More particle theory
This lesson covers:
- Gas pressure
- How temperature and volume affect gas pressure
- What diffusion is
Gas pressure
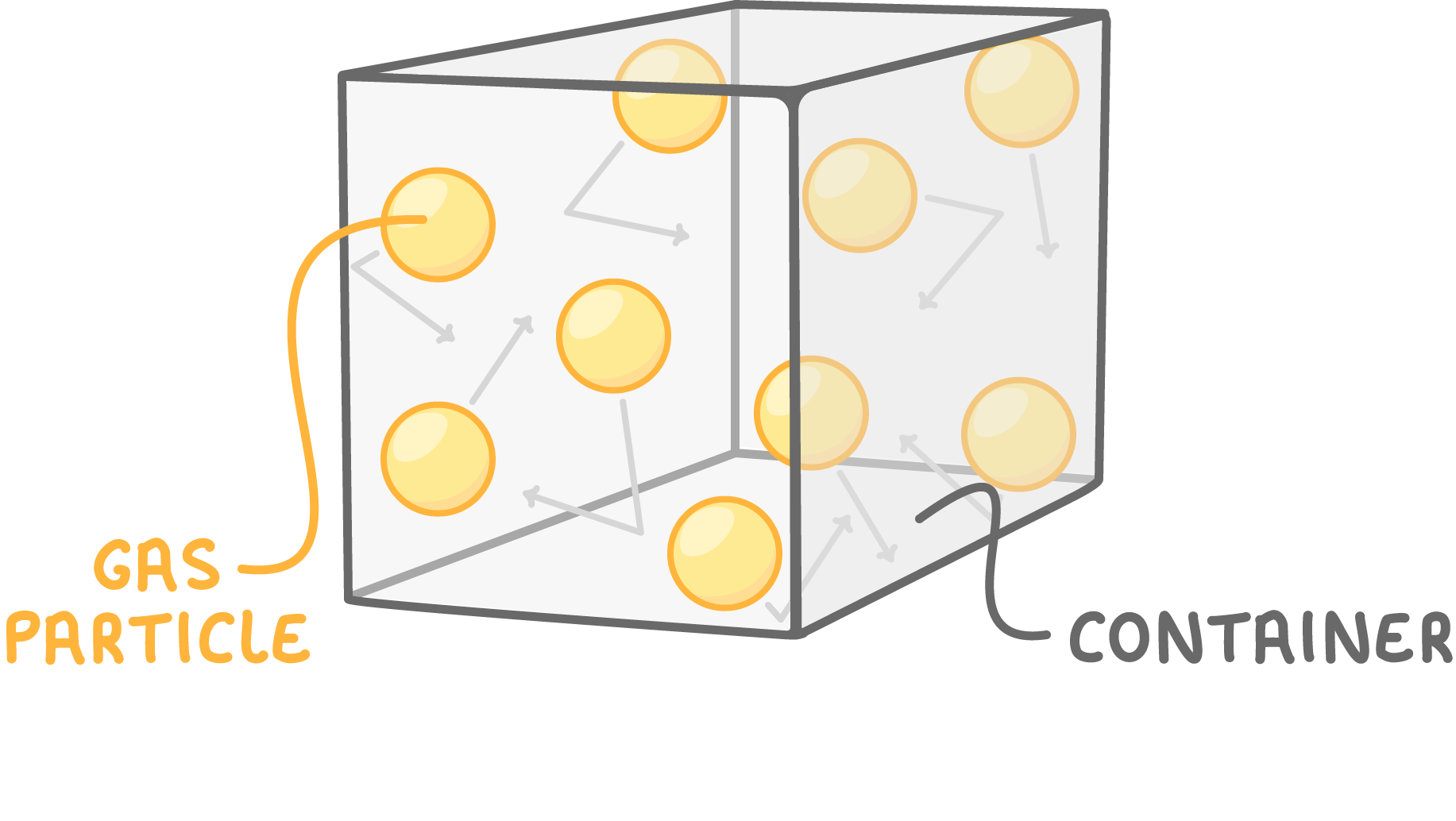
Gas pressure is caused by gas particles constantly colliding with surfaces like container walls.
More collisions results in greater pressure.
Temperature affects pressure
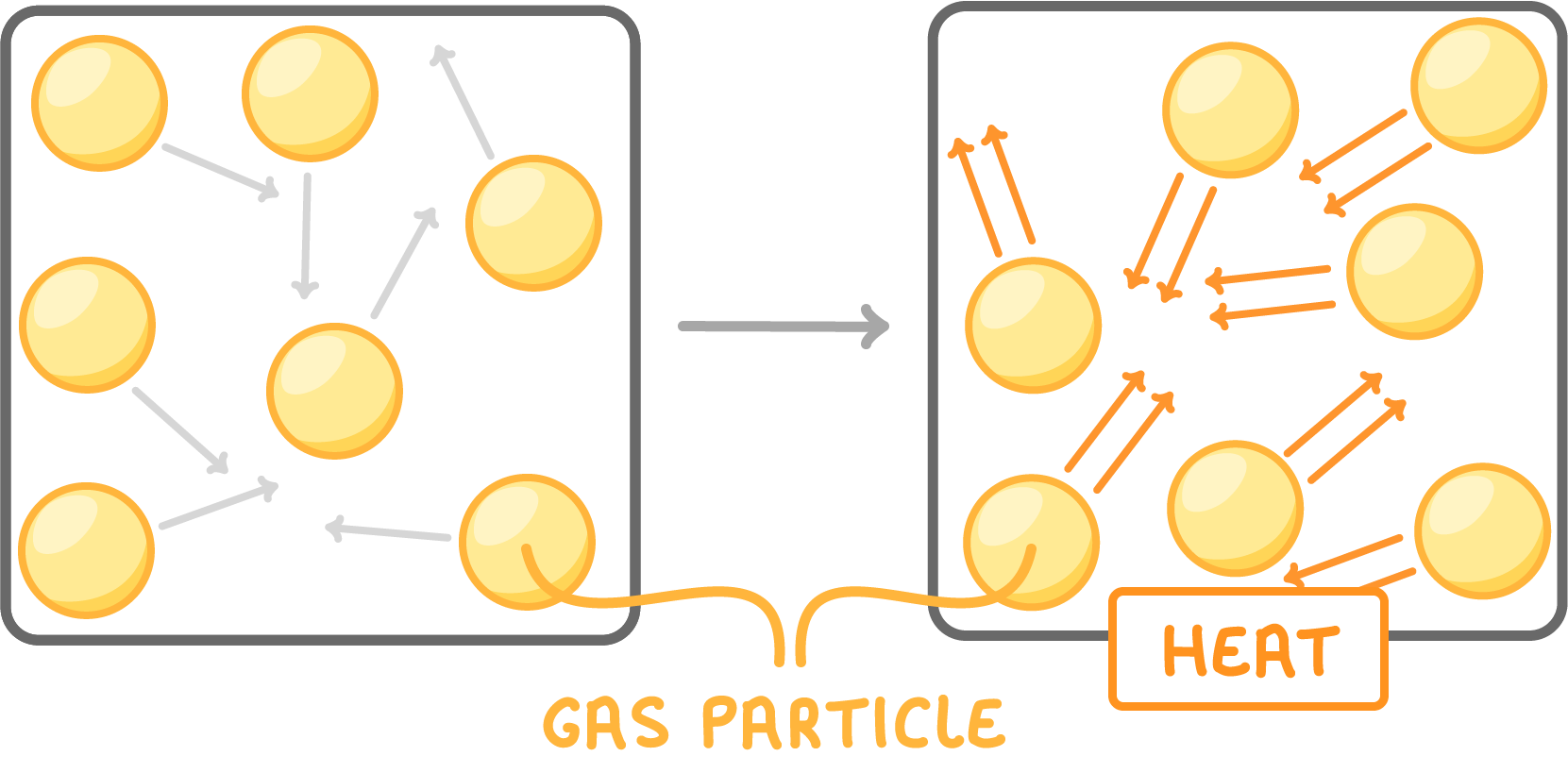
Increasing temperature makes particles move faster.
This increases pressure in two ways:
- Particles hit the walls harder.
- Particles collide with the walls more often.
Volume affects pressure
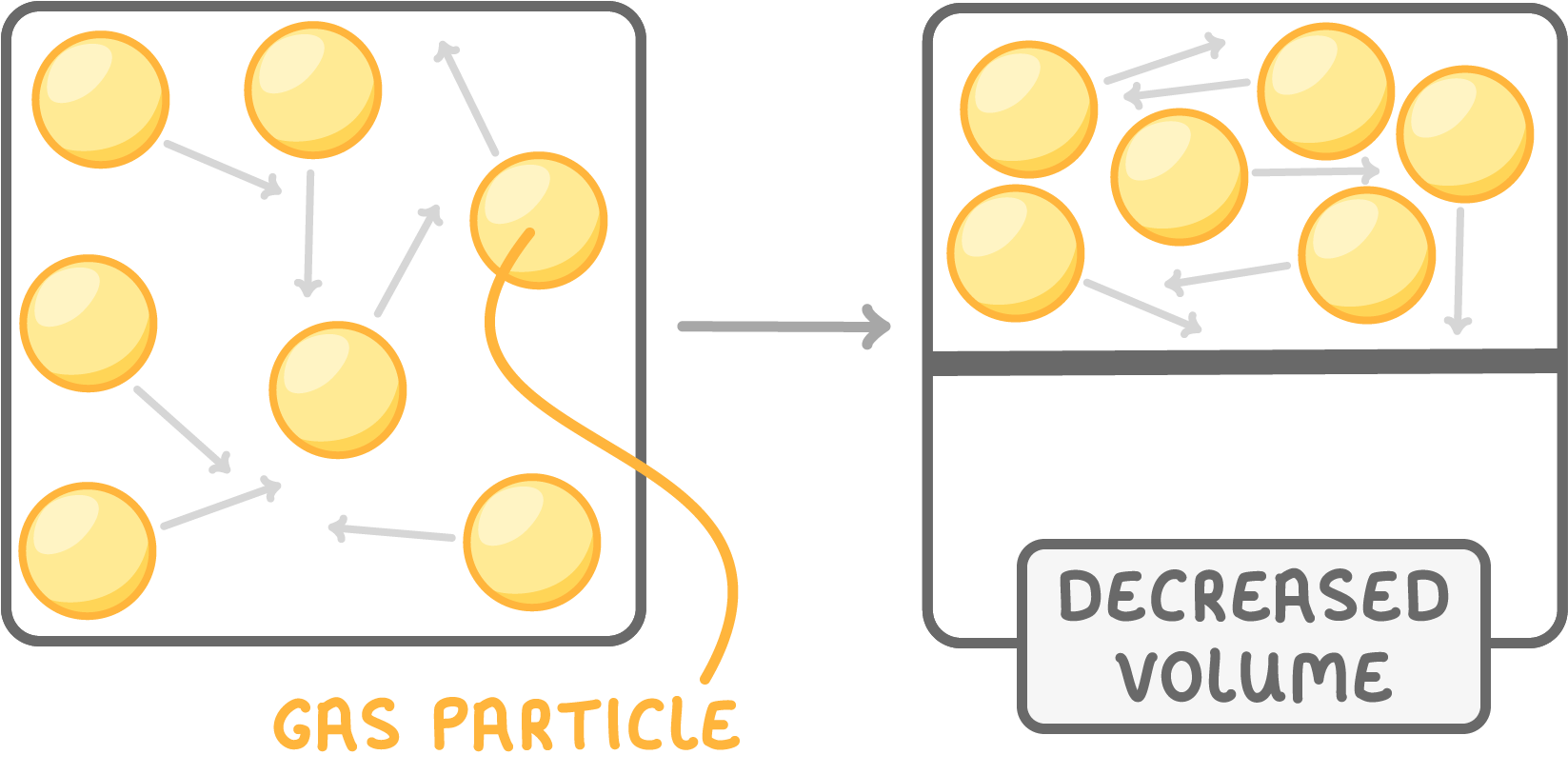
Decreasing volume squashes particles together into less space.
This increases pressure because more particles collide with the walls.
Diffusion
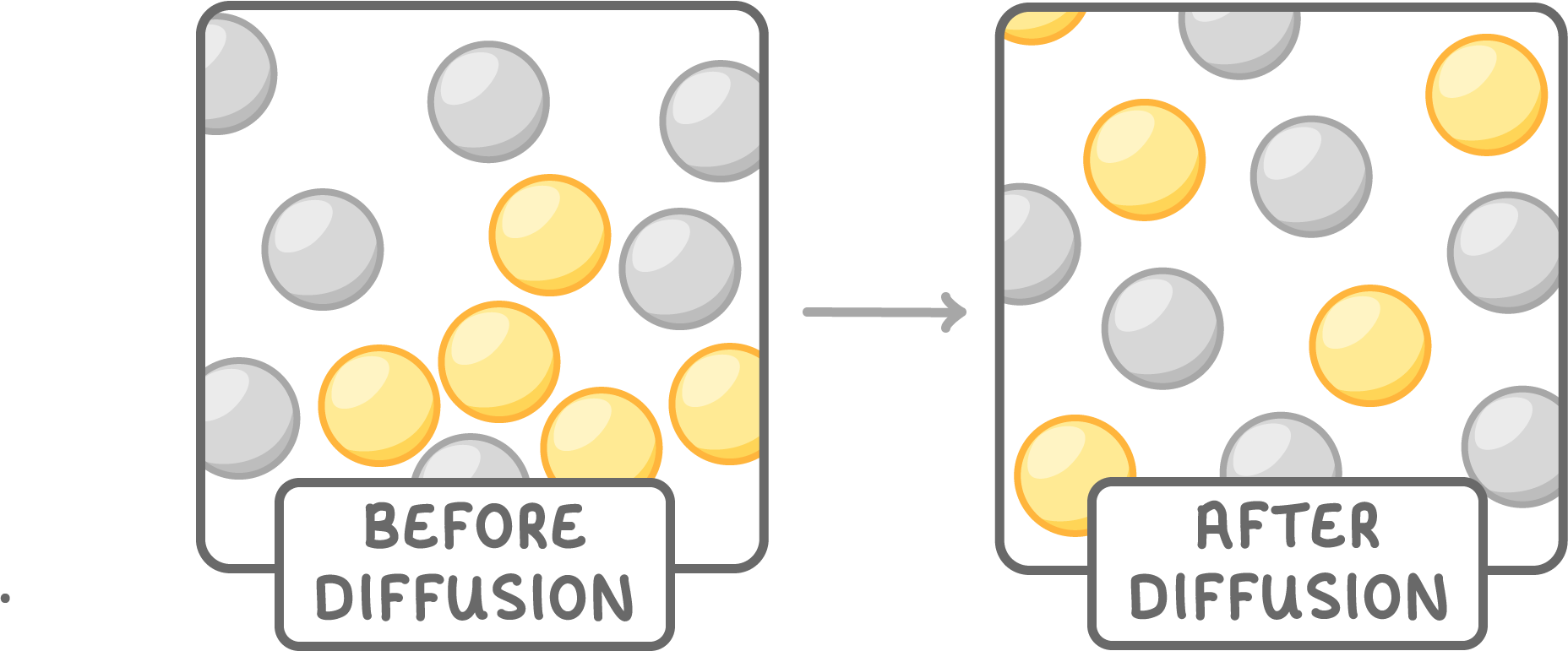
Diffusion is the spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until evenly distributed.
For example, perfume particles spreading through a room after it has been sprayed.
Diffusion takes place slowly because particles bump into air particles, changing their direction.