Mixtures
This lesson covers:
- What mixtures are
- Dissolving to form mixtures
- How temperature affects solubility
What are mixtures?
A pure substance contains only one type of element or compound.
A mixture contains two or more substances that are not chemically joined.
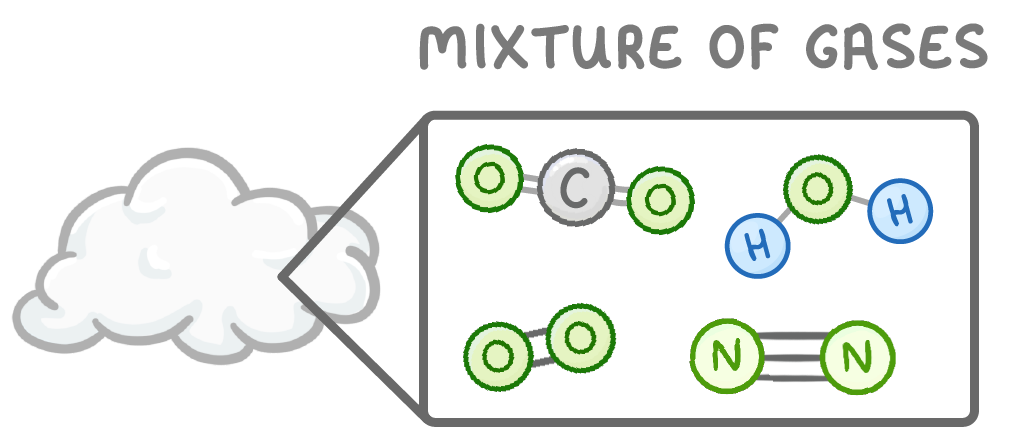
For example, air contains nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases mixed together. Seawater is another example of a mixture.
The components of a mixture maintain their properties and can be separated using physical methods.
Dissolving to form mixtures
Dissolving is a common way mixtures are formed.
When a solid dissolves in a liquid, the bonds between the solid particles break, allowing the particles to mix with the liquid particles.

These are some key terms that you need to know when talking about dissolving:
- Solute - This is the solid being dissolved.
- Solvent - This is the liquid the solute dissolves into.
- Solution - The mixture formed when solute dissolves.
- Soluble - A substance that dissolves.
- Insoluble - A substance that does not dissolve.
- Saturated - A solution that contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute it can hold.
- Solubility - How much solute can dissolve in a solvent before it becomes saturated.
No mass is lost when a solute dissolves

When a solute dissolves, it still exists in the solution. Even though the solute seems to disappear, no mass is lost.
The total mass of the solution will equal the mass of solvent plus the mass of solute.
For example, if 30g of salt is dissolved in 100g of water, the final solution will have a mass of 130g.
How temperature affects solubility
Usually, more solute can dissolve at higher temperatures as the particles move faster and more energetically.
However, some solutes are insoluble in certain solvents no matter the temperature. For example, salt does not dissolve in petrol.