)
Glycogen
Starch
Polypeptide
Cellulose
|
Which of the following are examples of carbohydrate monomers?
(Select all that apply)
Fructose
Amino acids
Fatty acids
Glucose
|