Measuring Ventilation
This lesson covers:
- Measuring lung capacity
- How to measure lung volume
- How to calculate ventilation rate
Measuring data on lung function, volume, and capacity There are various instruments that can measure the flow of air into and out of the lungs, providing data on lung function and capacity. Some examples of instruments that provide data on lung function include:
|
Measuring lung volume We can use spirometer traces to work out the volume of air in the lungs and create graphs like the one below. 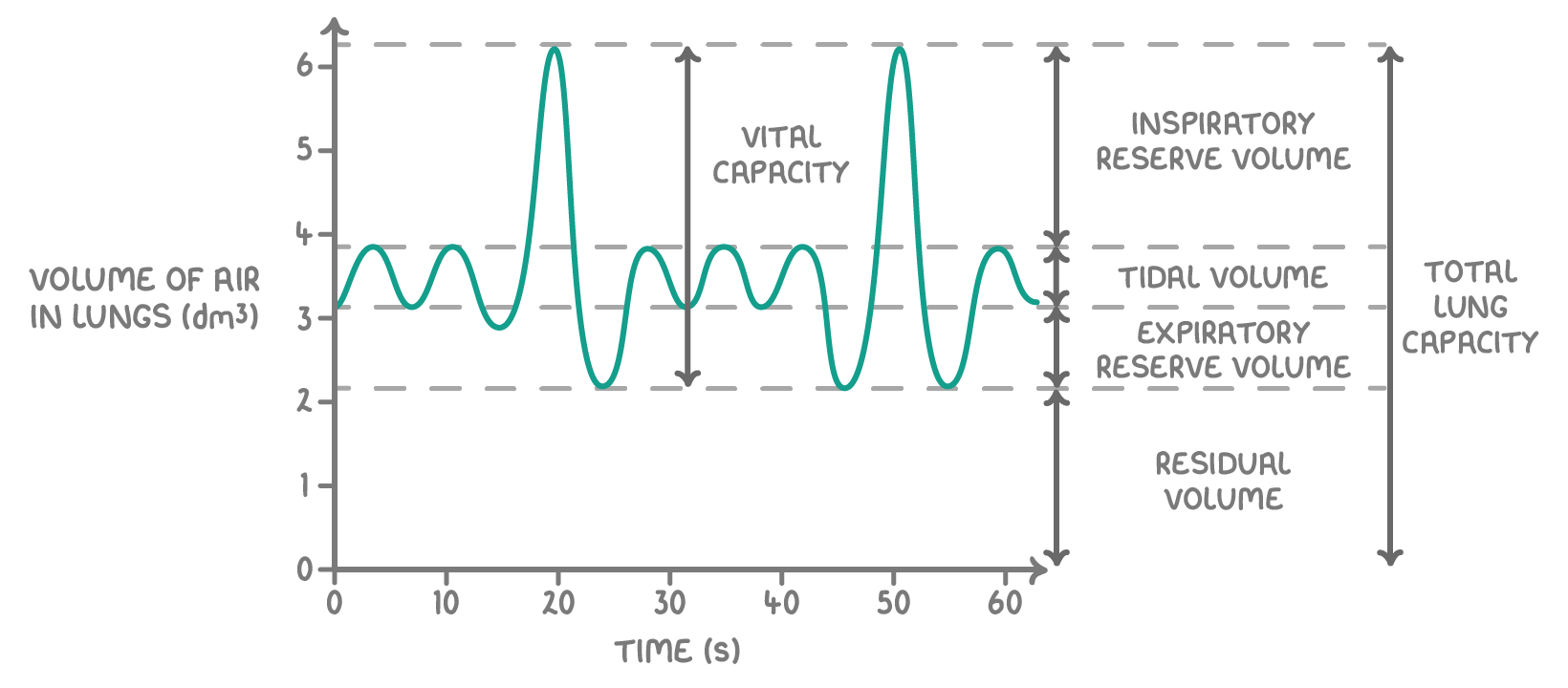 |
Using this graph, you can calculate:
|
Calculating oxygen consumption Oxygen consumption is the volume of oxygen used per minute. If we had a spirometer trace, we could also measure oxygen consumption. This is the slope of a spirometer trace. We can calculate oxygen consumption as the change in the volume of gas in the spirometer over a period of time and divide this value by the time taken. |
Ventilation rate Ventilation rate is the volume of oxygen inhaled per minute. Ventilation rate can be calculated as follows:
|
Worked example - Calculating ventilation rate
An individual took 15 breaths in a minute. Their tidal volume was measured as 500 cm3.
Calculate their ventilation rate in dm3 min-1.
Step 1: Equation
ventilation rate = tidal volume × breathing rate
Step 2: Conversion
to convert cm3 into dm3, divide by 1,000
tidal volume =1,000500 dm3
tidal volume =0.5 dm3
Step 3: Substitution and correct evaluation
ventilation rate =0.5×15
ventilation rate =7.5 dm3 min−1