Adrenal Glands
This lesson covers:
- The location and structure of the adrenal glands
- The hormones produced by the adrenal cortex
- The hormones produced by the adrenal medulla
Location and structure of the adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are a pair of small, triangular endocrine glands located above each kidney. They are essential components of the body's endocrine system.
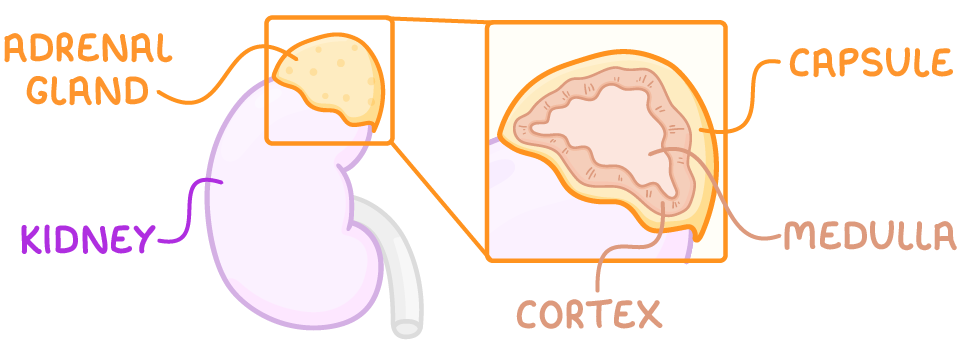
The adrenal glands consist of two main regions, surrounded by a capsule:
- Adrenal cortex – The outer region of the glands, responsible for producing vital steroid hormones.
- Adrenal medulla – The inner region at the centre of the glands, known for producing catecholamine hormones.
Hormones produced by the adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex synthesises and releases three groups of steroid hormones, each with specific functions.
| Type of hormone | Functions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Glucocorticoids | Regulate metabolism by controlling the conversion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates to energy. Control blood pressure and stress responses. Regulate the immune response and suppress inflammation. | Cortisol, corticosterone |
| Mineralocorticoids | Maintain blood pressure by balancing salt and water in the blood and body fluids. | Aldosterone |
| Androgens | Regulation of sexual characteristics and cell growth. | Testosterone |
The release of these hormones is regulated by chemical signals from the hypothalamus and kidneys, ensuring the adrenal glands' efficient function within the endocrine system.
Hormones produced by the adrenal medulla
The adrenal medulla produces catecholamines, which are hormones that prepare the body for stressful or dangerous situations.
These are released when the sympathetic nervous system is stimulated.
Adrenaline and noradrenaline
The two main catecholamine hormones are adrenaline and noradrenaline, which work together to help the body respond to stress and activate the body's fight-or-flight response. Some of their main effects are listed below.
Adrenaline:
- Increases heart rate and blood pressure to increase blood flow to the muscles and brain.
- Increases blood glucose levels.
- Increases breathing rate.
- Dilates bronchioles.
Noradrenaline:
- Increases heart rate.
- Expands air passages.
- Dilates pupils.
- Narrows blood vessels in organs like the gut to reduce blood flow to regions that aren't helpful in the stress response.