Carbohydrates: Introduction
This lesson covers:
- The elements that carbohydrates contain
- The role of carbohydrates in living organisms
- The different types of carbohydrates
What are carbohydrates? Carbohydrates are biological molecules that contain the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
The general formula for a carbohydrate is Cx(H2O)y. |
Roles of carbohydrates
Functions of carbohydrates in living organisms:
- Energy supply for cells - This is the main role of carbohydrates.
- Energy storage - Sugars can be stored as complex carbohydrates (e.g. starch or glycogen).
- Structural components - Cellulose and chitin are used in cell walls.
- Cellular recognition - Glycoproteins help cells identify each other and communicate.
- Building blocks for biological molecules - Deoxyribose and ribose can be used to make nucleic acids.
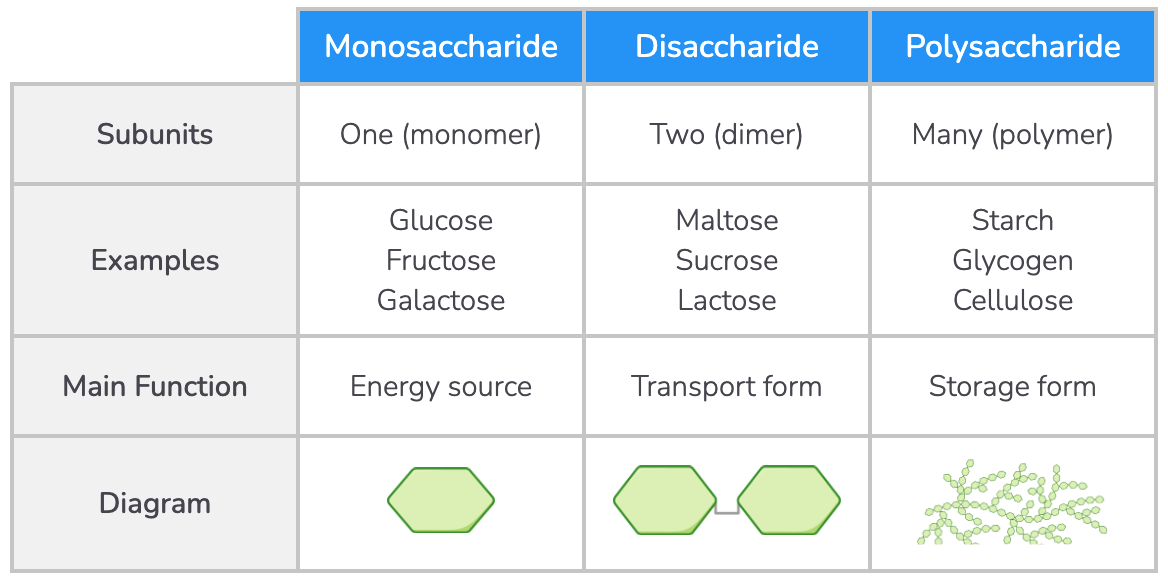
Types of carbohydrates
There are three types of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.