Animal Pathogens and Diseases
This lesson covers:
- The different types of pathogen
- How pathogens are transmitted
- Examples of communicable diseases
Pathogens Communicable (or infectious) diseases are those that can be passed from one organism to another. They are caused by microorganisms known as pathogens. There are four types of pathogen you need to know: |
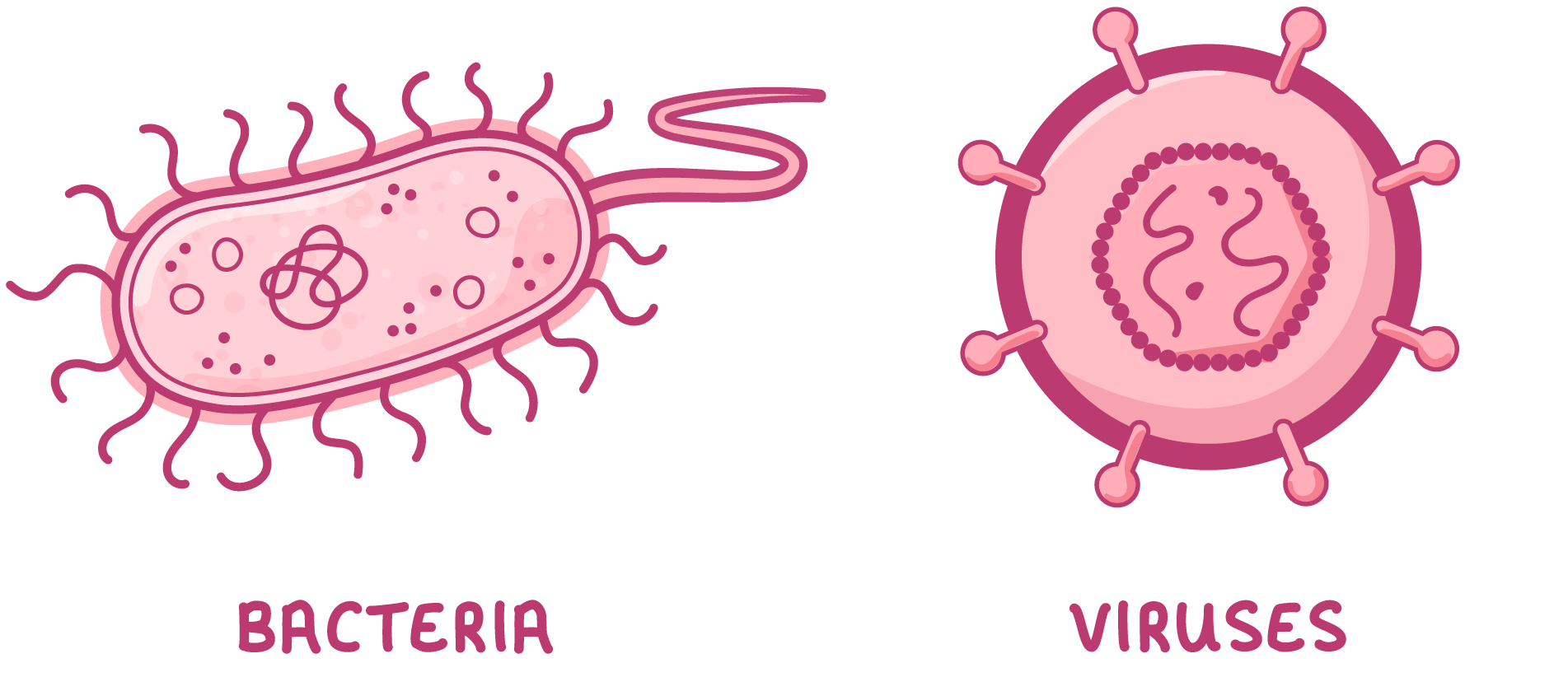  |
|
Modes of transmission Communicable diseases can be passed from one organism to another via direct or indirect transmission. |
Direct transmission Pathogens can be transferred directly from one organism to another. This transfer can take place in several ways:
|
Indirect transmission Communicable diseases can also be passed from one organism to another using an intermediate (e.g. water or another organism). This transfer can take place in several ways:
|
The risk of communicable disease is increased by certain factors:
|
Examples of communicable diseases You need to be able to describe the cause and transmission of the following communicable diseases:
|