Random Sampling
This lesson covers:
- Key biodiversity terminology and the different levels of biodiversity
- Sampling techniques for plants and animals
- How to prevent sampling bias and reduce the effects of chance
Defining biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of organisms in an area.
Levels of biodiversity:
- Habitat diversity - The number of habitats.
- Species diversity - The number of species and the number of individuals in each species.
- Genetic diversity - The variation in alleles within a population of a species.
High genetic biodiversity allows for better adaptation to a changing environment and resistance to disease.
Key terms related to biodiversity:
- Species - A group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring.
- Habitat - The place where a species lives within an ecosystem.
Sampling techniques
You need to know about a few different methods of sampling animals and plants.
Sampling animals
There are a several techniques for sampling animals you need to know.
Techniques for sampling animals:
- Pooter - This samples small insects by sucking air containing the insects into a plastic container via a tube.
- Sweep net - This samples insects in long grass or air, where the net is swept in a 'figure of eight' motion.
- Pitfall trap - This samples small, ground-crawling animals like insects and spiders by catching them in a hidden trap.
- Tree beating - This samples the invertebrates living in a tree or bush by shaking or beating the tree to dislodge insects onto a white sheet below.
- Kick sampling - This samples river organisms by kicking a river bank and catching organisms downstream in a net.
Sampling plants and non-motile animals using quadrats
A quadrat is a frame used to sample the organisms in an area. They are typically used to sample plants, or animals that don’t move around much (non-motile animals).
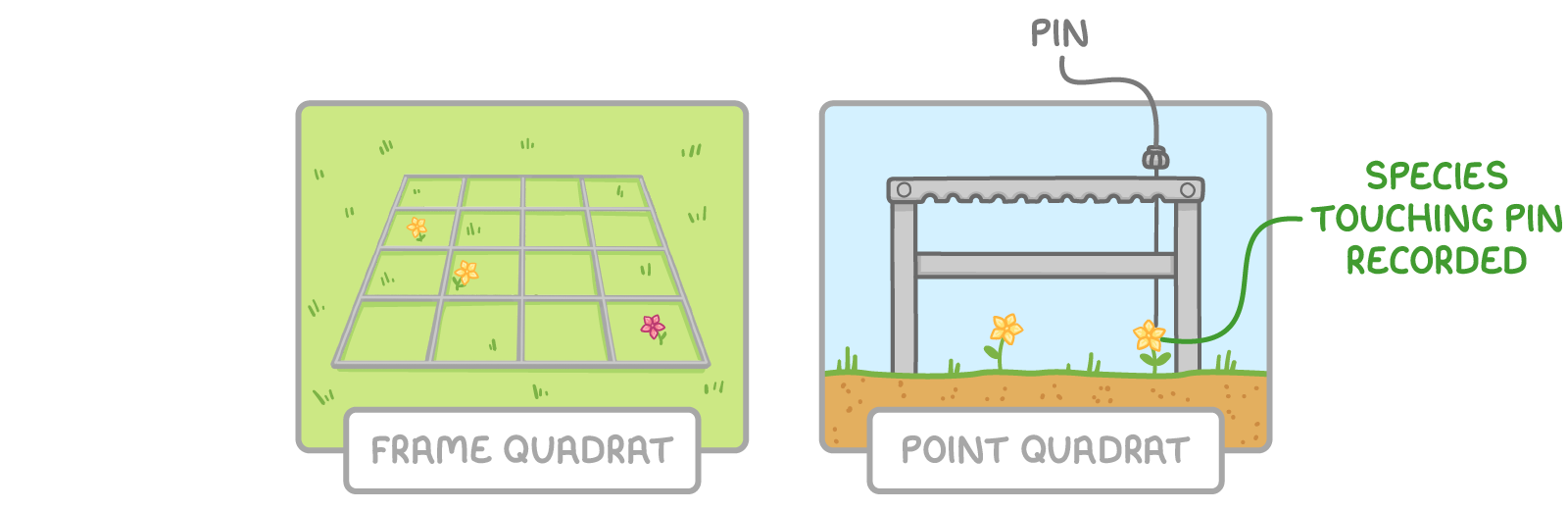
There are two types of quadrat you can use:
- Frame quadrat - This is a square frame divided into a grid. The type and number of species within each section of the quadrat is recorded.
- Point quadrat - This is a frame with a horizontal bar, through which pins are pushed at set intervals to touch the ground. Each species the pin touches is recorded.
Methods of estimating the number of individuals in a frame quadrat:
Density - The number of individuals of a species in a 1 m2 quadrat.
Frequency - Calculated as number of total squares in a quadratnumber of times a species is found in a quadrat×100.
Percentage cover - An estimate of the area within a quadrat that a species covers.
How to prevent sampling bias and reduce the effects of chance
Random sampling is important to ensure the samples are representative of the whole area.
The best way to prevent sampling bias is to:
- Eliminate any human involvement in choosing the samples by carrying out random sampling.
- Take measurements of individuals selected randomly from the population of organisms being investigated.
We can minimise the effect of chance in random sampling by:
- Using a large sample size.
- Analysing the data collected.