Metals & Non-Metals
This lesson covers:
- The properties of metals and non-metals
- The features of transition metals
gain / lose / positive / negative
When metal atoms react, they electron(s) from their outer shell.
This creates ions with a charge.
|
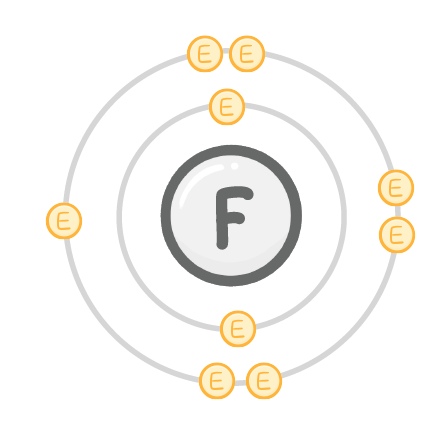
Fluorine atoms have 7 electrons in their outer shell. In chemical reactions, do they gain or lose electron(s)?
Gain
Lose
|
Select three general properties of metals:
Brittle
Malleable
Sonorous (produce a ringing sound when struck)
Low density
Good conductors of heat
Low boiling and melting points
|

metallic / malleable / brittle / shiny
Metals are very strong, as the ions are held together by bonds.
They also tend to be , which means they can bend without breaking.
Non-metals, in contrast, break easily, and so are said to be .
|
Many transition metals can be used as catalysts. What is the definition of a catalyst?
A metal which produces a ringing sound when struck
A substance that can speed up a chemical reaction without being used up
A compound containing both metal and non-metal elements
|

Transition metals share the same properties as metals, however, they have their own section of the periodic table between groups 2 and 3.
These metals can create ions of different charges, and form different coloured solutions.