Reactions of metals with acids
This lesson covers:
- The products formed when metals react with acids
- How the reactivity of the metal affects the reaction
- Examples of the reaction of metals with acids
Acids and metals react to form new compounds
When acids and metals react, the products formed are a salt and hydrogen gas.
General equation: Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen
For example magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride (a salt) and hydrogen gas.
Word equation: Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid —> Magnesium chloride + hydrogen
Comparing Reactivity and Reactions
A metal's reactivity determines how it will react with acid.
Some metals are very reactive.
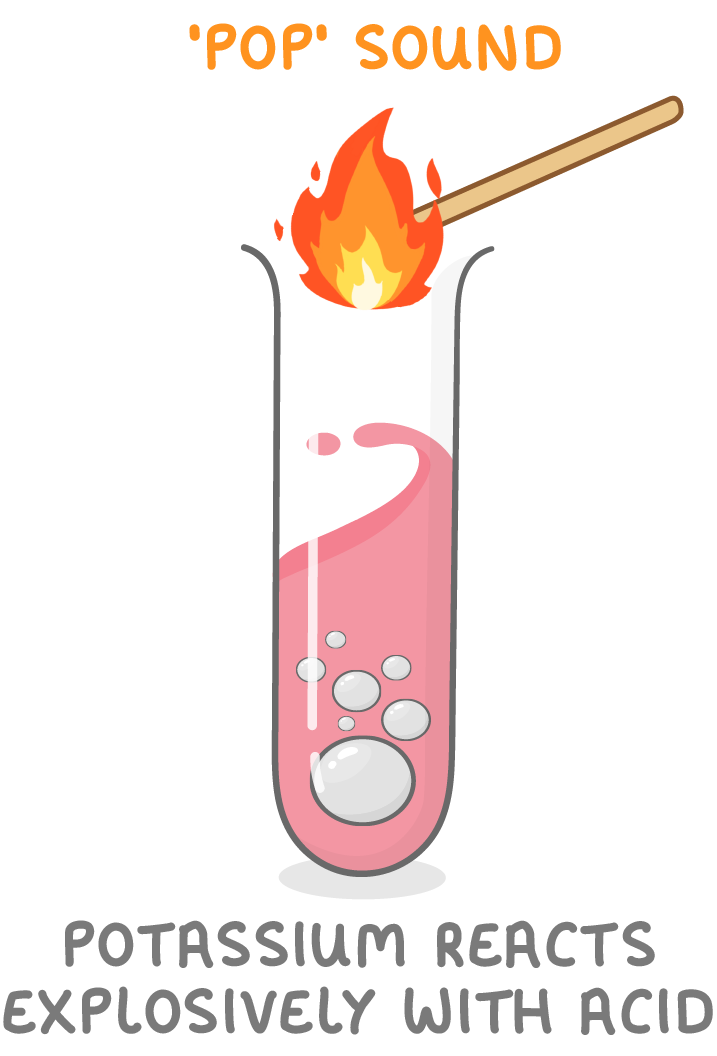

- Potassium, sodium, and calcium react violently with acids.
- You will see lots of gas bubbles produced, fire or even an explosion.
Some metals are moderately reactive.
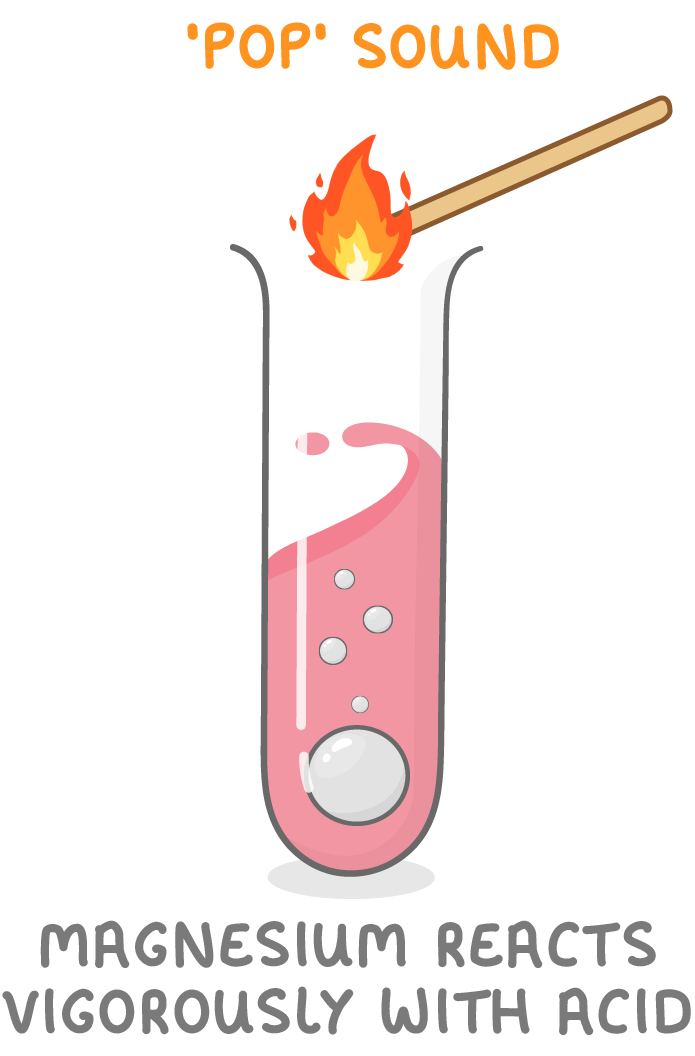

- Magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron, lead react fairly well with acids.
- You will see fizzing and bubbling caused by the gas produced.
Some metals are unreactive
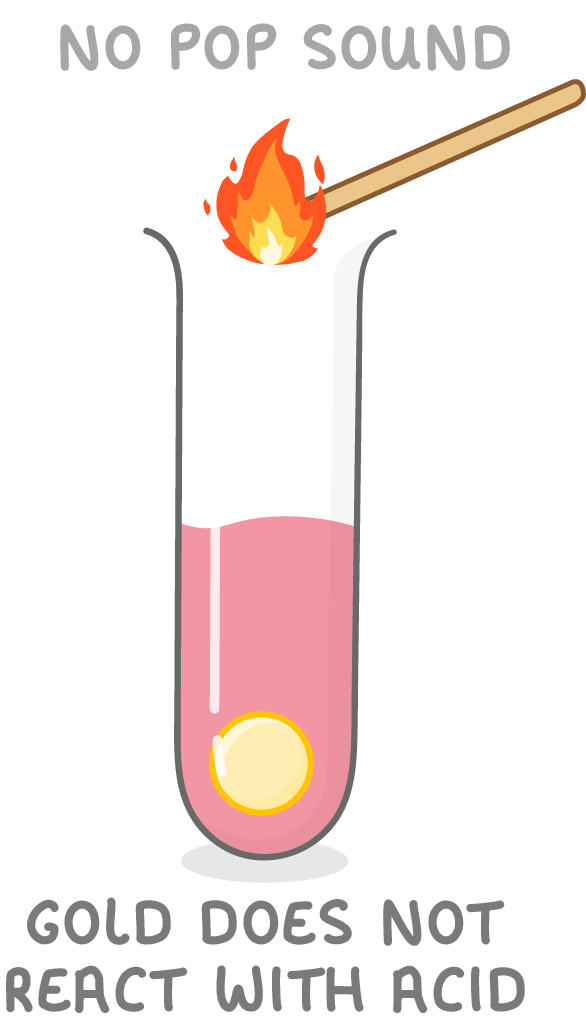
- Copper, silver, and gold are unreactive.
- You will see no change when they are placed in acids.
Examples of the reaction of metals with acids
When metals react with acids, the products formed depend on the acid used in the reaction.
zinc + hydrochloric acid —> zinc chloride + hydrogen
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
magnesium + sulfuric acid —> magnesium sulfate + hydrogen
Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2