Neutralisation
This lesson covers:
- What happens when an acid reacts with an alkali
- How to make salts through neutralisation
- Naming salts made through neutralisation
Neutralisation reactions
Neutralisation reactions occur when acids and alkalis react together.
Acid + Alkali → Salt + Water
When an acid and an alkali react, they form a neutral solution containing a salt and water.
Making salts by neutralisation - step 1
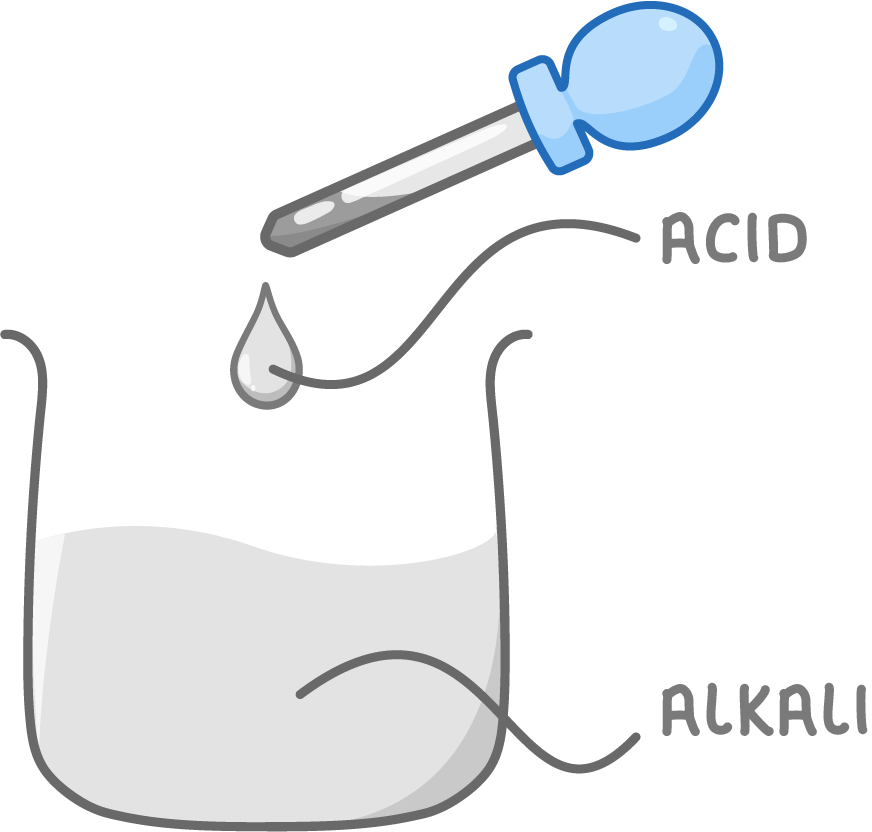
1Carefully add acid to alkali drop by drop.
Making salts by neutralisation - step 2
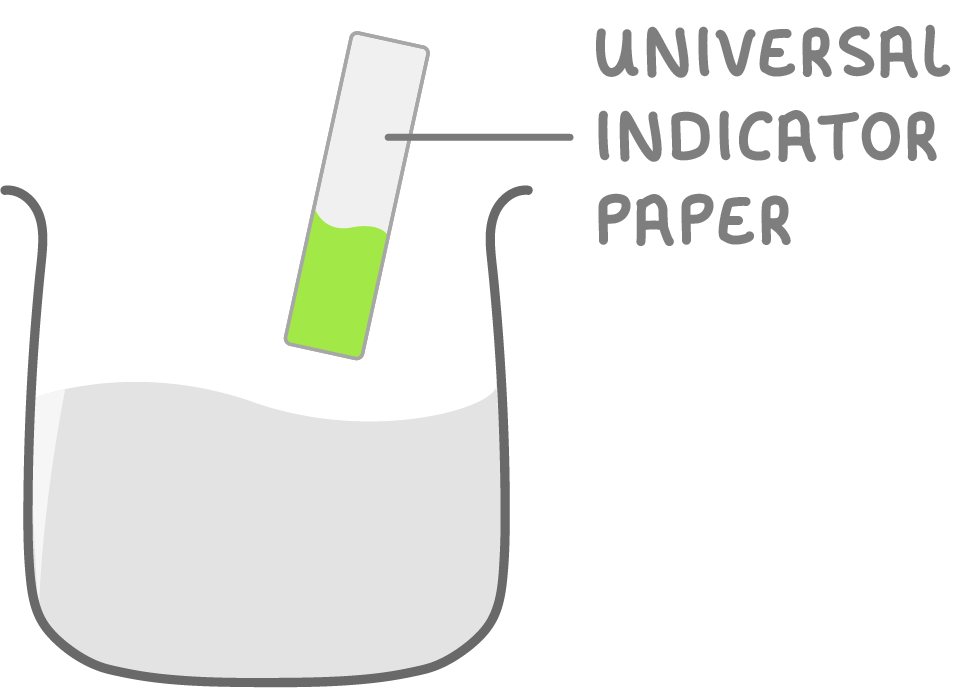
2Universal indicator paper will turn green when solution reaches a neutral pH.
Making salts by neutralisation - step 3
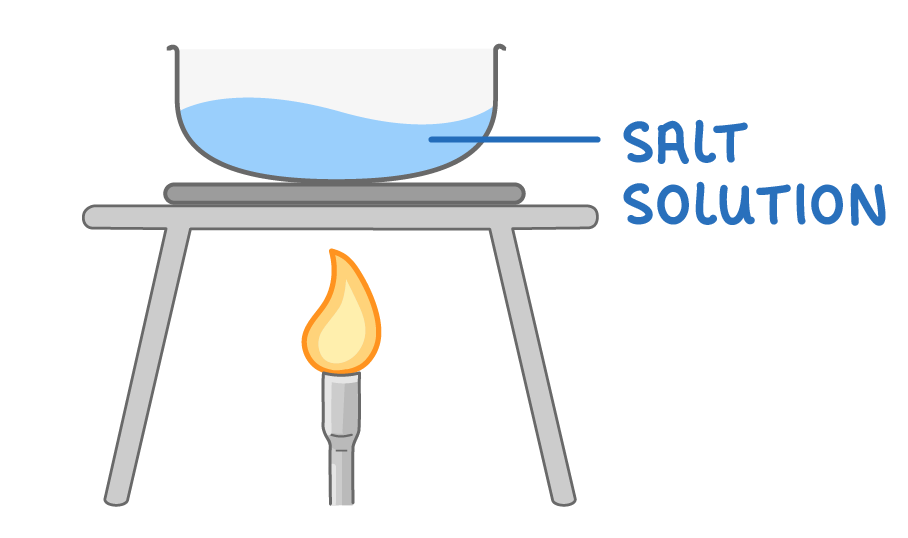
3Heat the neutral salt solution in evaporating dish to boil off some of the water.
Making salts by neutralisation - step 4
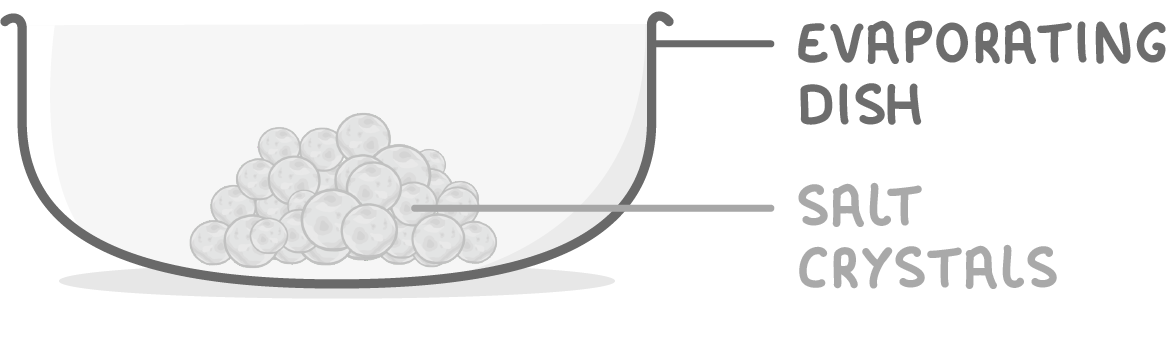
4Allow remaining solution to cool and evaporate slowly overnight leaving salt crystals.
Naming salts
The type of salt produced can be controlled by the type of acid reactant used.
- Hydrochloric acid makes chloride salts e.g. sodium chloride.
- Sulfuric acid makes sulfate salts e.g. copper sulfate.
- Nitric acid makes nitrate salts e.g. sodium nitrate.