Metal and non-metal oxides
This lesson covers:
- How metals and non-metals react with oxygen to form oxides
- Acidic and alkaline properties of metal and non-metal oxides
- Reactions of metal oxides with acids
- Reactions of non-metal oxides with alkalis
Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides
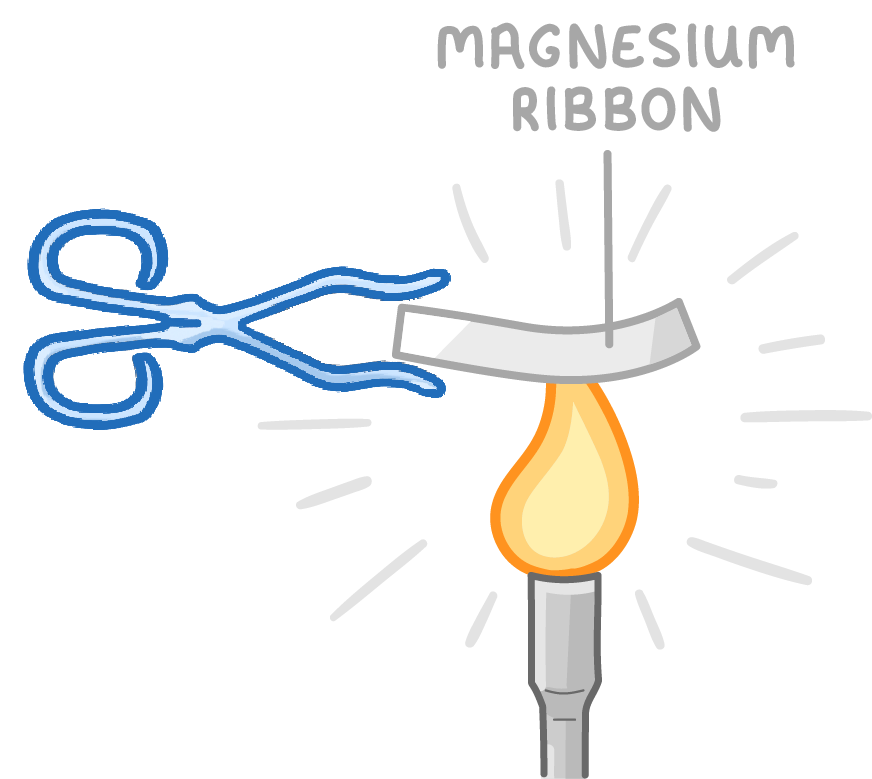
Metals can react with oxygen gas to produce metal oxides.
For example:
- Magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide
Metal oxides are alkaline
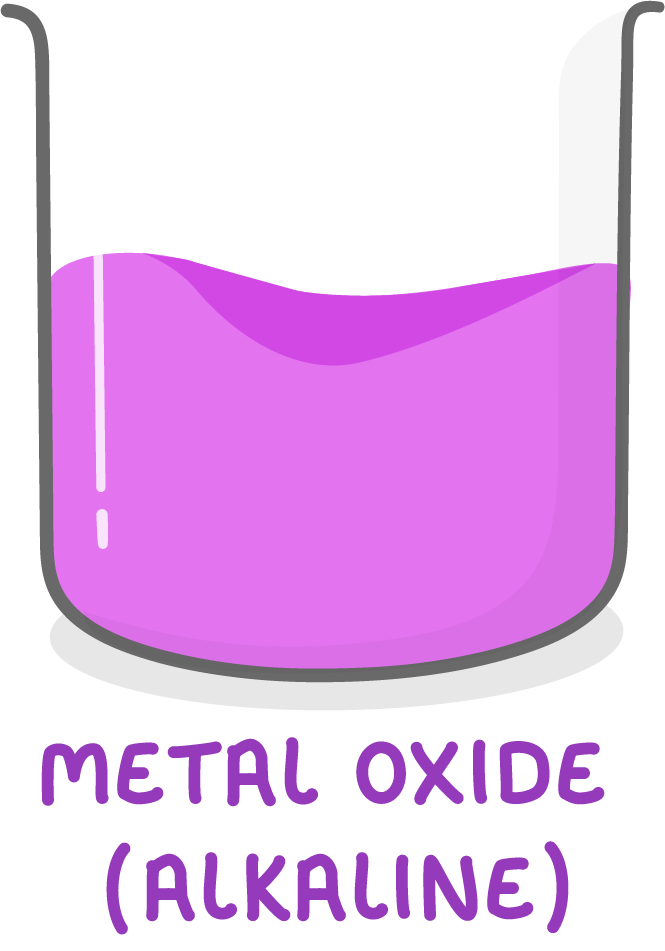
Metal oxides exhibit alkaline properties.
This means metal oxides can react with acids to produce salts and water.
Examples:
- Hydrochloric acid + copper oxide → copper chloride + water
- Sulfuric acid + zinc oxide → zinc sulfate + water
- Nitric acid + magnesium oxide → magnesium nitrate + water
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metal oxides
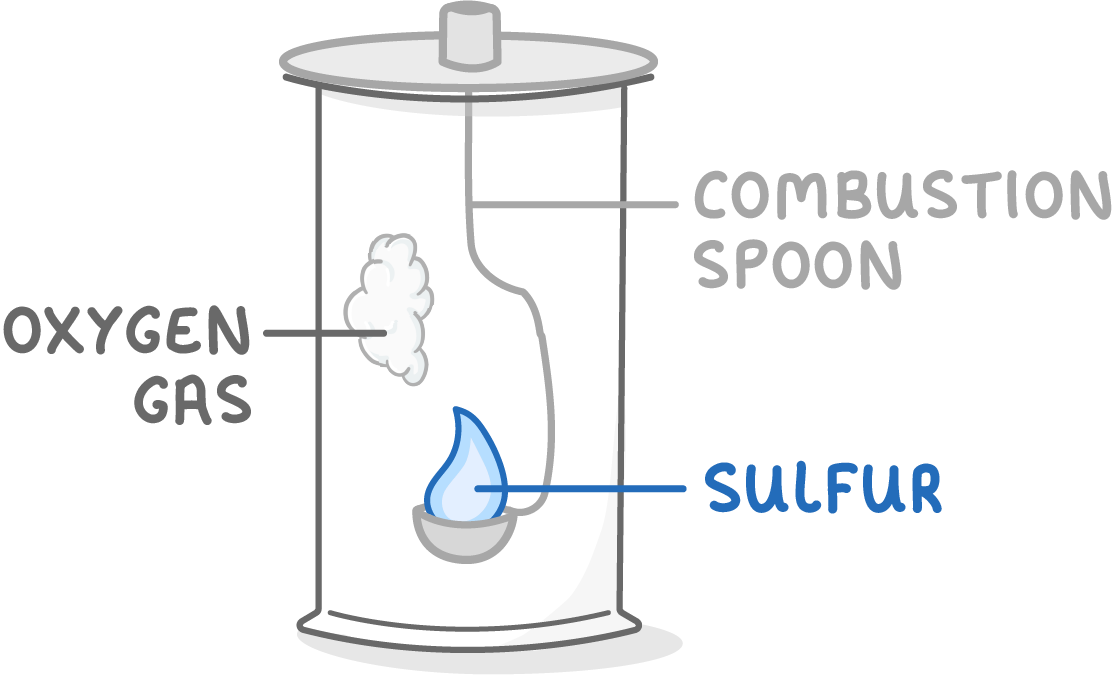
Non-metals can also react with oxygen to produce non-metal oxides.
For example:
- Sulfur + oxygen → sulfur dioxide
Non-metal oxides are acidic

Non-metal oxides exhibit acidic properties.
This means non-metal oxides react with alkalis to produce salts and water.
Example:
- Sodium hydroxide + carbon dioxide → sodium carbonate + water