Organisation of the Nervous System
This lesson covers:
- The structural organisation of the nervous system
- The functional organisation of the nervous system
- The divisions of the autonomic nervous system
The structural organisation of the nervous system
The mammalian nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (shown in purple below) and the peripheral nervous system (shown in green below).
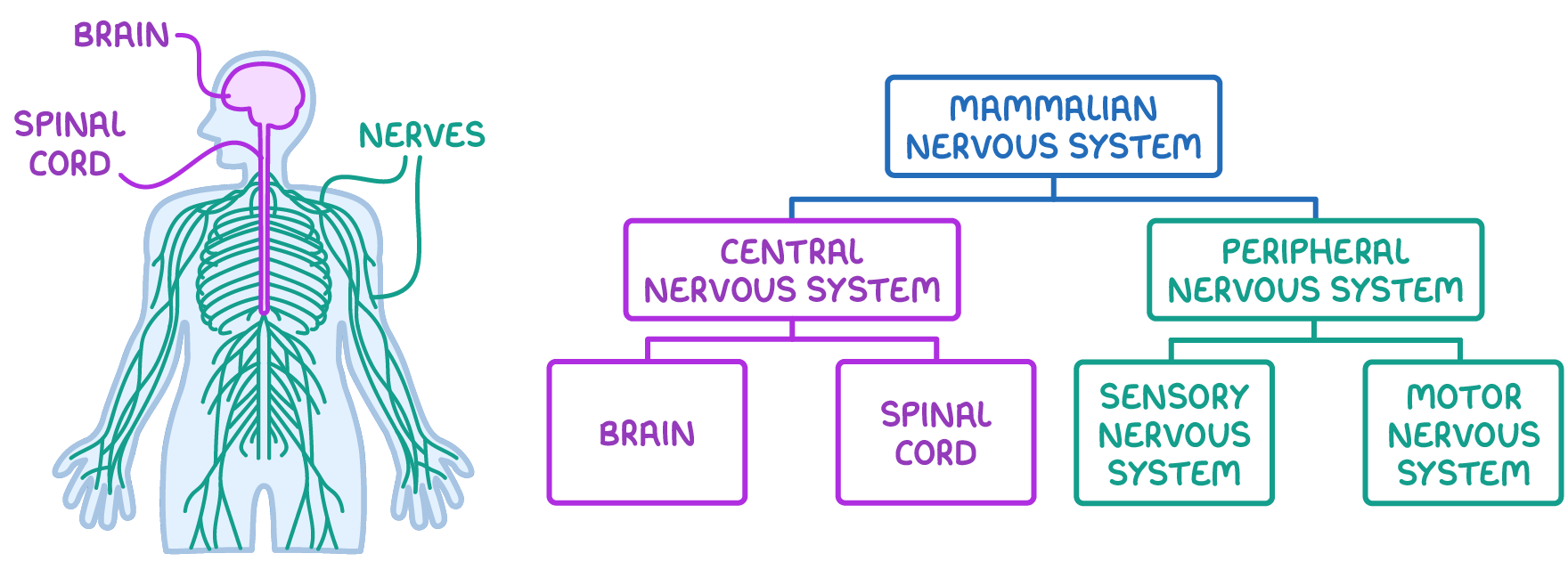
The central nervous system (CNS)
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- Serves as the primary command centre for the body.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- Consists of all the nerves (made up of nerve cells called neurones) that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
- This facilitates bi-directional communication.
The peripheral nervous system has two further divisions:
- The sensory nervous system - This consists of sensory neurones that carry nerve impulses from receptors to the CNS.
- The motor nervous system - This consists of motor neurones that carry nerve impulses from the CNS to effectors like muscles and glands.
The functional organisation of the nervous system
The nervous system operates through distinct yet interconnected divisions.
These can be functionally divided as follows:
- The somatic (voluntary) nervous system - This is controlled consciously, for voluntary muscle movements.
- The autonomic (involuntary) nervous system - This is controlled subconsciously, for involuntary activities such as the heartbeat and digestion.
Although we can control some autonomic functions, like adjusting our breathing rate, the nervous system mostly operates without our conscious awareness. This lets the brain focus on complex tasks without the distraction of managing fundamental physiological activities.
The divisions of the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is split into two divisions that usually have opposite effects on body functions.
These divisions of the autonomic nervous system and some of their key features are shown in the table below.
| Division of the autonomic nervous system | Function | Typical effect on activity levels | Neurotransmitters used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sympathetic nervous system | Activates the 'fight or flight' response | Increases activity levels | Adrenaline and noradrenaline |
| Parasympathetic nervous system | Activates the 'rest and digest' response | Decreases activity levels | Acetylcholine |