Chemical reactions
This lesson covers:
- What happens to atoms in chemical reactions
- How mass is conserved in chemical reactions
- Signs that a chemical reaction has occurred
Atoms rearrange in reactions
For example, lets take the reaction of magnesium and copper sulfate:
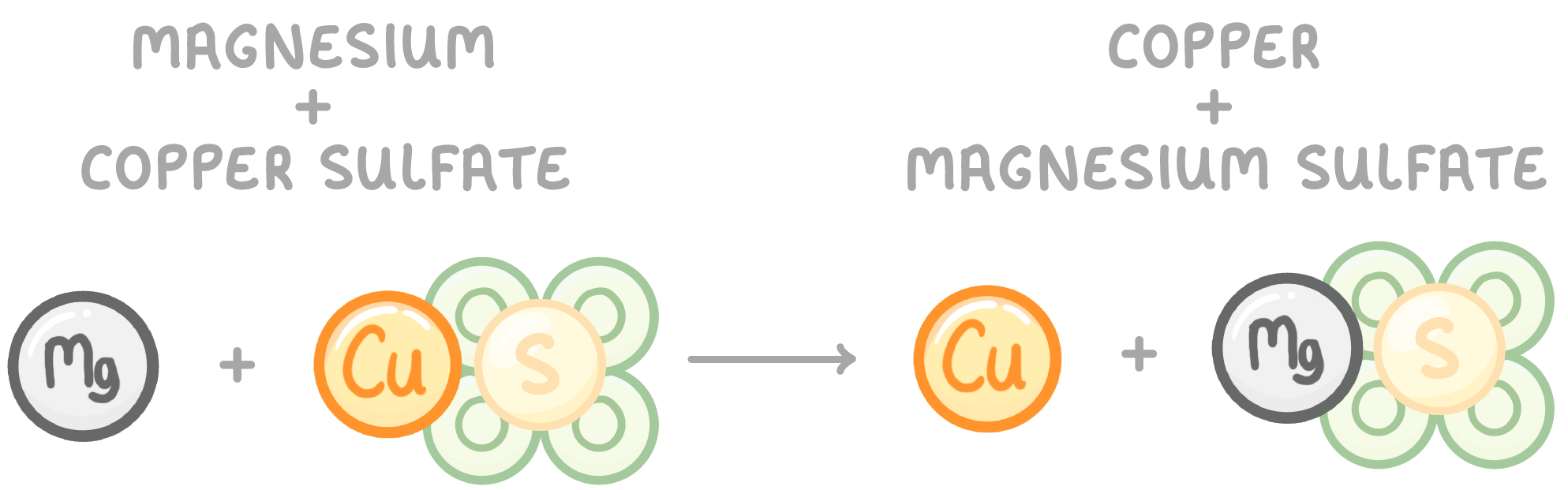
In chemical reactions, the atoms are rearranged into new formations - they break bonds and form new bonds.
The atoms move around but are not created, destroyed or fundamentally changed.
Mass does not change
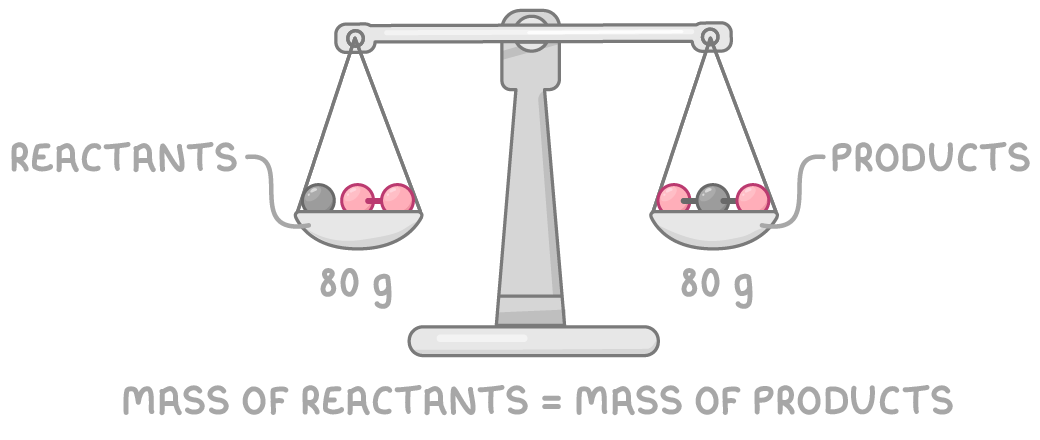
The total mass stays the same before and after a chemical reaction.
This is because the total number of atoms is the same in the reactants and products.
While energy is given out or absorbed, causing temperature changes, no atoms are lost so mass is conserved.
Signs of a reaction
There are visible changes during a reaction show that atoms have rearranged themselves:
- A colour change.
- A gas is produced.
- A solid is formed.
- There is a temperature change.
Example of changes during a chemical reaction
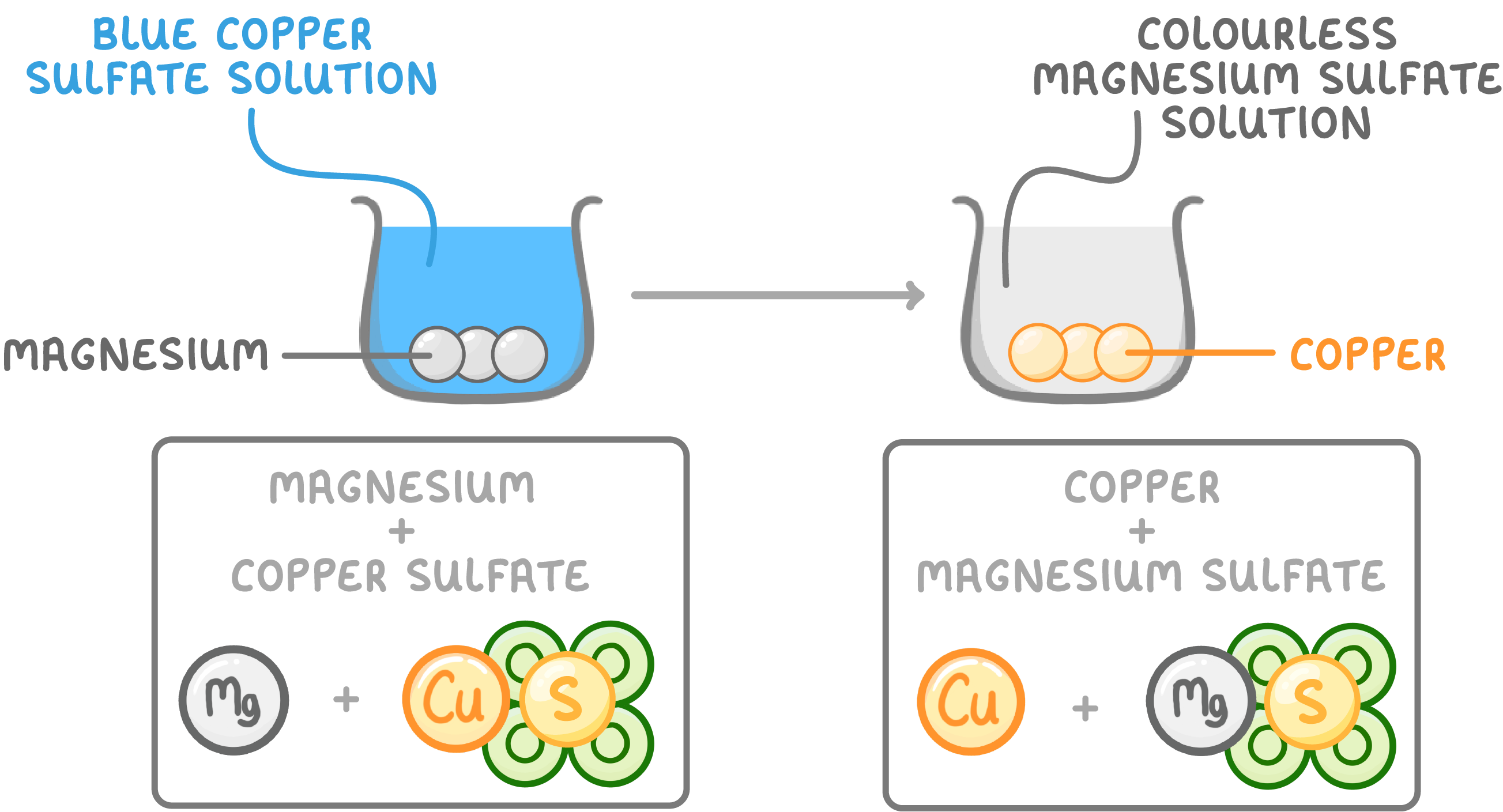
For example, magnesium reacting with blue copper sulfate:
- Magnesium sulfate is formed and the liquid turns colourless.
- Copper is formed and the solid turns a copper colour.
- Heat is released.
- However, the total mass will stay the same.