Addition Polymers
This lesson covers:
- How alkenes can combine in an 'addition reaction' to become a long chain polymer
- How to the draw 'monomer units' and 'repeating units' of a polymer
- How to name polymers
What name is given to the small molecules that combine together to form a polymer?
Hydrocarbons
Compounds
Monomers
|
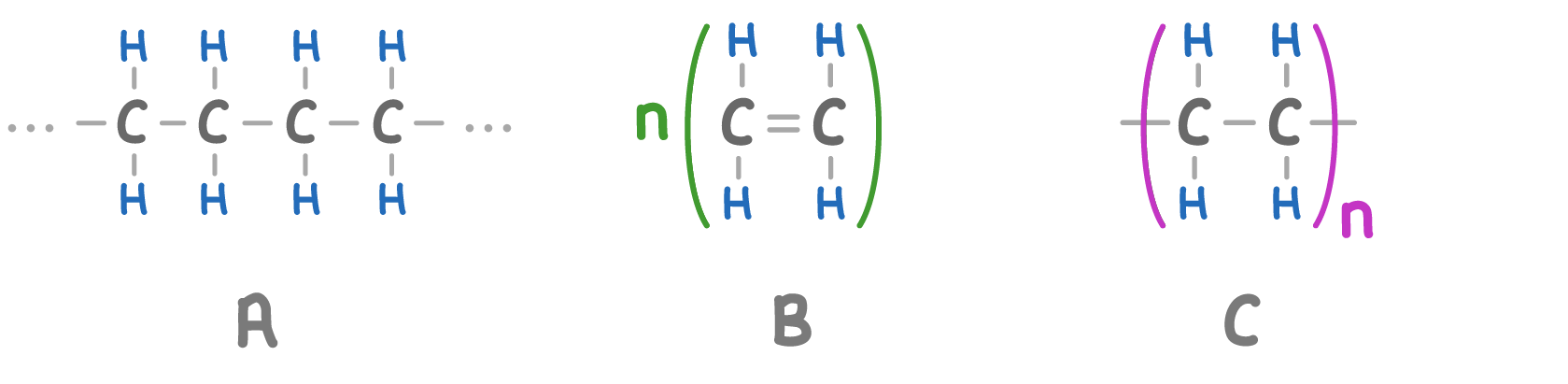
Match the letters A to C on the diagram above with the following labels:
Repeating unit:
Polymer:
Monomer:
|
Which of the following does not contain a C=C double bond?
Poly(propene)
Propene
Bromopropene
|
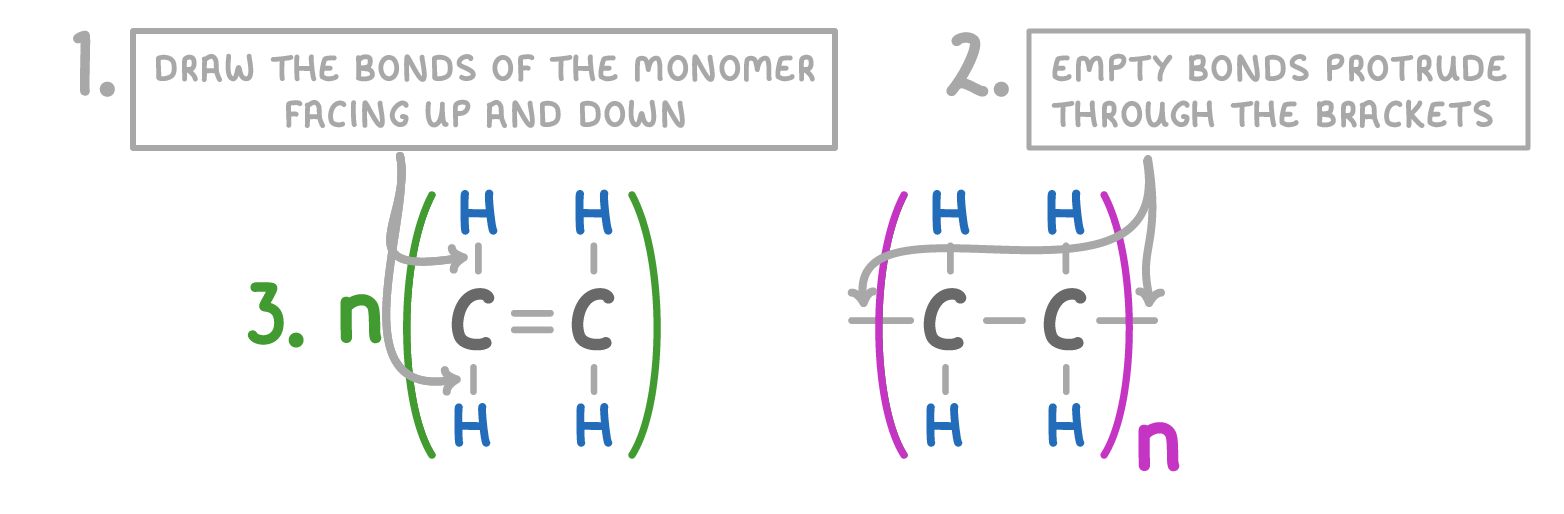
The three things to remember when drawing monomers and repeating units:
- Draw the bonds of the monomer vertically up and down.
- Have the empty bonds go through the brackets in the repeating unit.
- Have the 'n' to signify a large number of monomers and repeating units.
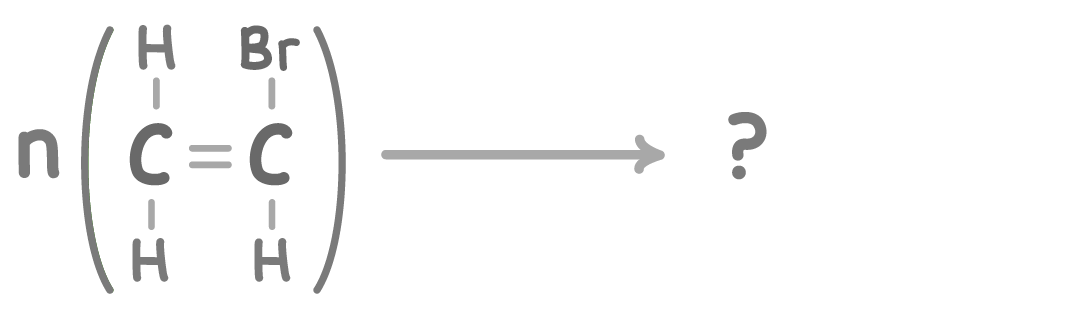
Using pen and paper, complete the equation above by drawing the repeating unit.
When you're ready to check your answer, press 'Continue'.
|
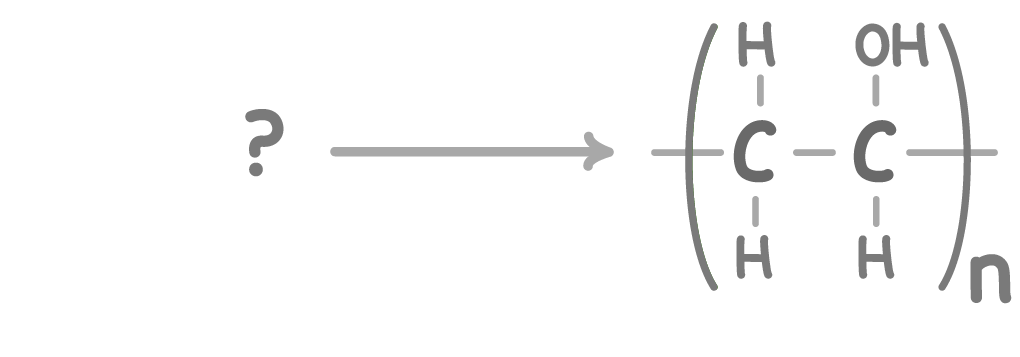
Using pen and paper, complete the equation above by drawing the monomer.
When you're ready to check your answer, press 'Continue'.
|
How to name polymers
- Take the alkene name
- Put brackets around it
- Add 'poly' to the front of the name, before the first bracket.
So ethene would become , while chloroethene would become .
|
Many bromopropene molecules combine in an addition reaction to form a polymer.
What is the name of the polymer formed?
|
What is the name of the monomer that would make the polymer poly(tetrafluoroethene)?
Fluoroethene
Chloropropene
Tetrafluoroethene
Phenylethene
|
A is a large molecule that is made from multiple smaller monomers.
|
Alkenes join together by __________ polymerisation.
positive
addition
condensation
|
Which of these could not be used as a monomer in addition polymerisation?
Propene
Ethene
Butane
Butene
|