Structure of the Mammalian Nervous System
This lesson covers:
- An introduction to nerves and neurones
- The structural organisation of the nervous system
An introduction to nerves and neurones
The mammalian nervous system mainly consists of nerves. Nerves are made up of many nerve cells called neurones.
Key features of neurones:
- They carry information directly to their target cells.
- They transfer information in the nervous system at very high speeds in the form of nerve impulses.
- They coordinate the activities of sensory receptors, decision-making centres in the central nervous system, and effectors like muscles and glands.
The structural organisation of the nervous system
The mammalian nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (shown in purple) and the peripheral nervous system (shown in green).
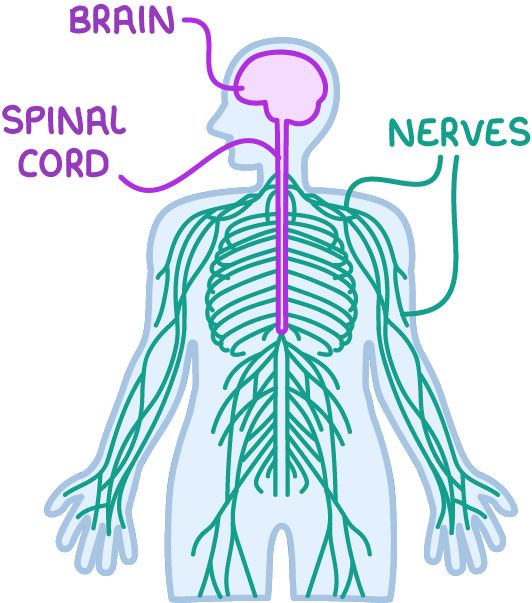
The central nervous system (CNS)
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- Serves as the primary command centre for the body.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- Consists of all the neurones that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
- Includes the neurones in spinal nerves (attached to the spinal cord) and cranial nerves (attached to the brain).