Codominance
This lesson covers:
- What codominance is
- How codominance is represented in genetics
- An example of codominance in flower colour
What is codominance?
Codominance occurs when two different alleles are equally expressed in an organism's phenotype. Unlike typical dominant-recessive gene relationships, both alleles in codominance share equal dominance.
This means that both alleles are visible in the organism's observable characteristics, leading to a phenotype that is a mixture of both alleles rather than just one.
How to show codominance in genetic diagrams:
- An uppercase letter is used to signify the gene (e.g. C for the colour of a particular trait in an organism).
- Superscript uppercase letters indicate the alleles (e.g. CR and CW for red or white colouration).
- Avoid lowercase letters to prevent the implication of recessiveness.
An example of codominance in flower colour
The flower colour in snapdragons demonstrates codominance.
The alleles responsible for snapdragon flower colour are:
- CR - Responsible for a high production of red pigment.
- CW - Leads to a low production of red pigment.
There are three potential flower colours based on these alleles:
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| CRCR | Red flowers |
| CWCW | White flowers |
| CRCW | Pink flowers |
In pink snapdragons, the blended colour results from the combined influence of both alleles: the CR allele generates a certain amount of red pigment, while the CW allele contributes minimally, creating a pink hue.
Worked example - Identifying offspring phenotypes with codominant alleles
Shorthorn cattle may have red, white, or roan coloured coats. The alleles CR and CW are codominant and produce the roan coat colour.
Identify the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation in a cross between a cow with a white coat and a bull with a red coat.
Step 1: State the parents’ genotypes and gametes
as the parents are not roan coloured, they must be homozygous for the coat colour alleles
white coat parent genotype - CWCW, gametes CW
red coat parent genotype - CRCR, gametes CR
Step 2: Perform a cross to identify the genotypes of the F1 generation
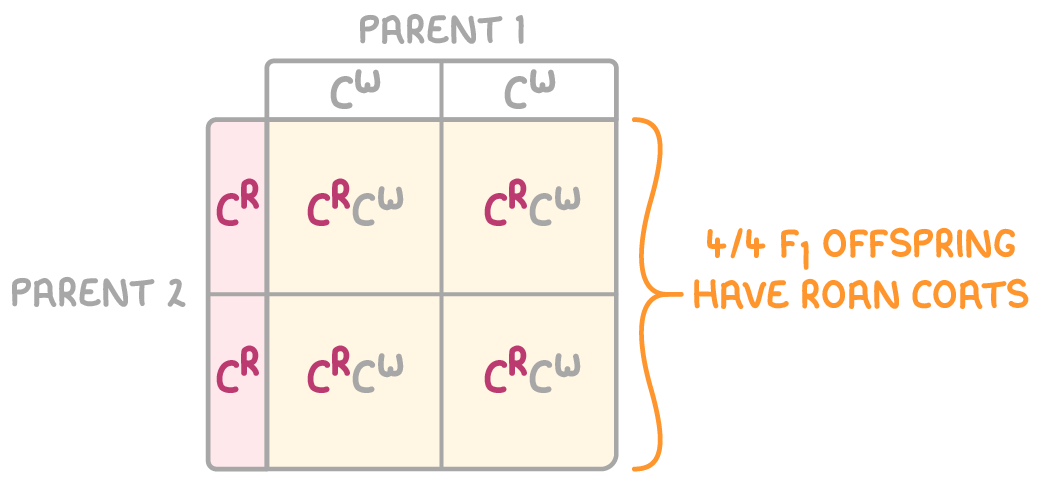
Step 3: Perform a cross between F1 offspring to identify the genotypes of F2 generation
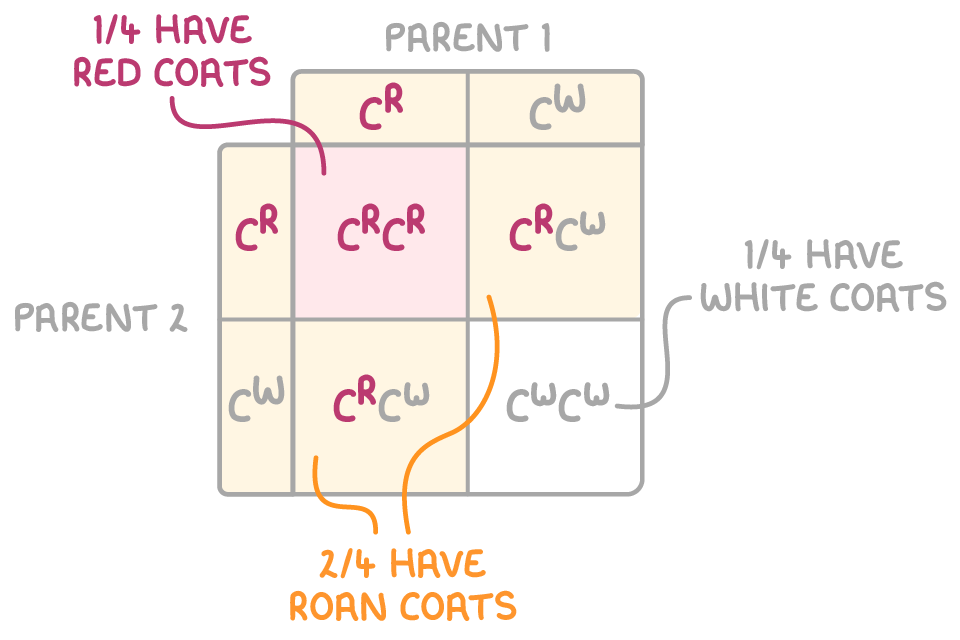
Step 4: State the ratio of F2 offspring phenotypes
F2 offspring genotypes: 1 CRCR, 2 CRCW, 1 CWCW
as the alleles are codominant, when they are heterozygous they produce a blended roan phenotype