The periodic table
This lesson covers:
- The organisation of the periodic table
- Properties of different groups of elements
- Using the periodic table to predict reactivity
Properties of elements
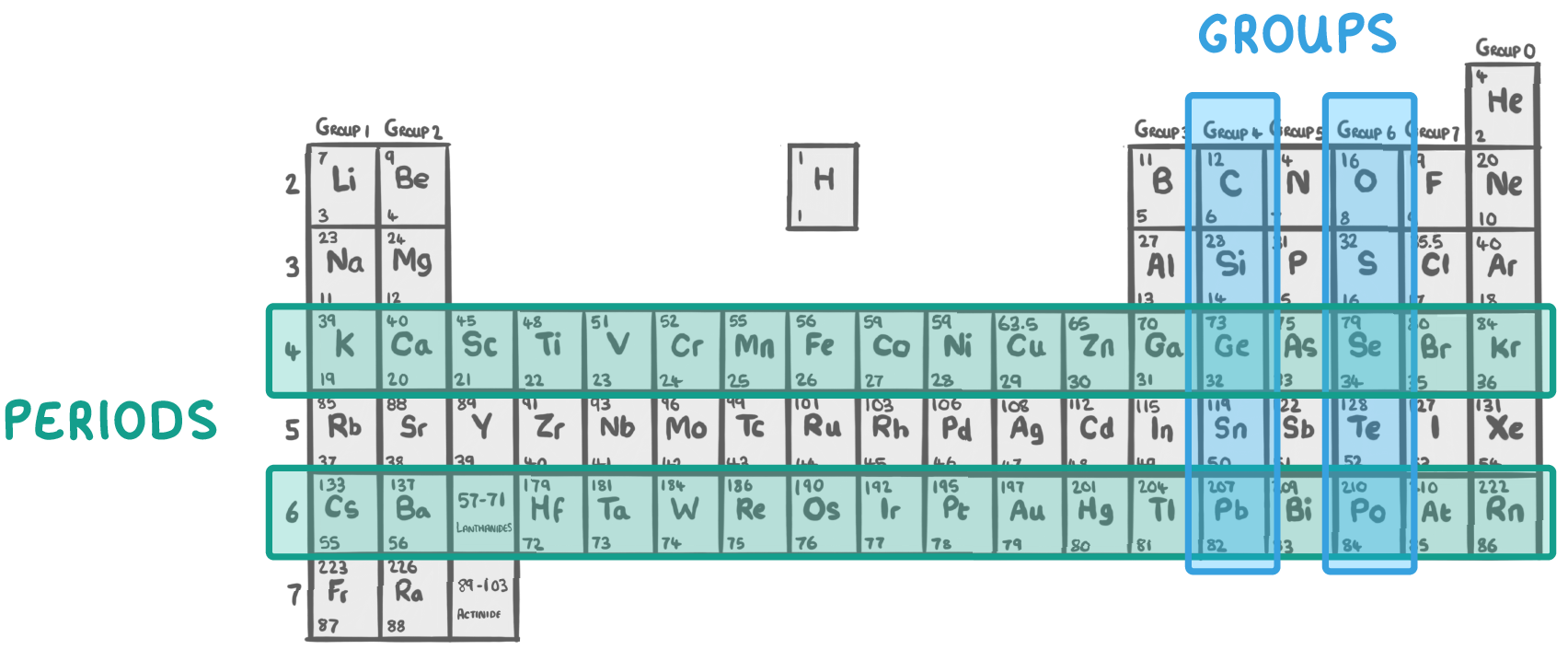
The periodic table is a table of all the chemical elements.
- In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev organised the elements into a table ordered by increasing atomic weight.
- Mendeleev noticed that elements with similar chemical and physical properties occurred at regular intervals.
- He arranged the elements into a table with:
- Horizontal rows called periods.
- Vertical columns called groups.
Groups of elements
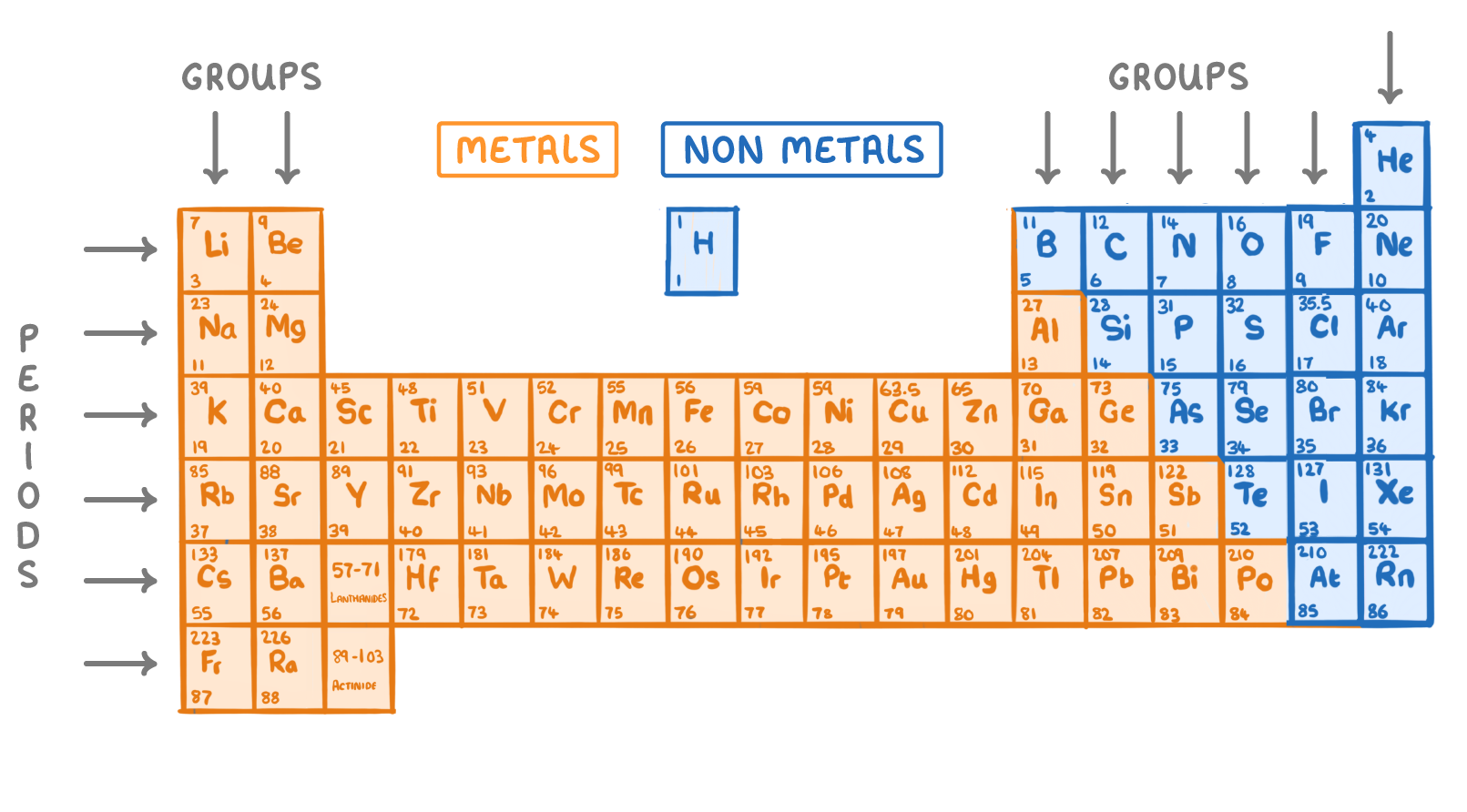
The table organises elements into periods and groups based on properties:
- Periods - The 7 horizontal rows. Properties of elements change gradually moving down each period.
- Groups - The 18 vertical columns. Properties of elements in the same group are similar.
- Metals - Found on the left and in the middle of the periodic table.
- Non-metals - Found on the right side of the periodic table.
Predicting reactivity
The position of elements in groups gives clues about how reactive they are.
Group 1 - The alkali metals
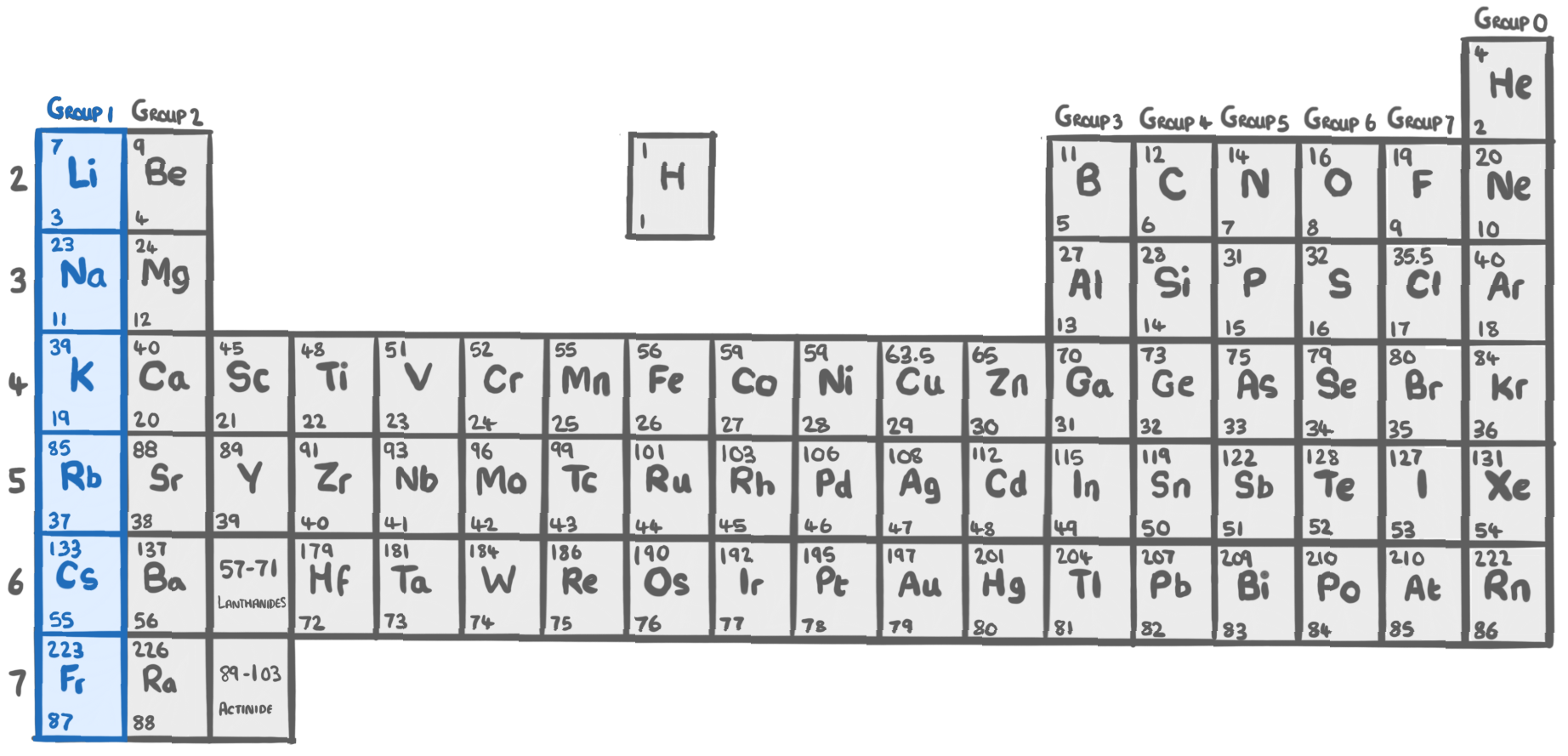
- Group 1 elements are on the far left side of the periodic table
- They are the most reactive metals.
- Their reactivity increases moving down the group.
Group 7 - The halogens
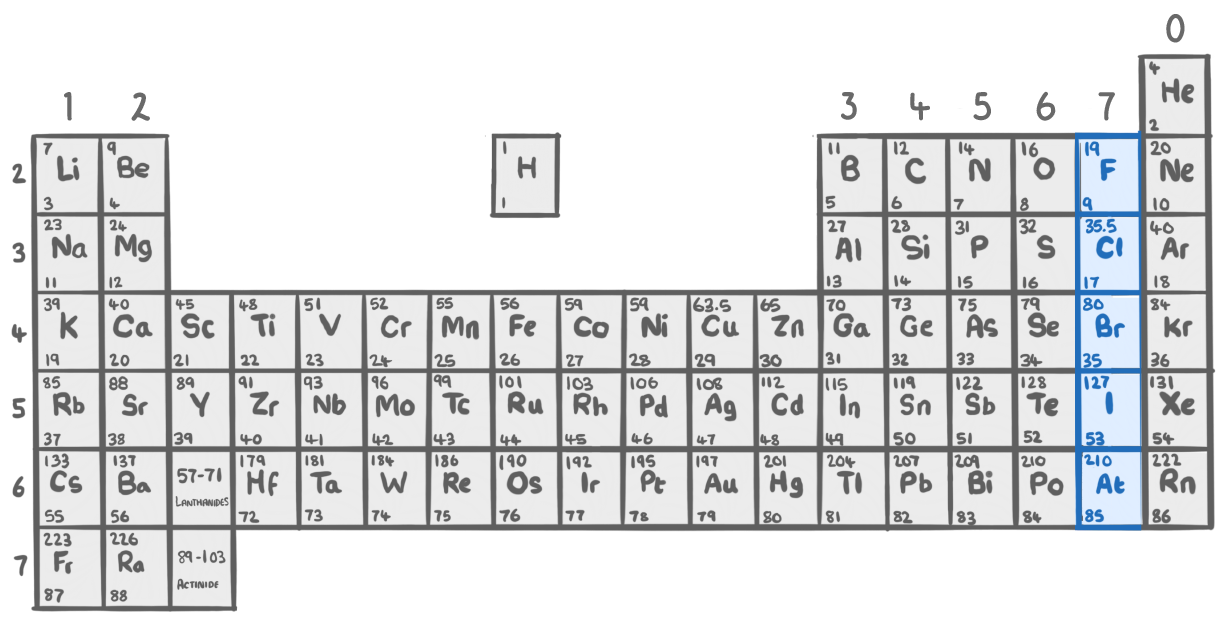
- Group 7 elements are on the far right side of the periodic table
- They are reactive non-metals.
- Their reactivity increases moving up the group.
Group 0 - The noble gases
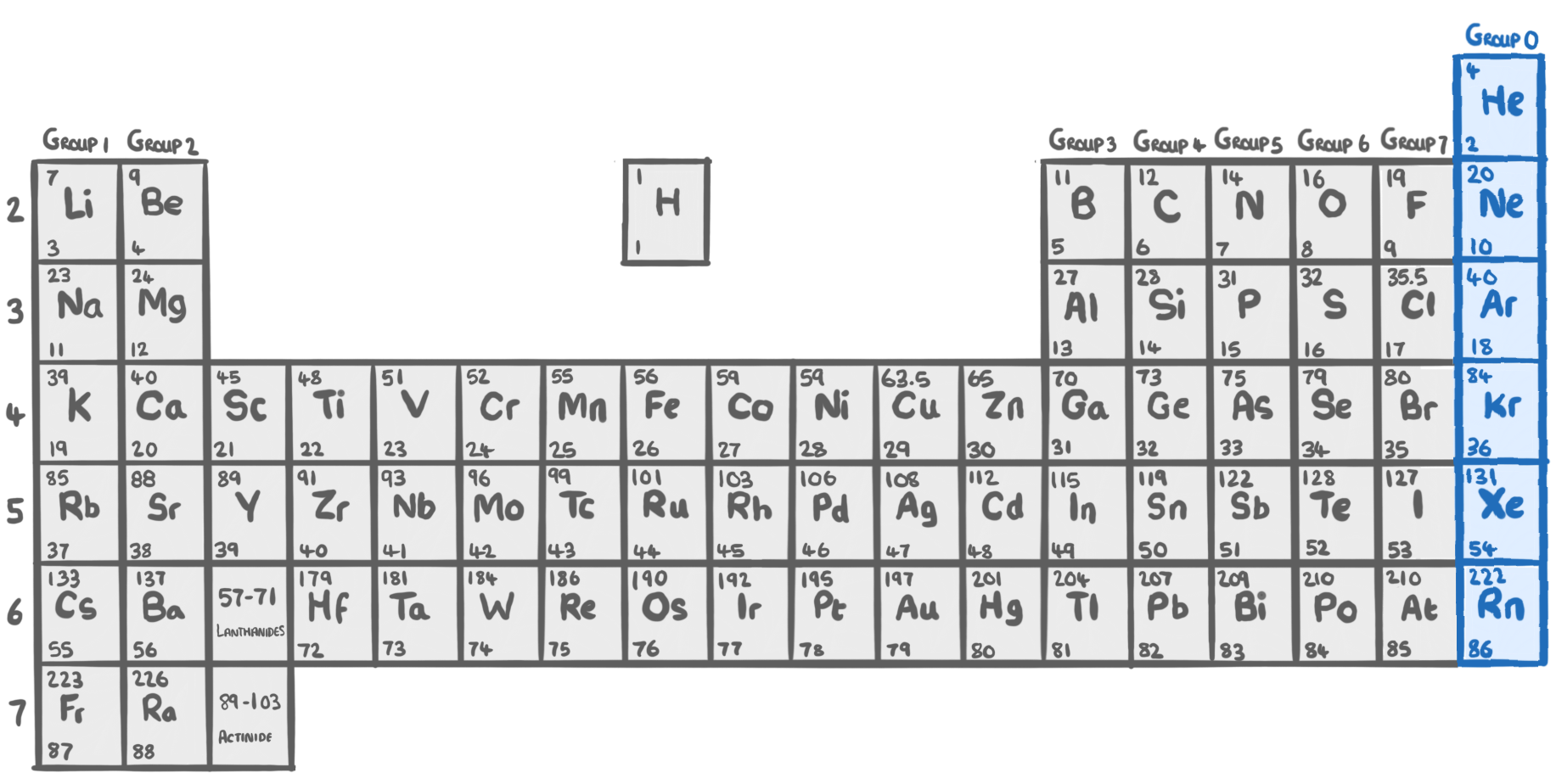
- Group 0 elements are on the far right side of the periodic table
- They are very unreactive.
- They have a stable outer shell of electrons.