Particle theory
This lesson covers:
- How the particles in matter behave
- How the particles differ in solids, liquids and gases
Particle behaviour determines the state
The properties of a substance depend on the behaviour of its particles.
The key factors are:
- Energy of the particles.
- Strength of forces between particles.
- Arrangement of the particles.
The same material can exist as a solid, liquid or gas - its state depends on its particles.
Particles in solids
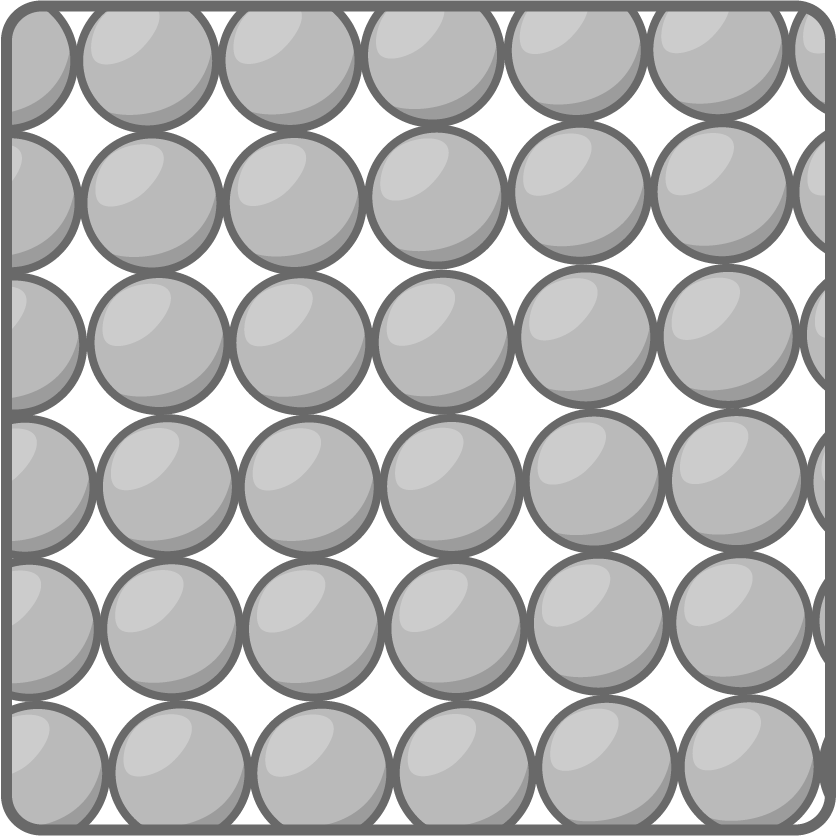
- Particles in a solid have low energy and vibrate in fixed positions.
- Strong forces between the particles, keep particles in an orderly, close-packed arrangement.
- The particles can't move freely so solids keep a fixed shape and volume.
- Solids are hard to compress as the particles are already tightly packed.
- Solids are usually dense as many particles occupy a small volume.
Particles in liquids
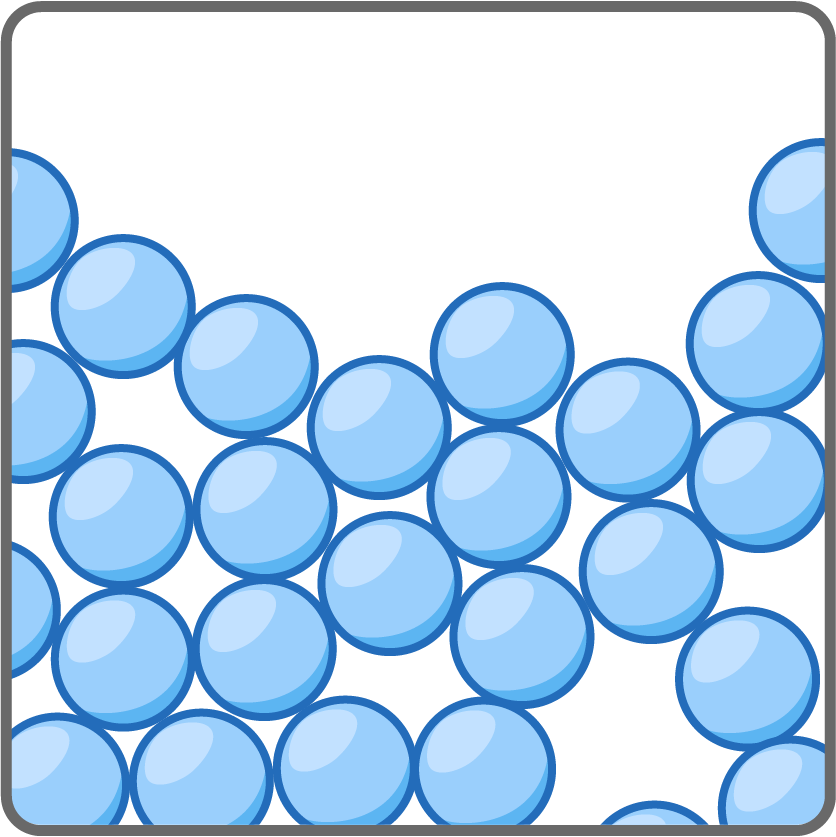
- Particles in a liquid have more energy and can move around each other.
- Forces of attraction between the particles, keep particles close but they can slide past one another.
- Liquids flow to fill a container but keep a constant volume.
- Liquids are hard to compress as the particles still close together.
- Liquids are quite dense but less dense than solids.
Particles in gases
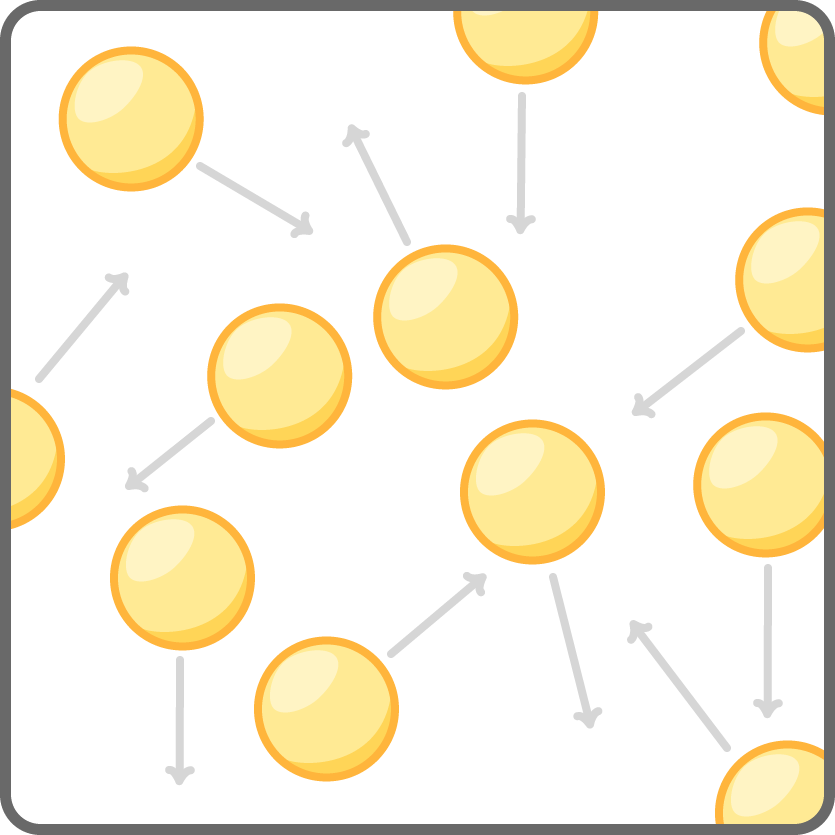
- Particles in a gas have high energy and move very fast in all directions.
- There are almost no forces of attraction between the widely spaced particles.
- Gas have no fixed shape or volume so can expand to fill any container.
- Gases are easy to compress as particles have lots of space between them.
- Gases are very low density as particles spread through a large volume.