Plant Hormones: Auxins
This lesson covers:
- What plant growth factors are
- The key roles of auxins
- How IAA controls growth by elongation
- How IAA influences apical dominance
Plant growth factors
Plant growth factors, sometimes called plant hormones or plant growth regulators, are chemicals that influence plant development mainly by modulating cell elongation and division.
Plant hormones can interact with each other in various ways, as they may be:
- Synergistic - This is when different hormones work together, giving a greater response than they would on their own.
- Antagonistic - This is when different hormones have opposing effects, like one promoting growth and one inhibiting it. The balance between them determines the response of the plant.
Introduction to auxins
Auxins, particularly indoleacetic acid (IAA), are crucial plant growth factors. Auxins like IAA are synthesised in the growing tips (meristems) of shoots and roots, where the cells are dividing.
They regulate various aspects of plant growth, such as:
- Cell expansion and differentiation.
- Suppression of lateral bud growth (apical dominance).
- Directional growth responses (tropisms).
Auxins have different effects on different plant tissues:
- High auxin concentrations inhibit root growth, and promote shoot growth.
- Low auxin concentration promote root growth and inhibit shoot growth.
The role of IAA in shoot elongation
Auxins like IAA play a key role in shoot growth via cell elongation.
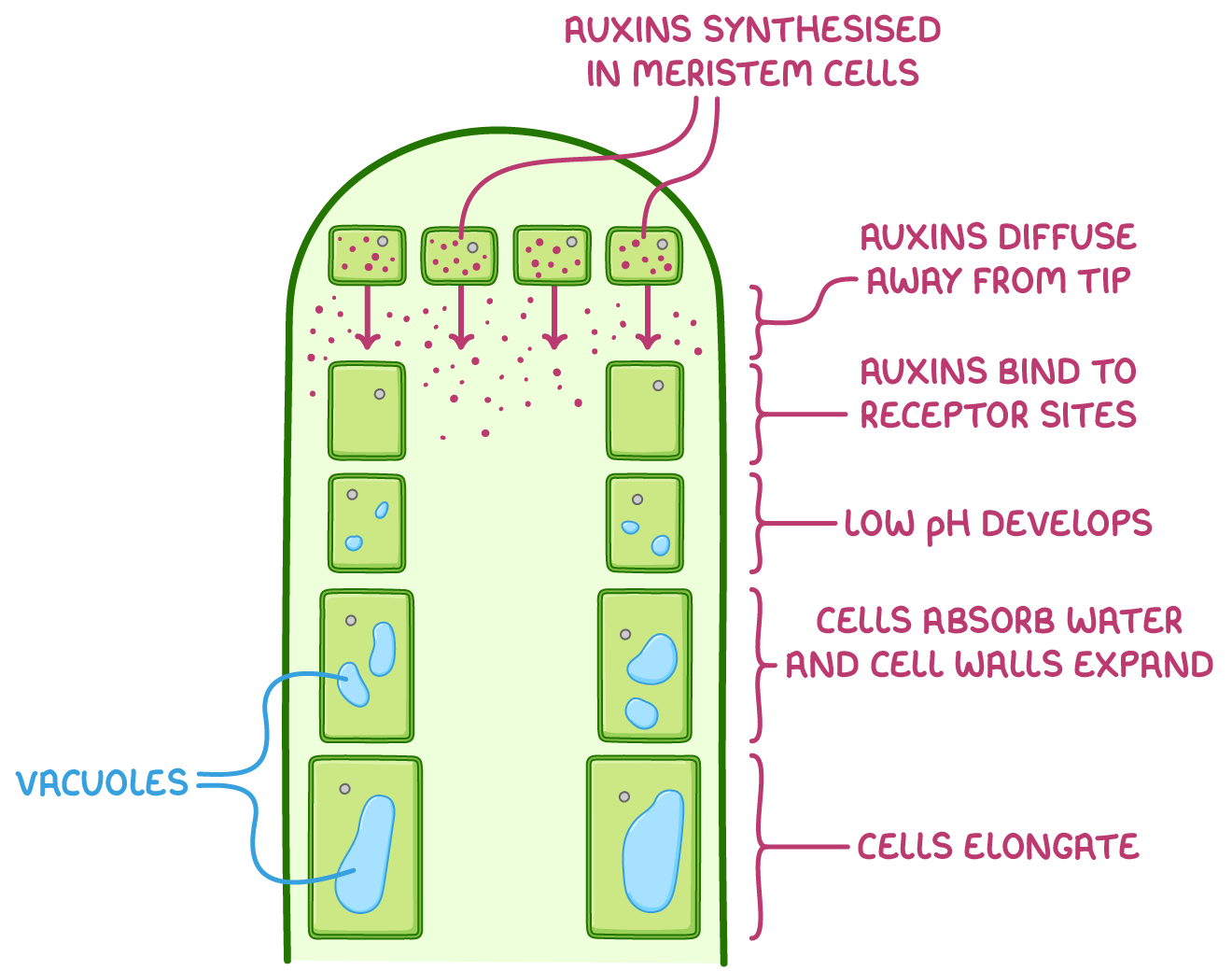
This occurs as follows:
- Auxins are synthesised by the meristem cells in shoot tips.
- Auxins diffuse down the shoot away from the tip.
- Auxins bind to receptor sites on cell-surface membranes.
- A low pH develops in cell walls.
- The cells absorb water by osmosis, forming vacuoles and increasing the internal pressure, causing the cell walls to expand.
- Cells elongate and the plant grows.
The role of IAA in apical dominance
IAA is synthesised at the shoot tips. It stimulates the growth of the main, apical shoot and suppresses the growth of lateral shoots. This is called apical dominance.
The removal of the apical bud, and thus the source of IAA, releases the inhibition on lateral bud growth. This allows for bushier plant development.