Types of Oxides (Amphoteric/Neutral)
This lesson covers:
- How to categorise oxides as acidic, basic, or amphoteric
- The factors that determine if an oxide will be acidic, basic, or amphoteric
- Examples of acidic, basic, and amphoteric oxides
Acidic oxides & basic oxides
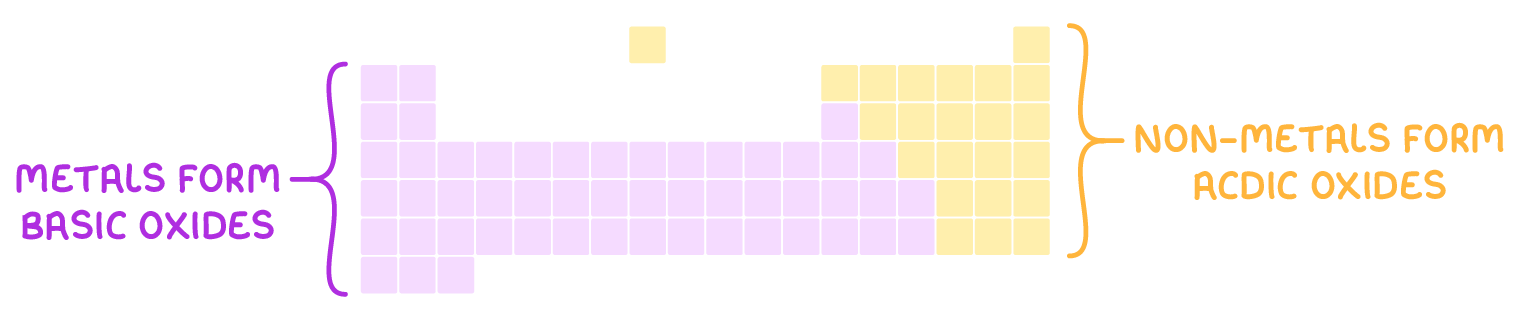
Oxides, compounds containing oxygen and another element, are often classified based on their reactions:
Acidic oxides - react with bases to produce salts and water. They are typically formed by non-metals, which are located on the right side of the periodic table.
| Examples of acidic oxides |
|---|
| CO |
| NO |
| SO |
Basic oxides - react with acids to also form salts and water. These oxides usually come from metals found on the left side of the periodic table.
| Examples of basic oxides |
|---|
| NaO |
| CaO |
| CuO |
Amphoteric oxide properties
Amphoteric oxides exhibit both acidic and basic properties:
- Amphoteric oxides can react with both acids and bases, forming salts and water in each reaction.
- They are generally formed by elements situated near the metal-nonmetal border on the periodic table.
Example: Reactions involving amphoteric aluminium oxide
Aluminium oxide (Al2O3) can react with both acids and bases.
- It acts like a base when reacting with an acid (hydrochloric acid):
- Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
- It acts like an acid when reacting with a base (sodium hydroxide):
- Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Other notable amphoteric oxides include zinc oxide (ZnO) and lead(II) oxide (PbO).
Which type of oxide reacts with bases to produce salts and water?
Amphoteric oxides
Acidic oxides
Basic oxides
|
Which of the following is an example of an acidic oxide?
Na2O (sodium oxide)
Al2O3 (aluminium oxide)
CO2 (carbon dioxide)
|
Which type of oxide is typically formed by non-metals?
Amphoteric oxides
Basic oxides
Acidic oxides
|
Which of the following is an example of a basic oxide?
Na2O (sodium oxide)
Al2O3 (aluminium oxide)
CO2 (carbon dioxide)
|
Which type of oxide can react with both acids and bases?
Basic oxides
Acidic oxides
Amphoteric oxides
|