Filtration & Crystalisation
This lesson covers:
- The definitions of solute, solvent, and solution
- The processes of filtration, evaporation, and crystallisation
A small amount of sodium chloride is dissolved into a beaker of water. Which of the following is the solvent?
Beaker
Sodium chloride
Water
|
simple / indivisible / soluble / insoluble
Solid substances that can dissolve in liquids are described as .
Solids that cannot dissolve are described as .
|
True or False? Filtration involves using a Bunsen burner flame to evaporate a solvent from a solution.
True
False
|
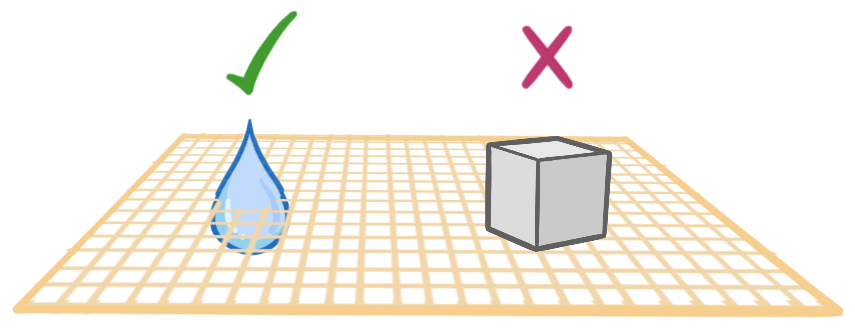
Filter paper is full of small holes that are large enough to allow liquid particles to move through, but too small to allow solids through. This separates the solids from the liquids in filtration.
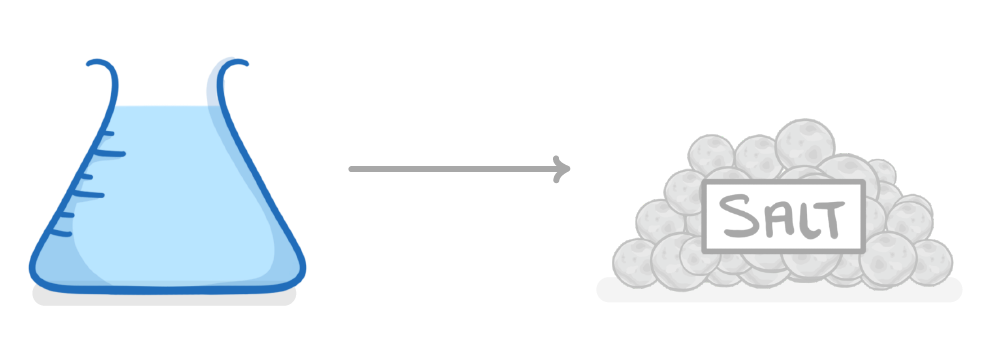
What is the best method to obtain a sample of salt from a salt solution?
Fractional distillation
Filtration
Evaporation
|
Describe how you would carry out the process of crystallisation.
|

How would you separate pieces of rock from a solution of salt water?
Filtration
Distillation
Crystallisation
Evaporation
|