Molecular & Empirical Formulas
This lesson covers:
- What a 'molecular formula' is
- What an 'empirical formula' is
Molecular vs empirical formulae |
The molecular formula of a substance shows the actual number of atoms of each element present in a compound or molecule. |
For example, the molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6, which means that a glucose molecule contains: 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms. |
 |
The empirical formula of a substance is the simplest, whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound. This means that it doesn't tell you exactly how many atoms there are, just the ratio of the atoms of each element. |
For example, the empirical formula for glucose is CH2O, which means that the ratio of carbon : hydrogen : oxygen is 1 : 2 : 1. Or in other words, for every 1 carbon atom, there are 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom. |
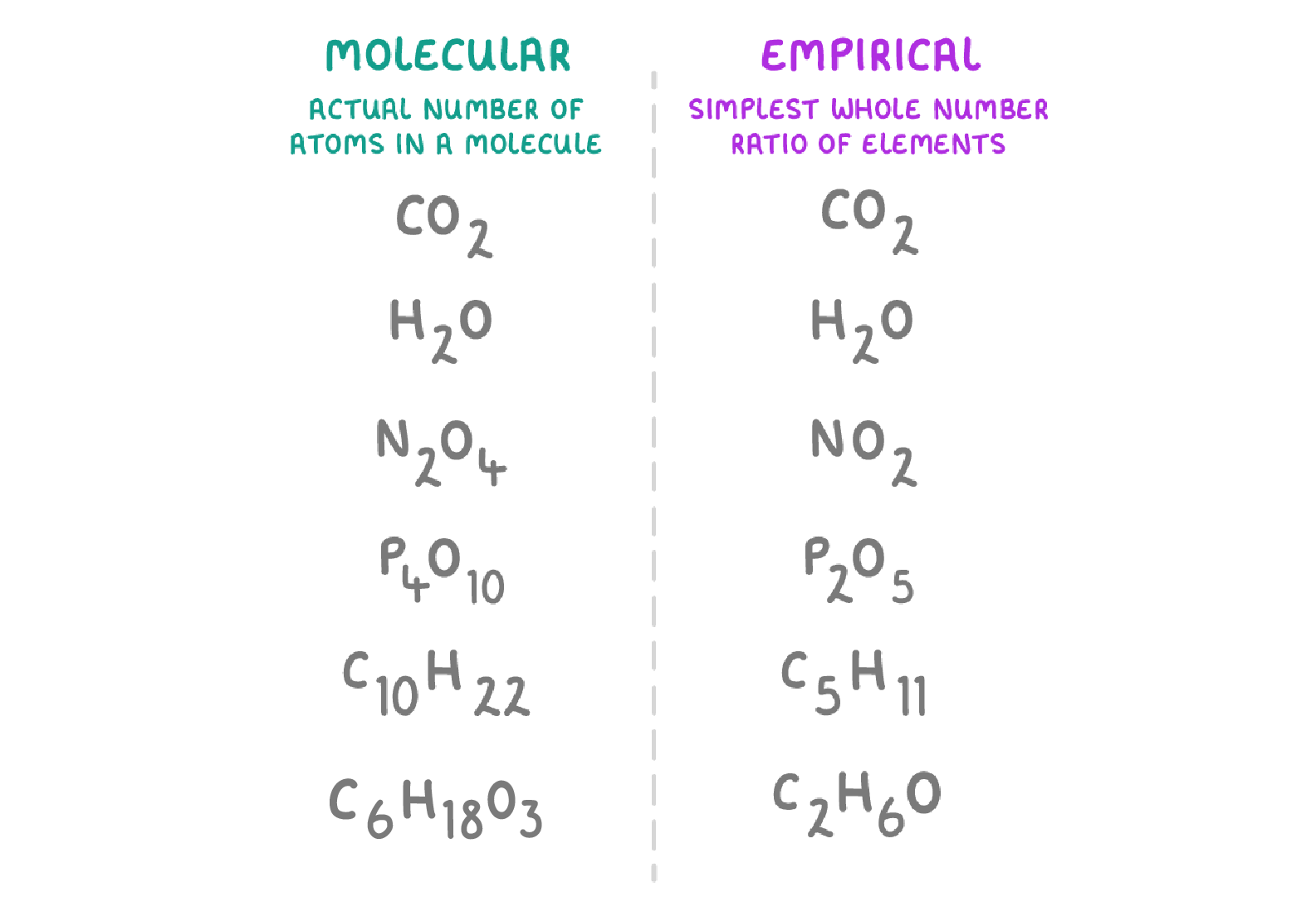
Some examples of substances molecular formulas and empirical formulas
How to find the empirical formula from a molecular formula |
To find the empirical formula from the molecular formula, all you do is find the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in the compound. As an example, let's find the empirical formula of ethane, C2H6 |
1Looking at the molecular formula of ethane (C2H6), we can see that the ratio of C : H atoms is 2 : 6 |
2To get the empirical formula, we need to simplify this ratio as much as possible. You can simplify the ratio 2 : 6 by dividing both sides by 2 - which gives you 1 : 3 |
3This 1 : 3 ratio means the empirical formula for ethane is 1 carbon atom for every 3 hydrogen atoms. |
4So the empirical formula for ethane is CH3 |
How to find the molecular formula from the empirical formula and Mr
Sometimes, you may be given the empirical formula and Mr of a compound, then asked to find the molecular formula.
To see how you'd do this, let's work through the following example:
'An unknown compound has an empirical formula of CH3, and an Mr of 30. Find the molecular formula of the compound.'
An unknown compound has an empirical formula of CH2O, and an Mr of 180.
Find the molecular formula of the compound.
C8H10O8
C8H12O4
C6H12O6
|
How to find the empirical formula from masses or percentages:
Sometimes, you'll be given the masses (or percentages) of the different elements in a compound and asked to find the empirical formula.
To see how you'd do this, let's work through the following example:
'A compound is found to contain 50.05% sulfur and 49.95% oxygen by weight. What is the empirical formula for this compound?'
What is the empirical formula of a compound that contains 46.3% lithium and 53.7% oxygen?
(You may need a periodic table)
Li2O
Li2O2
Li2O4
|
What is the empirical formula of a compound that contains 15.9% boron and 84.1% fluorine?
B2F3
BF3
B3F
|
Phosphorus reacts with oxygen to give a compound that is 43.7% phosphorus and 56.4% oxygen. What is the empirical formula of the compound?
P2O5
P1O2.5
PO
|