Exothermic reactions, endothermic reactions, and catalysts
This lesson covers:
- Exothermic reactions
- Endothermic reactions
- What are catalysts and how they work
- The advantages and disadvantages of catalysts
Endothermic reactions
Endothermic reactions take in energy from their surroundings, usually in the form of heat.
- Examples include thermal decomposition reactions.
- There is a fall in temperature as heat energy is taken in.
- Everyday uses include cold packs for sports injuries.
What are Catalysts?
Catalysts speed up the rates of chemical reactions without being used up themselves.
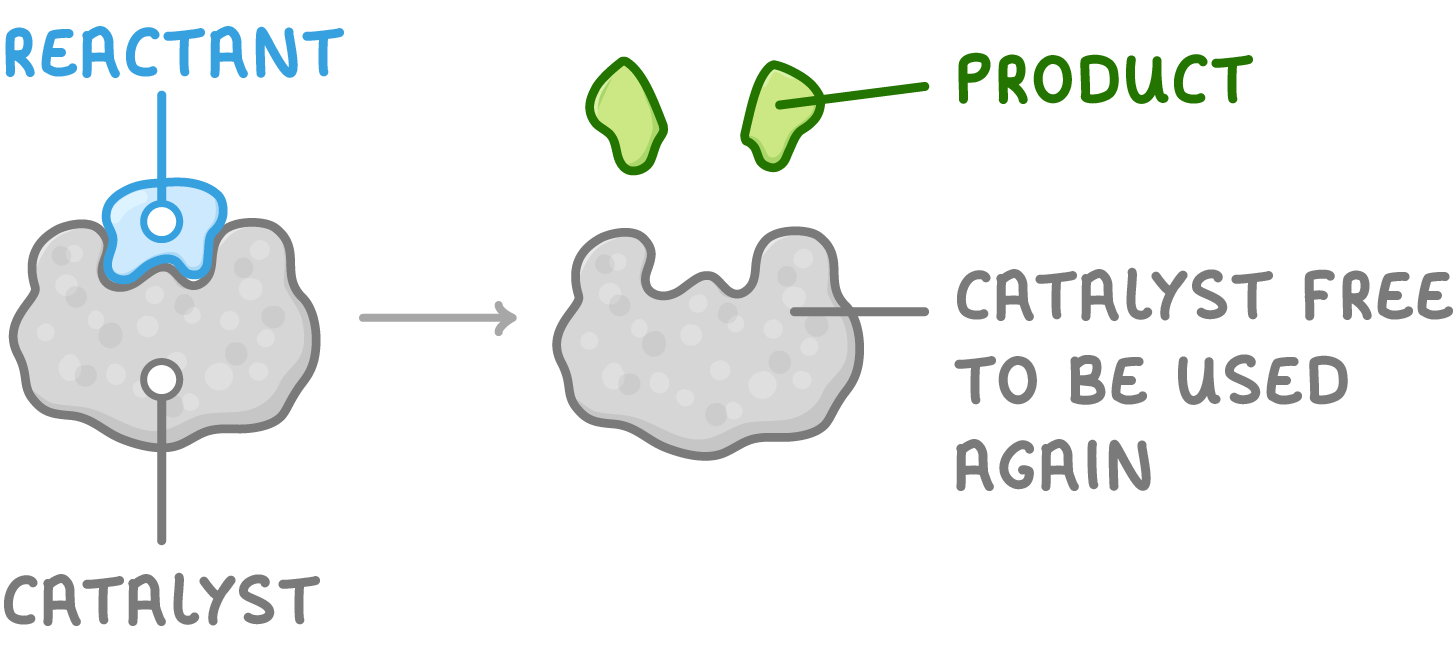
- They provide an alternative route for the reaction with a lower activation energy.
- This means the minimum energy needed to start the reaction is lowered.
- So a lower temperature can be used.
- Catalysts can be reused multiple times.
Advantages and disadvantages of using catalysts.
Catalysts are useful in many industrial applications.
Advantages of using catalysts
- They increase the speed of reactions.
- They allow reactions to occur at lower temperatures.
- They increase the yield of products.
- They make processes more economical.
Disadvantages of using catalysts
- They are expensive to buy initially.
- Different reactions require different catalysts.
- They can become contaminated or 'poisoned'.
- They may need regular cleaning.