Hydrocarbons
This lesson covers:
- What 'organic chemistry' is
- What a 'hydrocarbon' is
- What an 'alkane' is
- The alkanes general formula: CnH2n+2
- What 'saturated' means for alkanes
Isomers |
Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas, this means they are made of the same atoms, but the atoms are arranged differently. |
 |
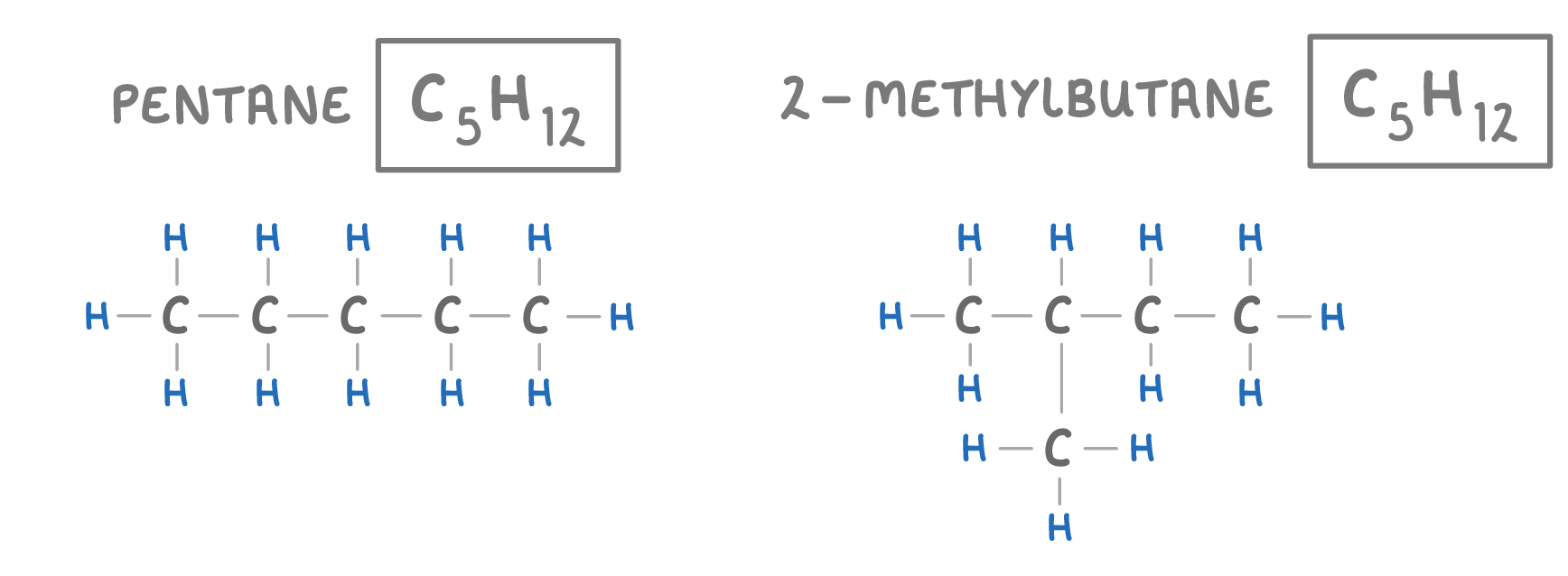 For example, the two molecules above both have the formula C5H12 - meaning 5 carbon atoms and 12 hydrogen atoms. However the atoms are arranged differently, which is why they have different names. |
Organic chemistry is about molecules that contain which element?
Iron
Magnesium
Argon
Carbon
|
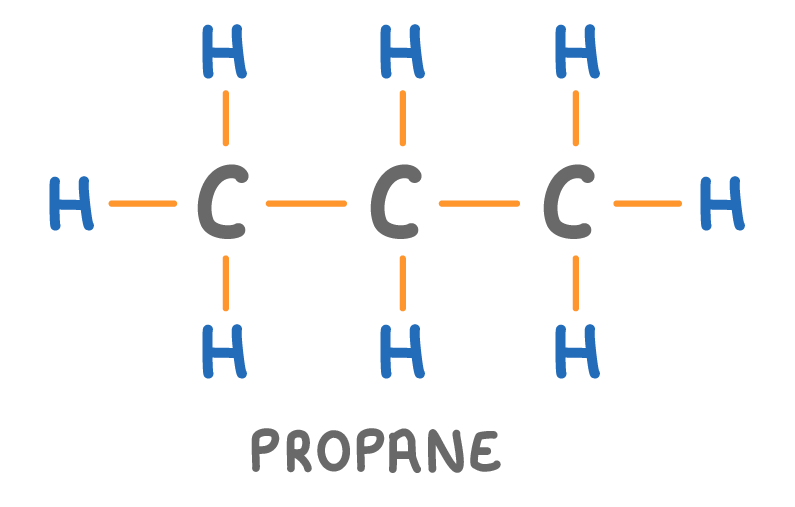
Is the molecule above a hydrocarbon?
Yes
No
|
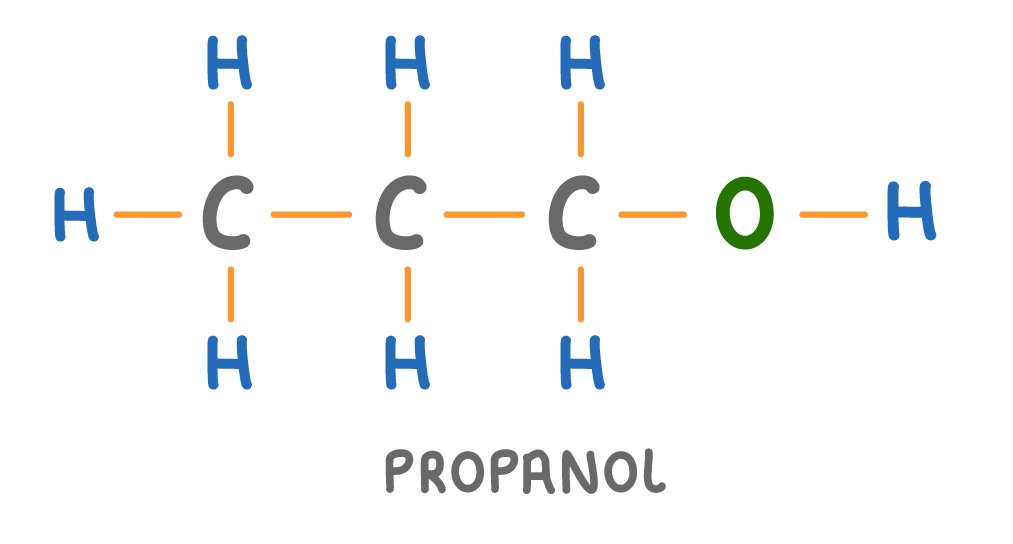
Is the molecule above a hydrocarbon?
Yes
No
|
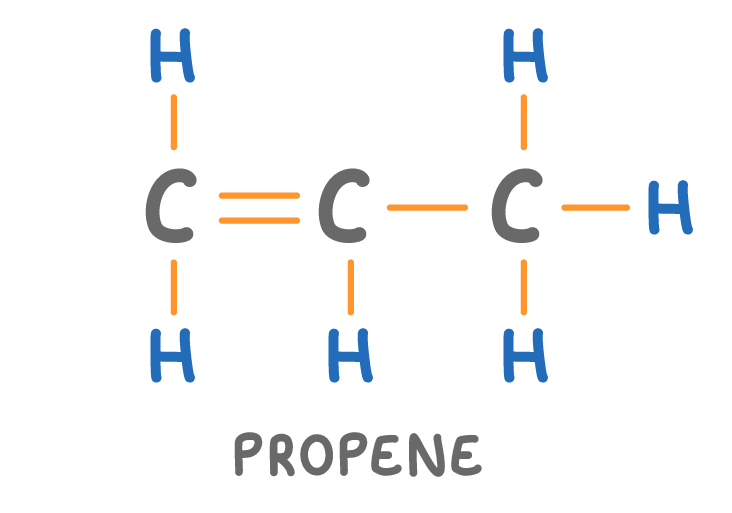
Is the molecule above a hydrocarbon?
Yes
No
|
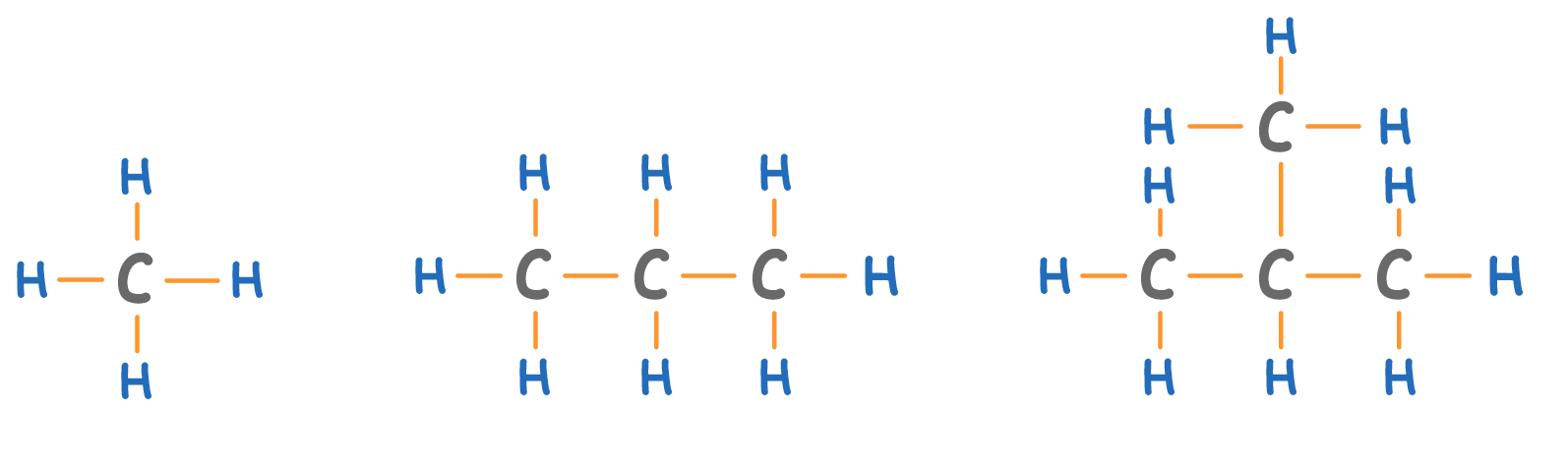
Alkanes are a homologous series of molecules that contain:
- Only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Only single bonds (alkanes have no double bonds).
What is the definition of a homologous series?
|
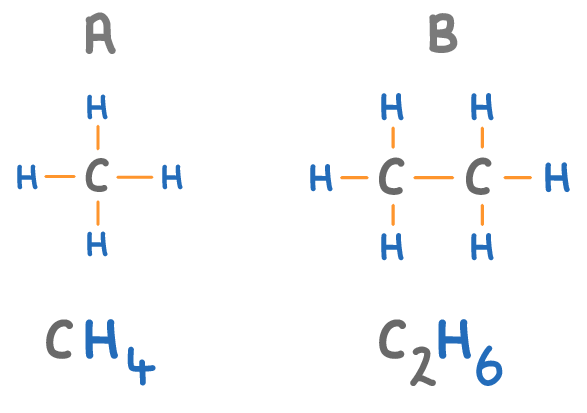
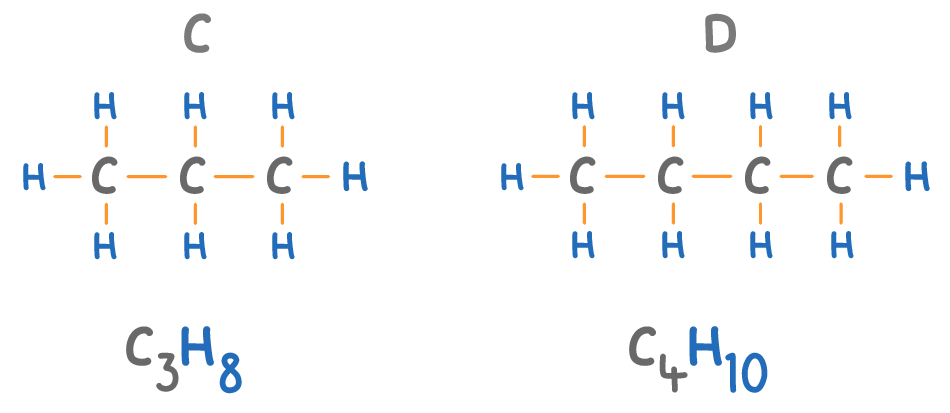
The names of alkanes always end in 'ane'.
Match the molecules A to D on the diagram above with their names:
Methane:
Butane:
Ethane:
Propane:
|
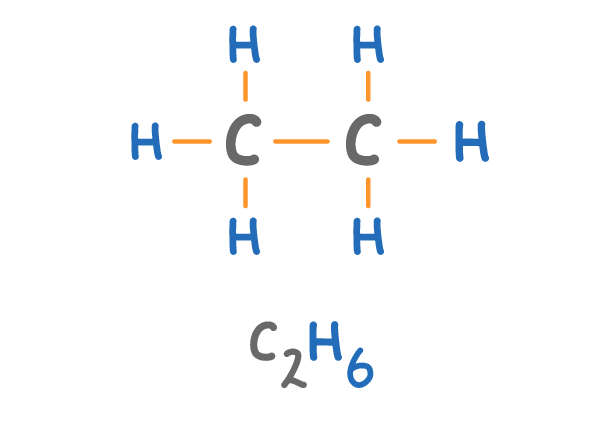
Which alkane is shown above?
Ethane
Propane
Methane
Butane
|
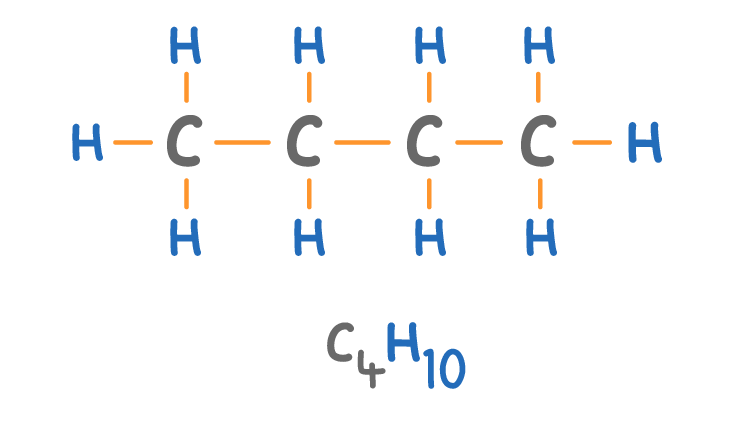
Which alkane is shown above?
Ethane
Butane
Methane
Propane
|
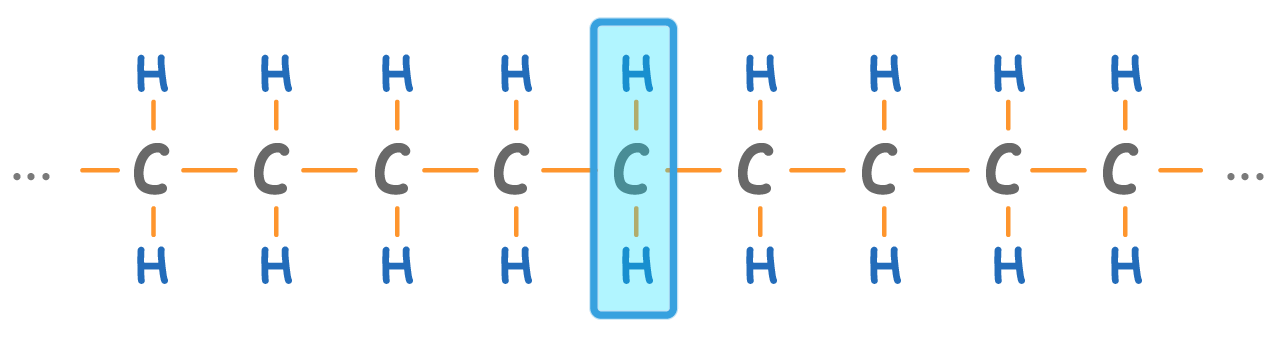
The alkane 'chain' can be very long. Longer alkanes simply have more CH2 groups (highlighted above) in the chain.
Each homologous series has its own general formula, which allows you work out how many atoms of each element a molecule will have.
What is the general formula for alkanes?
(Remember that 'n' represents the number of carbon atoms)
CnH2n+2
CnHn
CnH2n
|
How many hydrogen atoms are there in an alkane with 5 carbon atoms?
hydrogen atoms
|
An alkane only has single covalent bonds. There are no double bonds or triple bonds.
What is another way to describe hydrocarbons with only single bonds?
Unsaturated
Saturated
Lone molecules
|
What is the definition of a hydrocarbon?
|