Properties of metals
This lesson covers:
- Location of metals on the periodic table
- Properties of metals
Metals in the periodic table
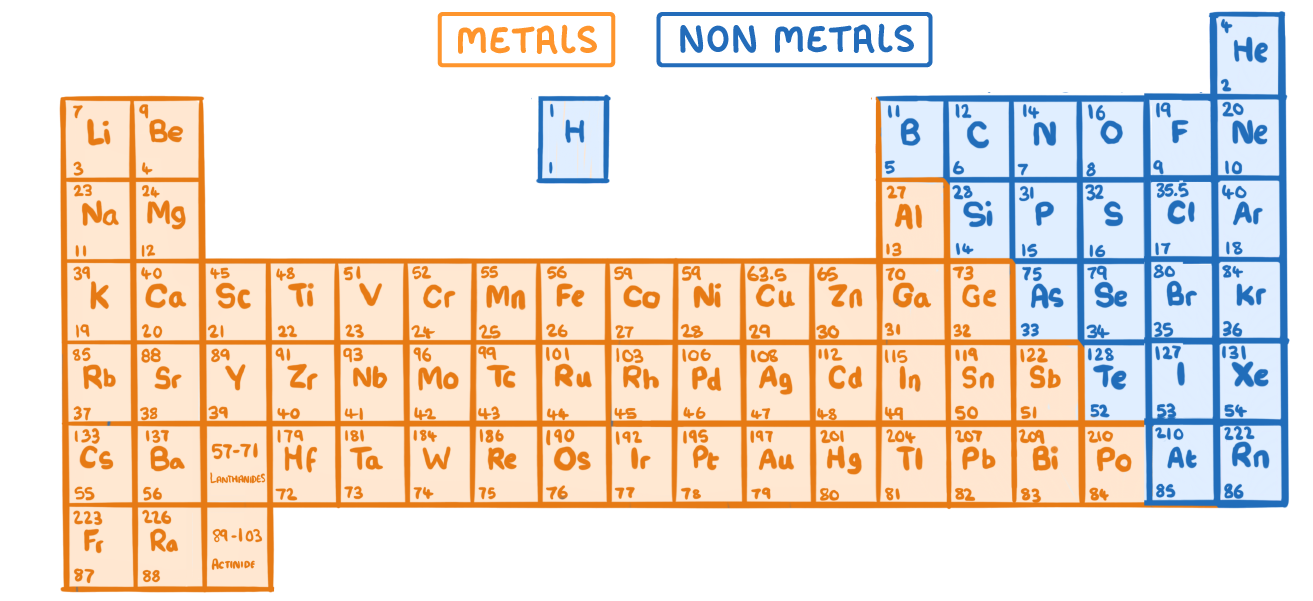
Most elements in the periodic table are metals.
They are found on the left and middle of the periodic table.
Properties of metals
Metals have several distinct properties that we use to identify them.
Metals conduct electricity
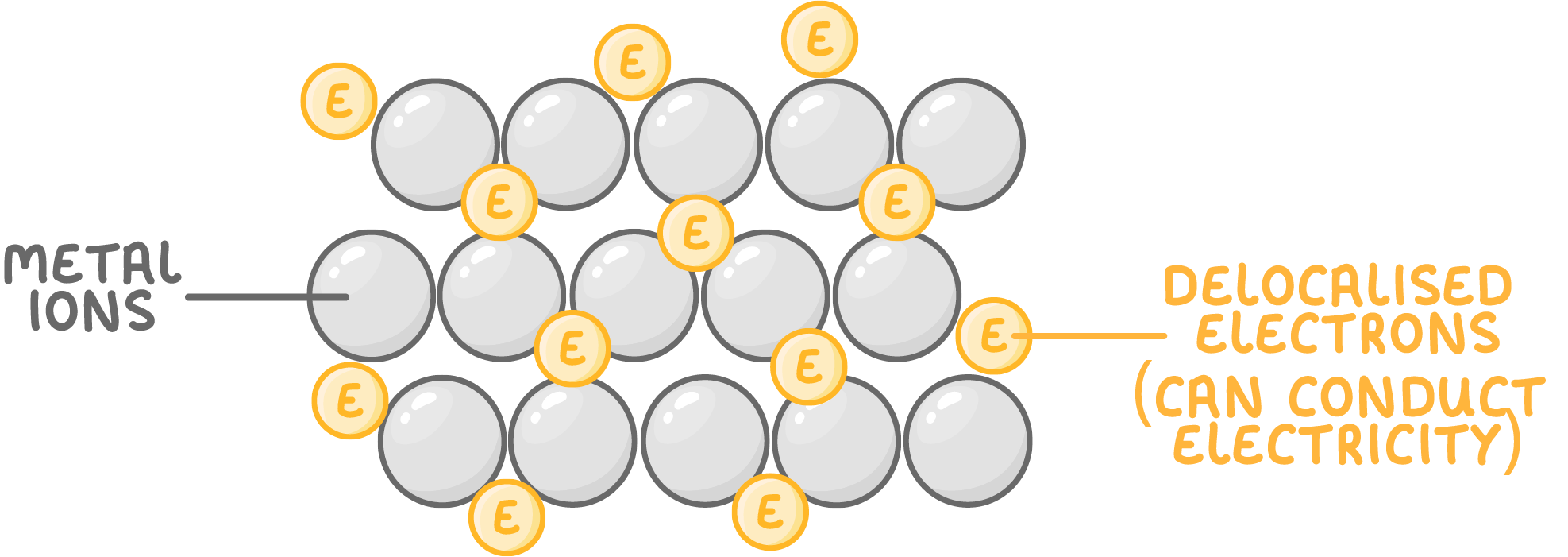
- Metals easily conduct electricity because they contain free or delocalised electrons.
- These electrons can move through the metal carrying electrical charge.
- An electric current is the flow of charge around a circuit.
- This makes metals useful for making electrical wires.
Metals conduct thermal energy
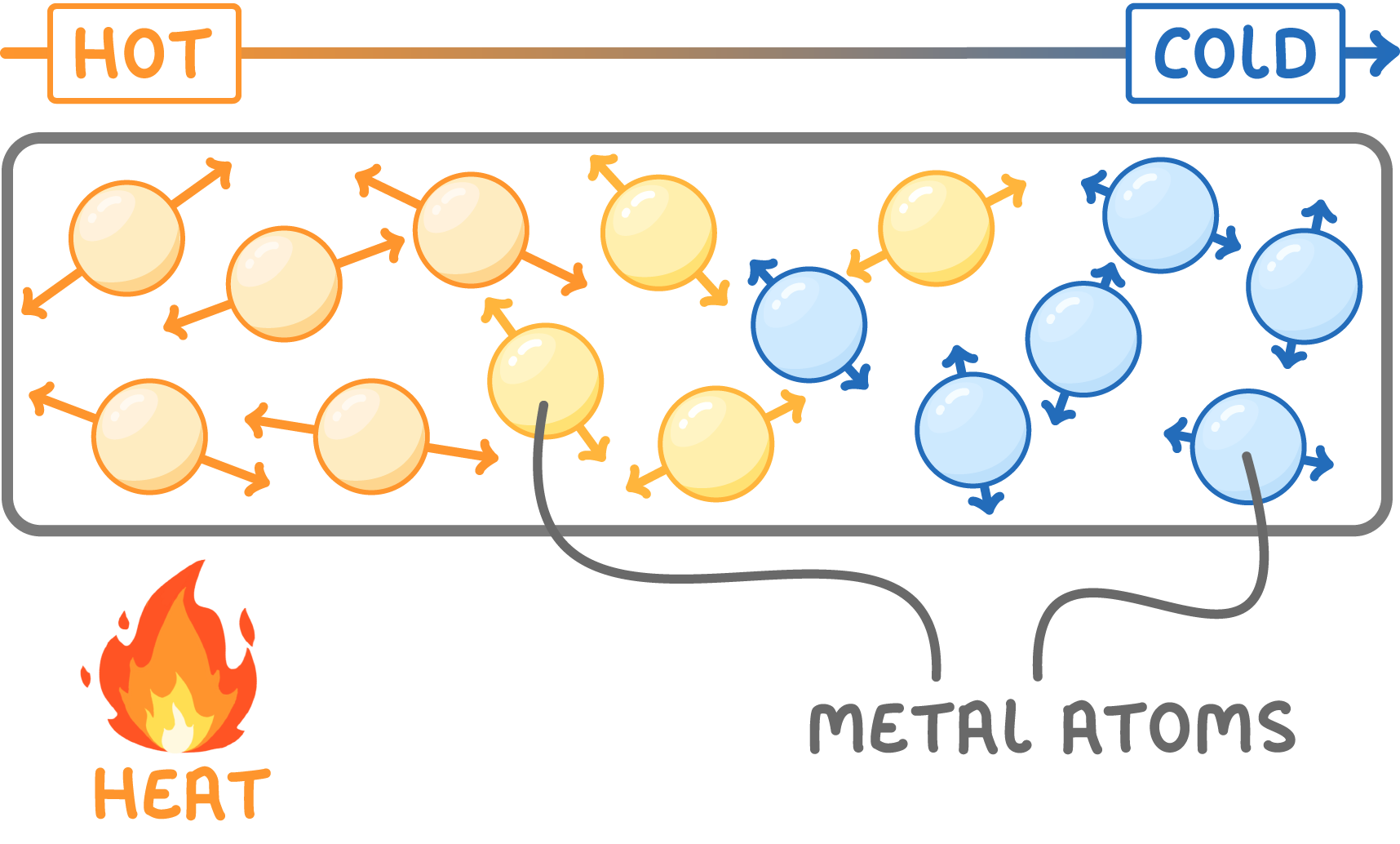
- Metals conduct heat because their atoms are tightly packed together.
- When heated, metal atoms vibrate and pass energy to their neighbouring atoms.
- Vibrations travel quickly down the metal from hot to cool areas.
- This makes metals useful for cooking pots and pans.
Metals are strong

- Metals are strong materials due to the strong bonds between their atoms.
- This makes them useful building materials.
Metals are malleable and ductile
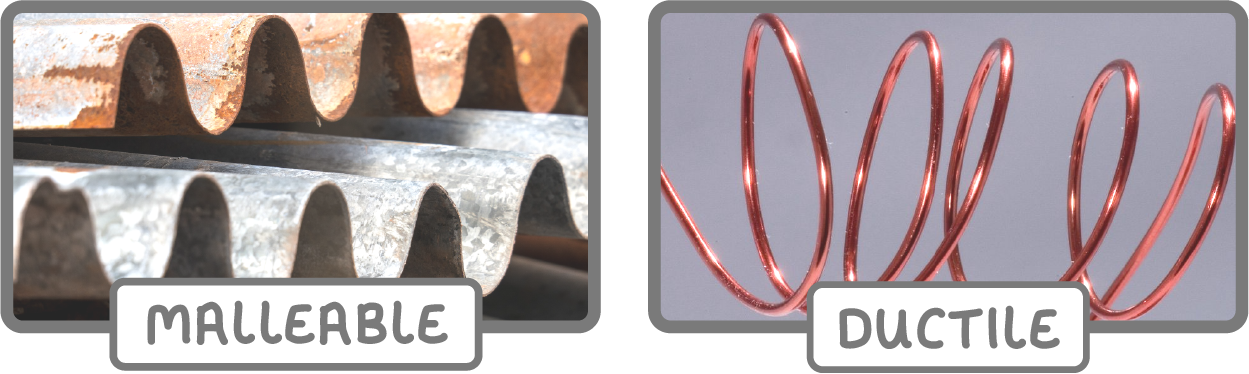
- Metals are malleable and ductile because their atoms can slide over each other.
- Malleable means metals they be hammered, bent, and shaped without breaking.
- Ductile means that they can be drawn to wires.
Metals are shiny

- Polished metals strongly reflect light due to their smooth surface.
- This gives them a shiny appearance.
Metals are sonorous

- Metals produce a characteristic "ringing" sound when hit or struck.
- This makes them useful for making musical instruments.
Metals have high melting points
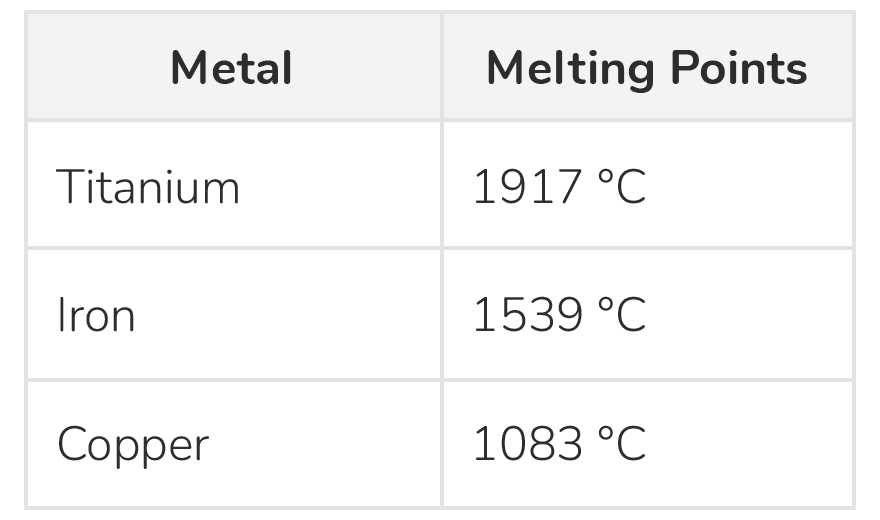
- Metals require a lot of energy to melt due to their strong bonds between atoms.
- This means that metals have very high melting points.
Metals are dense
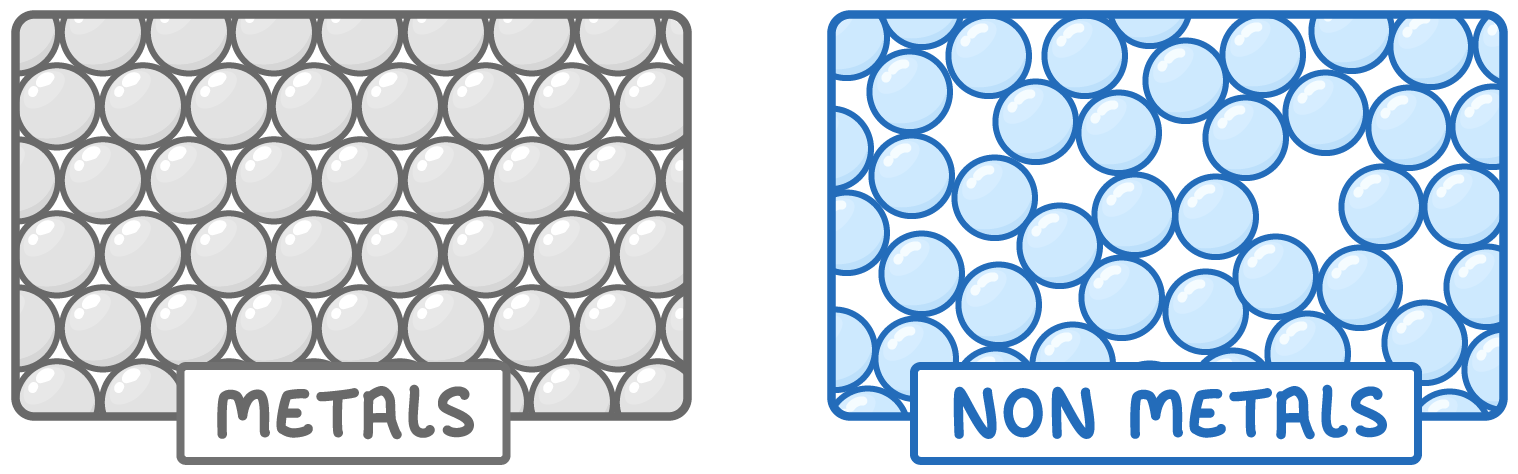
- Metals have a high density because their atoms pack tightly together.
- This means they feel relatively heavy for their size.
Metals form alloys
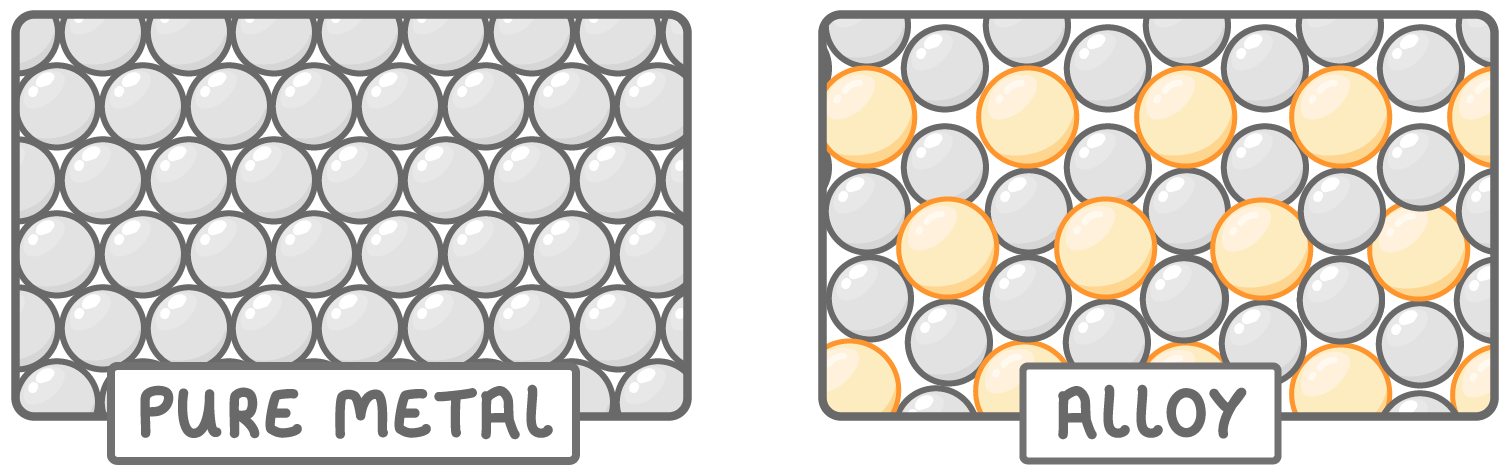
- When different metals are mixed together alloys are formed.
- Producing alloys combines the physical properties of the metals.
- This means that we can produce alloys with the particular properties we need.
Some metals are magnetic
- Only iron, nickel, and cobalt metals are naturally magnetic.
- Their alloys are also magnetic. For example steel is an alloy made from iron and so is also magnetic.