Ionic Bonding
This lesson covers:
- The principles of ionic bond formation
- How to draw ionic bonds using dot and cross diagrams
Atoms can g or l electrons to become charged particles called i.
|
Choose the correct description of how a lithium atom becomes a lithium ion.
Lithium gains a proton to become a positively charged ion
Lithium loses an electron to become a positively charged ion
Lithium gains one electron to become a positively charged ion
|
The group 1 metal potassium reacts with the group 7 halogen iodine.
Which atom receives an electron?
Iodine
Potassium
|
identical / opposite / identically / oppositely / ionic / covalent
Ions with charges will attract each other.
This force of attraction between charged ions forms an bond.
|
attract / repel / ionic / electrostatic
Oppositely charged ions each other.
This is called an force. This same force is also what attracts protons to electrons within atoms and ions.
|

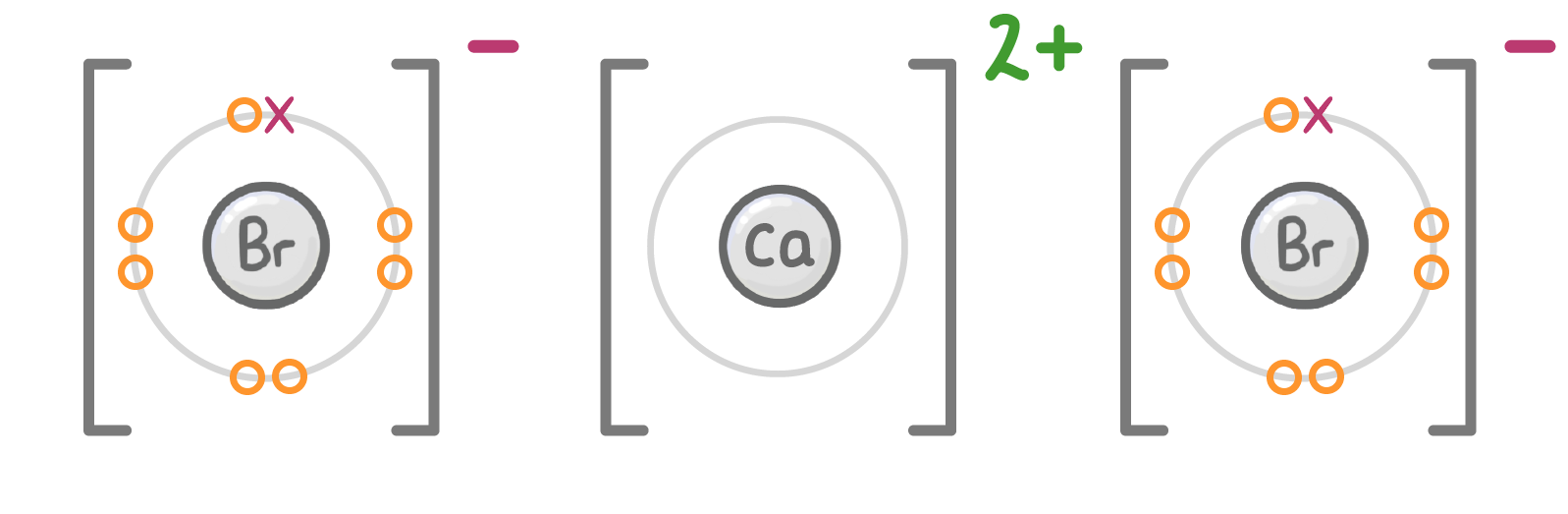
When drawing dot and cross diagrams, remember to surround the ion with square brackets and put the charge in the top right corner.
Make sure you arrange the ions in a way that reflects which charges will be attracted to each other. For example we placed the chloride ions on either side of the magnesium ion, because they'll be attracted to the positive charge.
Bromine and calcium can react together to form calcium bromide, an ionic compound. Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the ionic bonding between bromine and calcium (only draw the outermost electrons). (You may need a periodic table). When you're ready to check your answer, click the 'Continue' button. |
 |