The process of transcription
Transcription is the initial step in the synthesis of proteins. It involves creating an mRNA copy of a gene from the DNA template.
In eukaryotic cells, transcription takes place within the nucleus. This mRNA then exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where translation occurs.
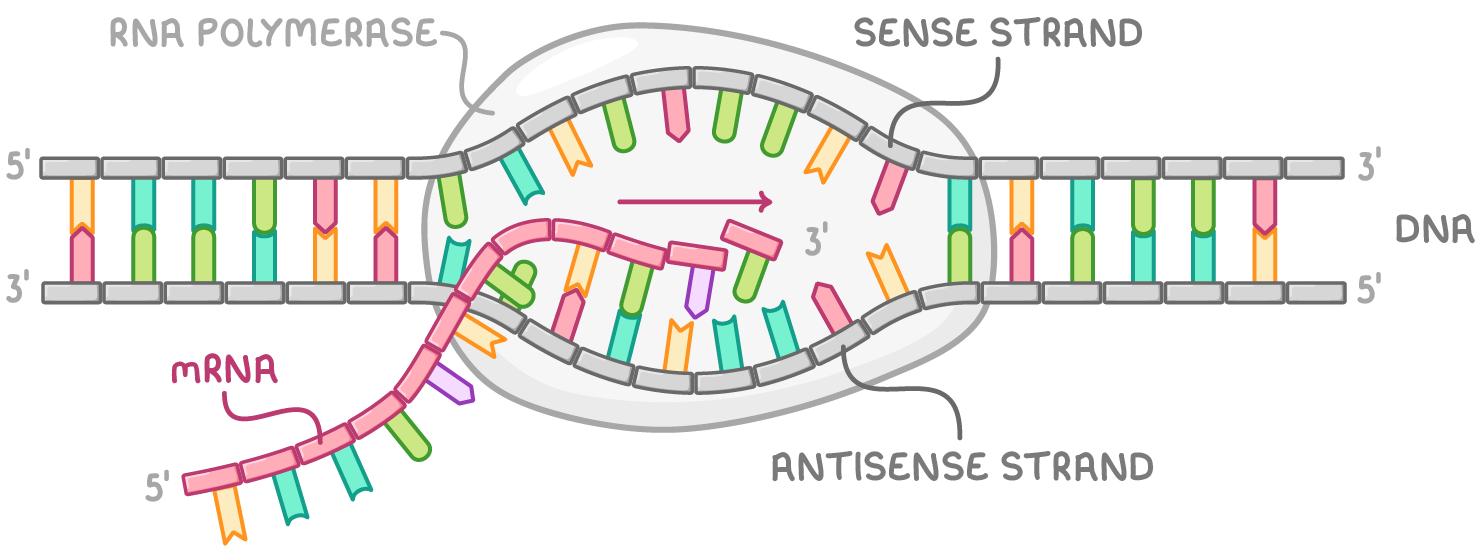
Key events in transcription:
- Transcription begins with the RNA polymerase enzyme binding to DNA.
- The hydrogen bonds between the DNA bases break, and the two strands of the double helix separate.
- The antisense strand acts as the template for mRNA synthesis.
- Free RNA nucleotides align with the DNA template through complementary base pairing.
- In the RNA molecule, uracil pairs with adenine, while adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
- RNA polymerase catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds between adjacent RNA nucleotides.
- A complementary mRNA strand is formed, carrying the same base sequence as the DNA sense strand.
- The process ends when RNA polymerase reaches a stop codon, detaches from DNA and terminates transcription.
- mRNA is released, detaches from DNA, and DNA rewinds into its double helix structure.
Protein Synthesis: Transcription
This lesson covers:
- The process of transcription