Limiting Factors
This lesson covers:
- Requirements for photosynthesis and its limiting factors
- How light intensity affects photosynthesis
- How carbon dioxide concentration affects photosynthesis
- How temperature affects photosynthesis
Requirements for photosynthesis
For photosynthesis to occur, the following are required:
- Photosynthetic pigments (e.g. chlorophyll) - These absorb light energy.
- Carbon dioxide - This provides carbon to make glucose.
- Water - This provides electrons and is a source of hydrogen ions (protons).
- Light - This provides energy to split water, to produce ATP, and to reduce NADP.
- A suitable temperature - This provides kinetic energy for reactions.
Limiting factors in photosynthesis
A limiting factor is a requirement that is in shortest supply. Increasing this factor allows the rate of photosynthesis to increase.
The main factors limiting the rate of photosynthesis are:
- Light intensity
- Carbon dioxide concentration
- Temperature
How light intensity affects photosynthesis
As light is required for photosynthesis, changing light intensity has a direct effect on the rate of photosynthesis.

This occurs as follows for different light intensities:
- Low light intensity - This limits the light-dependent stage, so not much ATP and reduced NADP are produced. This slows the light-independent stage, and the rate of photosynthesis is low.
- Intermediate light intensity - This produces more ATP and reduced NADP in the light-dependent stage, which regenerates RuBP in the light-independent stage more quickly. More GP gets converted to TP, and the rate of photosynthesis increases.
- Very high light intensity - There is more light than needed, so another factor like temperature becomes limiting and the rate plateaus.
The light compensation point is when the volume of oxygen produced and carbon dioxide absorbed in photosynthesis is balanced by the oxygen absorbed and the carbon dioxide produced by respiration.
How carbon dioxide concentration affects photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of the key reactants for photosynthesis, so changing CO2 concentration has a direct effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
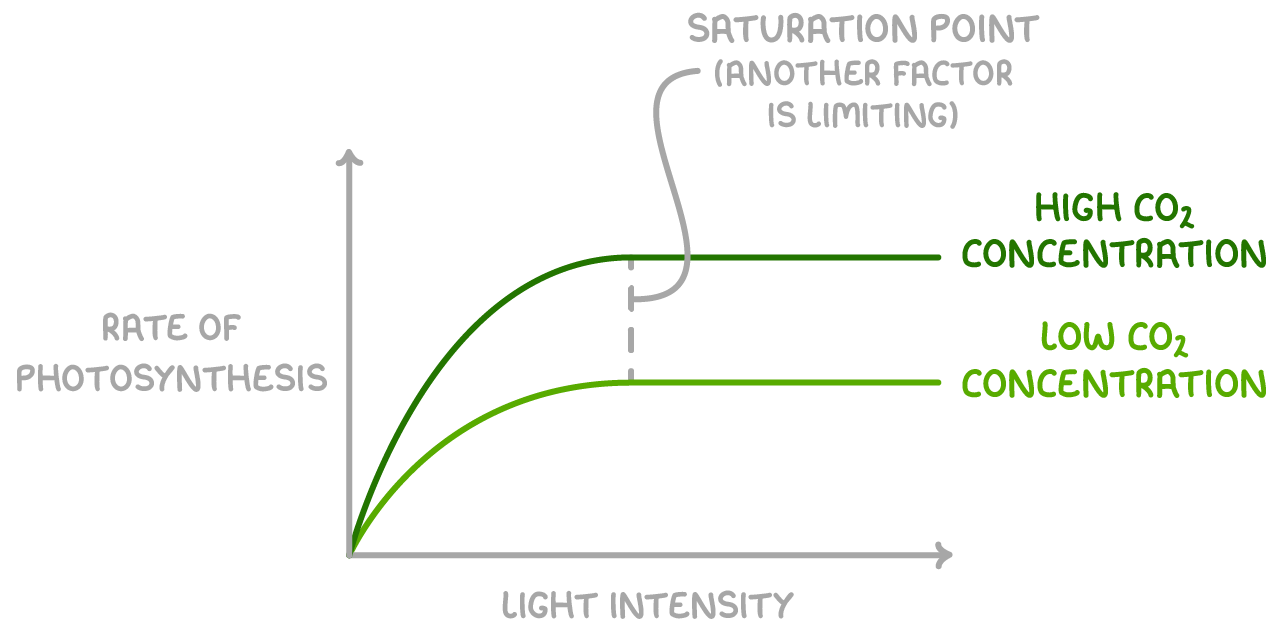
This occurs as follows for different CO2 concentrations:
- Low CO2 concentration - This limits the light-independent reaction as less CO2 is fixed, reducing the production of GP and TP. The rate of photosynthesis is low.
- Intermediate CO2 concentration - This allows faster production of GP and TP, increasing the rate of photosynthesis.
- High CO2 concentration - Another factor like light becomes limiting.
The saturation point is when the factor being measured is no longer limiting the reaction and something else is the limiting factor.
How temperature affects photosynthesis
Photosynthesis involves several different proteins and enzymes, so changing temperature has a direct effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
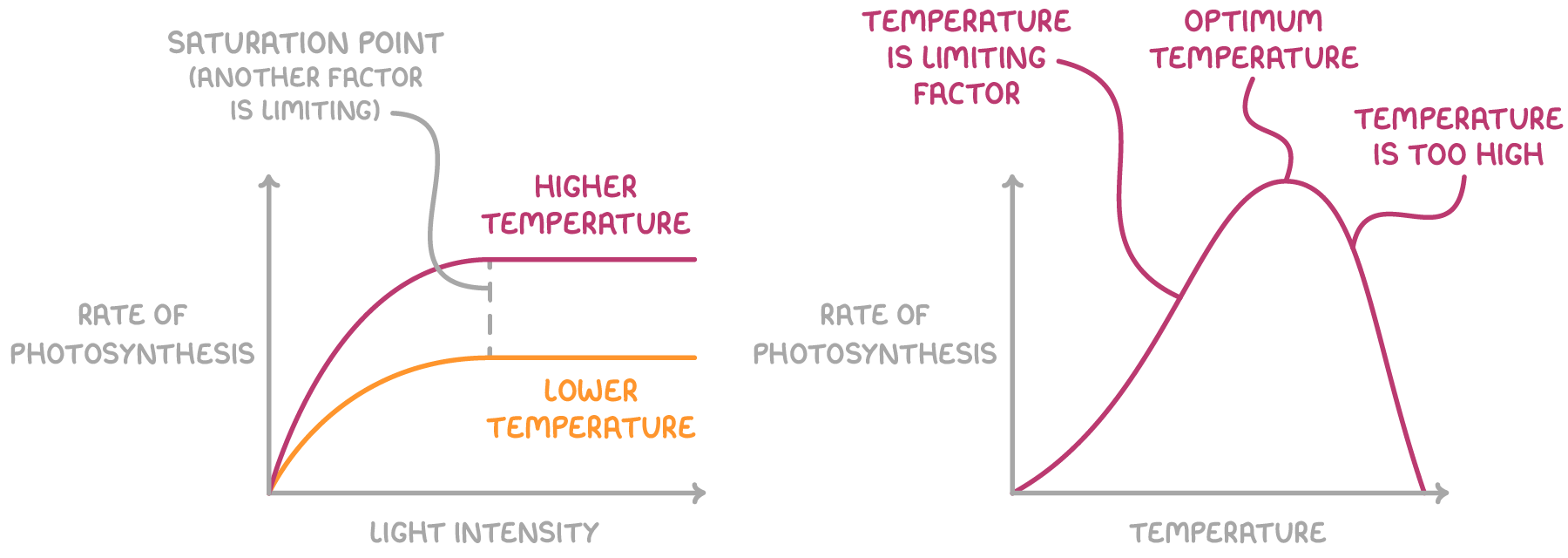
This occurs as follows for different temperatures:
- Low temperature - This provides little kinetic energy, slowing the enzyme-catalysed stages of photosynthesis, like the fixation of carbon dioxide controlled by rubisco. The rate of photosynthesis is low.
- Intermediate temperature - This increases the kinetic energy supplied to these reactions, increasing the rate of photosynthesis up to an optimum point.
- Very high temperature - This denatures enzymes, so the rate of photosynthesis drops sharply.