Structure & Function of the Brain
This lesson covers:
- The location of key brain structures
- The functions of different brain regions
- How the brain controls vital bodily processes
Introduction to the brain
The brain is contained within the skull and is the control centre of the central nervous system.
It receives and processes sensory information from receptor cells and the hormonal system about changes in the internal and external environment to produce a coordinated response.
It controls movement and physiological functions, and enables cognition and emotion.
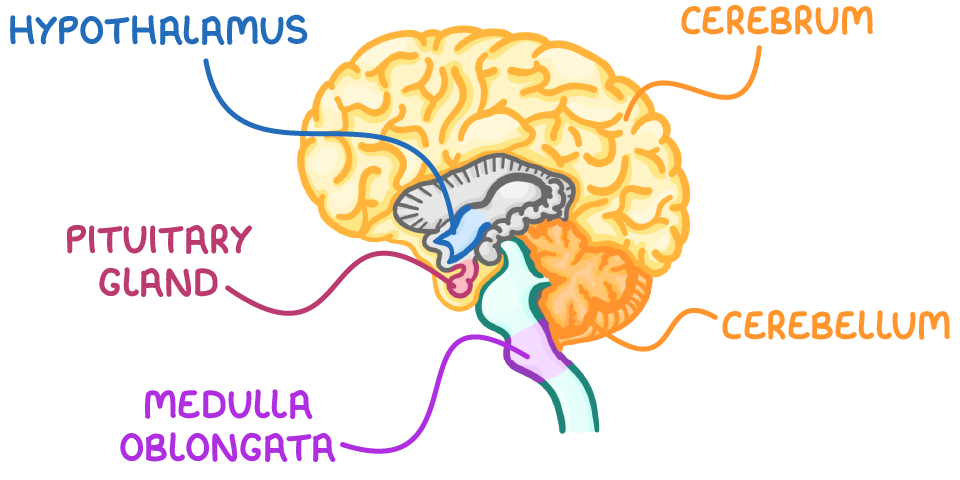
There are five key brain structures you need to know about:
- Hypothalamus
- Cerebrum
- Pituitary gland
- Medulla oblongata
- Cerebellum
The hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is located just below the middle part of the brain.
Functions of the hypothalamus:
- Homeostasis - It helps to regulate body temperature by sensing changes and initiating appropriate responses, such as triggering sweating or shivering.
- Water balance - It monitors and helps to regulate the composition of blood plasma, like the concentration of water and glucose in blood.
- Hormonal regulation - It regulates hormone secretion from the pituitary gland.
The cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It consists of two halves called the left and right cerebral hemispheres that receive sensory information, and has an outer layer called the cerebral cortex that has many folds.
Each sensory area within the cerebral hemispheres receives information from receptor cells located in sense organs. The information is then passed on to other areas of the brain, known as association areas, to be analysed and acted on.
Functions of the cerebrum:
- It processes sensory input, and so is crucial for processes like vision and hearing.
- It is involved in learning, memory, and higher-level thinking.
The pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is found just below the hypothalamus.
Functions of the pituitary gland:
- It produces, stores, and secretes hormones when triggered by the hypothalamus.
- The hormones it secretes prompt other glands, like the adrenal glands, to secrete their hormones.
There are two main sections of the pituitary gland:
- The anterior pituitary gland - It produces six hormones including follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which is involved in reproduction, and growth hormones.
- The posterior pituitary gland - It stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus including ADH, which is involved in urine production.
The medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata is located at the base of the brain, connecting it with the spinal cord.
Functions of the medulla oblongata:
- It involuntarily regulates breathing rate.
- It involuntarily regulates heart rate and blood pressure.
- It controls other autonomic nervous system functions like swallowing, peristalsis, and coughing.
The cerebellum
The cerebellum is located underneath the cerebrum.
Functions of the cerebellum:
- It is important for coordinating and fine-tuning skeletal muscle contractions.
- It is essential for maintaining unconscious functions like posture, balance, and involuntary muscular movement
It receives information about balance and the tone of muscles and tendons, and relays this information to the areas of the cerebral cortex involved in motor control.