The carbon cycle
This lesson covers:
- How carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere by photosynthesis
- How carbon moves through food chains
- How carbon dioxide returns to the atmosphere
Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
Plants and algae carry out photosynthesis using carbon dioxide from the air.
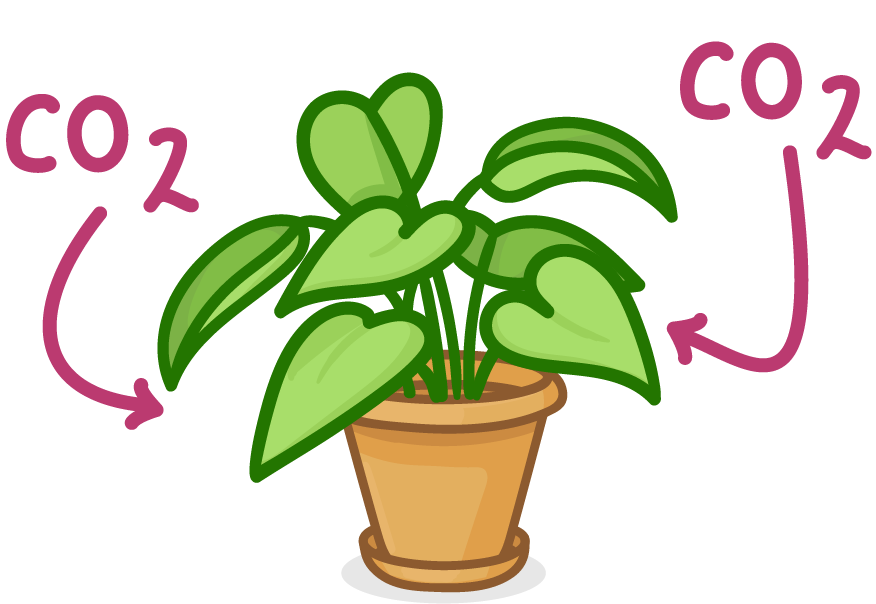
The equation for photosynthesis is:
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
- Plants use carbon from carbon dioxide to build carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- This removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Carbon moves through food chains

- When animals eat plants, they take in the carbon that the plants built.
- The animals use this carbon to build their own fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- The carbon continues to move through food chains when carnivores eat herbivores.
Carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere by respiration
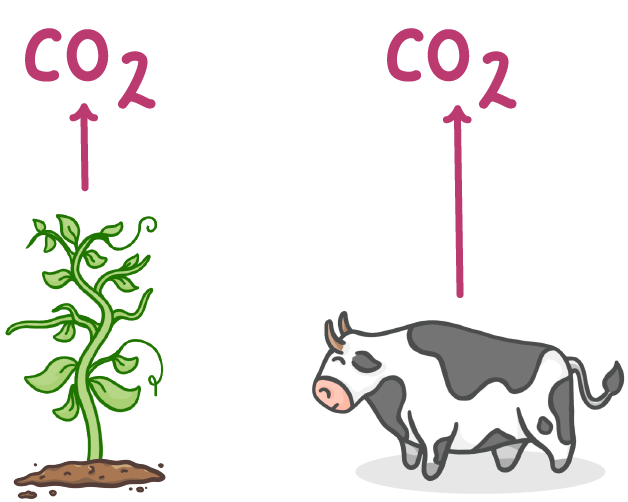
Both plants and animals carry out respiration. As they respire, they release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
The equation for respiration is:
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere by decomposition
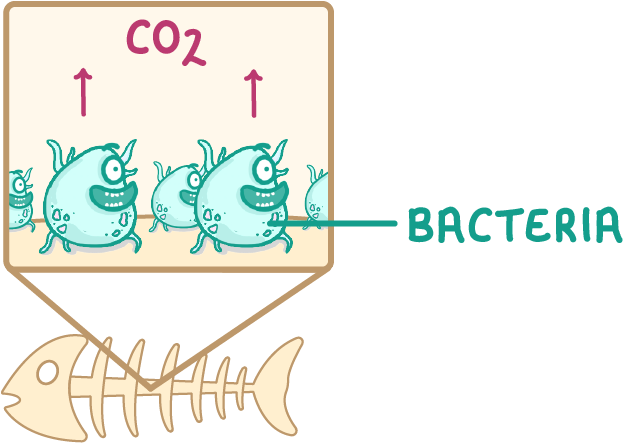
- When animals and plants die, decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down their remains, using it as a food source.
- Decomposers also break down animal waste, taking in the carbon from the waste as a food source.
- These decomposers also carry out respiration, which releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere by the combustion of fossil fuels

- Dead plant and animal remains that became buried underground were turned into fossil fuels like coal and oil.
- This process takes place over millions of years.
- When humans burn fossil fuels, the carbon in them is released as carbon dioxide.
The Carbon cycle
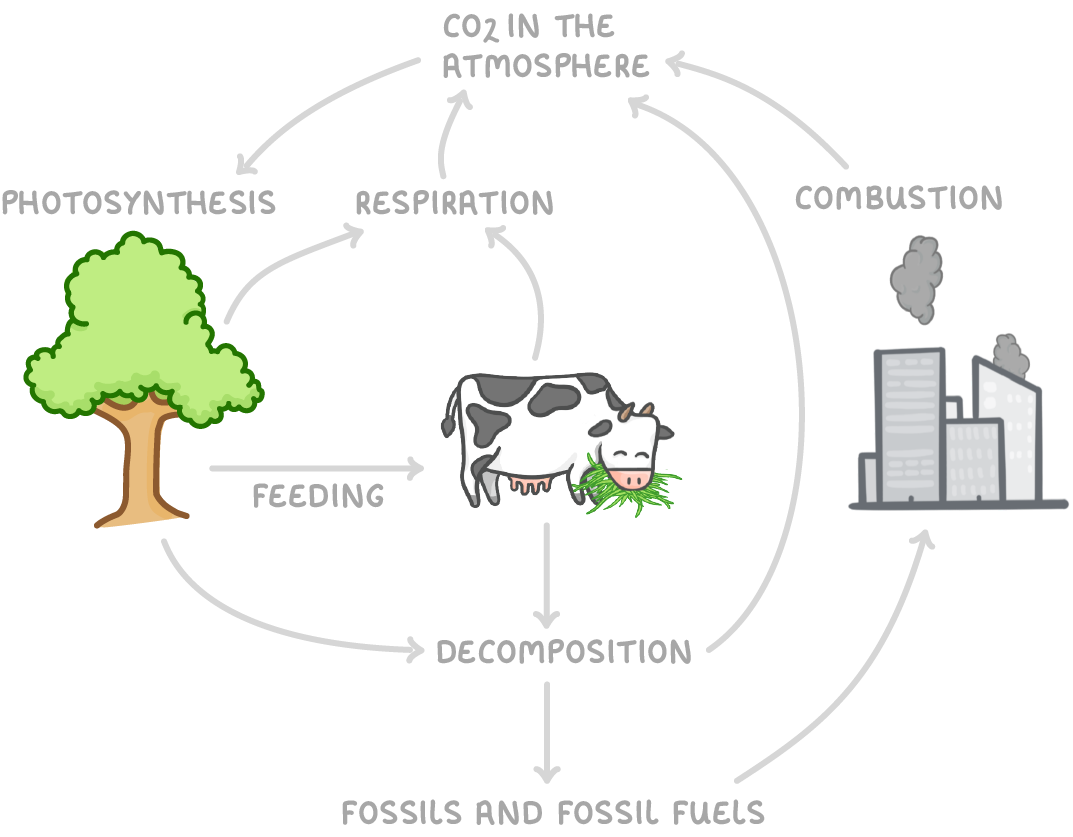
The diagram summarises the processes involved in the carbon cycle.
Note: Respiration, decomposition and combustion add carbon dioxide to the atmosphere and photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.