The atmosphere and climate change
This lesson covers:
- What gases make up the Earth's atmosphere
- How human activities increase carbon dioxide concentration
- The effects of increased carbon dioxide on climate change
The Earth's atmosphere
The gases surrounding a planet make up that planet's atmosphere.
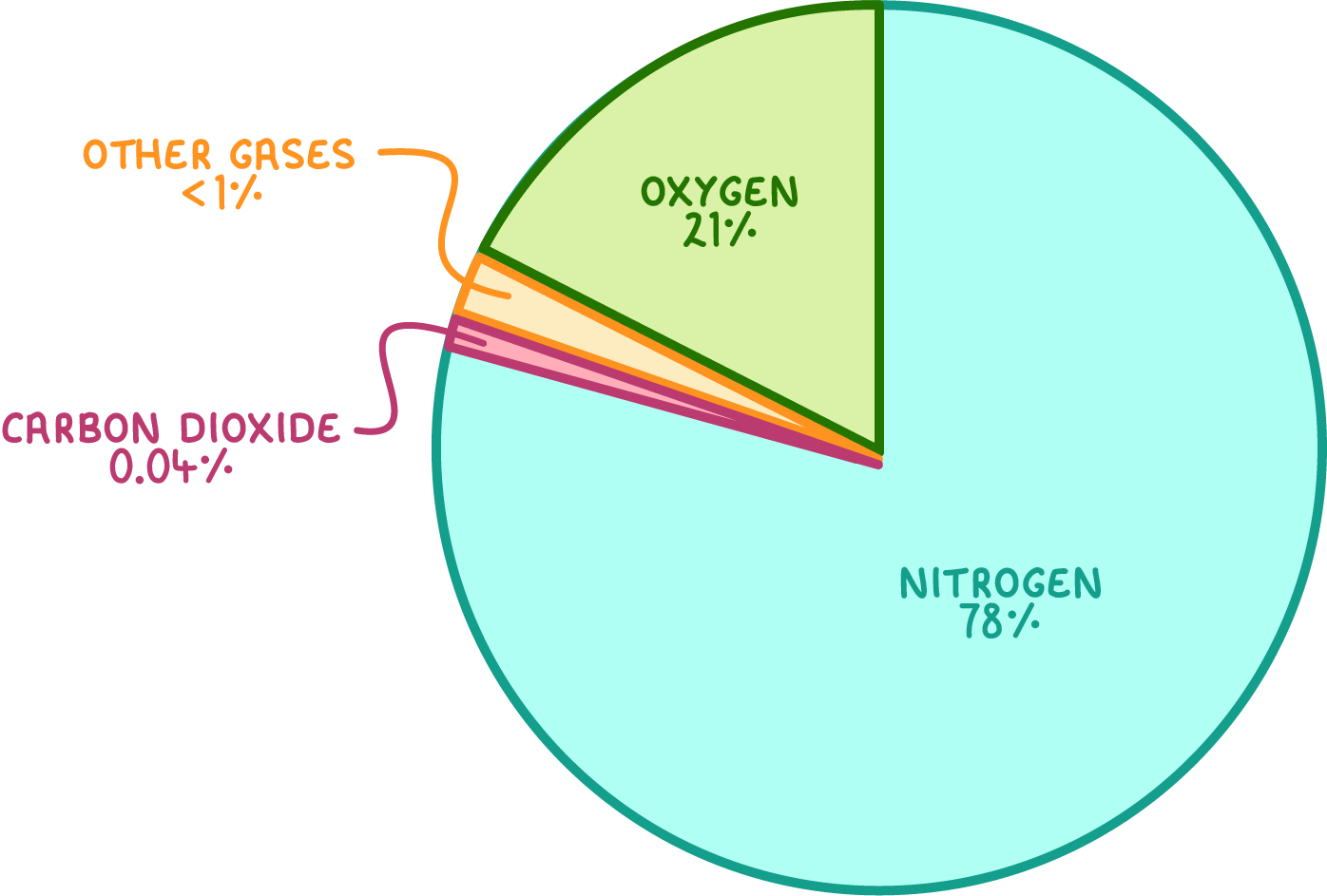
The Earth's atmosphere consists of:
- Nitrogen - 78%
- Oxygen - 21%
- Carbon dioxide - 0.04%
It also contains small amounts of other gases like water vapour and noble gases.
Human activities are increasing carbon dioxide concentration
Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is rising due to human activities and natural causes.

Examples of human activities increasing carbon dioxide concentration include:
- Burning fossil fuels to power vehicles and generate electricity releases carbon dioxide.
- Deforestation means less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere by photosynthesis.
Increasing carbon dioxide concentration affects the climate
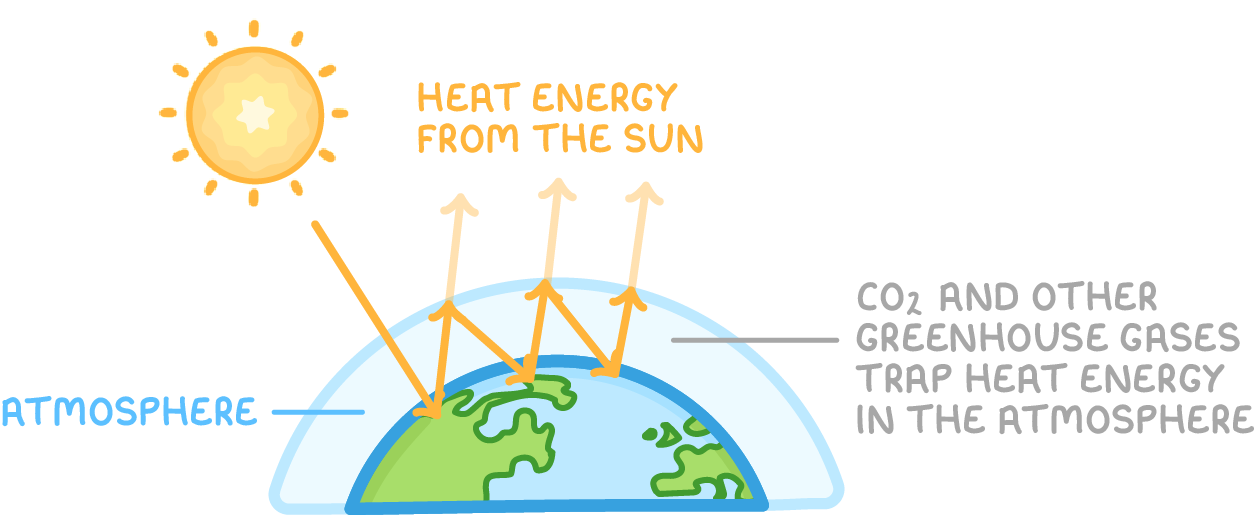
- Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that traps heat energy in the atmosphere.
- Increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases causes more heat energy to be retained rather than lost into space.
- Evidence shows the long term trend of rising Earth temperatures aligns with rising carbon dioxide concentration.
- The increase in the Earth's temperature is called global warming, which is a type of climate change.
Effects of climate change
Climate change can have serious effects such as:
- Melting of glaciers and ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica, causing sea levels to rise.
- Changes to rainfall patterns, making crop growth more difficult for farmers.