Identifying Evolutionary Relationships
This lesson covers:
- Who proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection
- How comparative biochemistry can be used to determine evolutionary relationships
- How evolutionary relationships can be represented on a family tree
Evidence for the theory of evolution by natural selection
Both Darwin and Wallace independently proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection.
They suggested that organisms best suited to their environment are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass on their advantageous characteristics to their offspring.
Evidence for evolution from comparative biochemistry
There are several lines of evidence that provide evidence for evolution. Comparative biochemistry is one form of evidence, which involves studying the molecular aspects of organisms to uncover evolutionary relationships.
Useful molecules to study evolutionary links:
- Cytochrome c - This is a highly conserved protein involved in cellular respiration, so slight changes can help identify evolutionary links.
- Ribosomal RNA - This molecule is integral to protein synthesis so it changes slowly, making it useful for showing connections between species that diverged long ago.
- Nuclear DNA - Species that are more closely related will have more similar DNA sequences.
- Mitochondrial DNA - This mutates faster than nuclear DNA, so differences in sequences show the origin of species and their subsequent migrations.
- Messenger RNA - Base sequences of mRNA are complementary to DNA so can assess DNA diversity.
- Amino acids - If they are closely related evolutionarily, two species have more similar amino acid sequences because they are determined by mRNA and DNA.
The 'molecular clock' hypothesis assumes a constant rate of mutation over time. The greater the number of differences in nucleotide sequences, the longer ago those individuals shared a common ancestor.
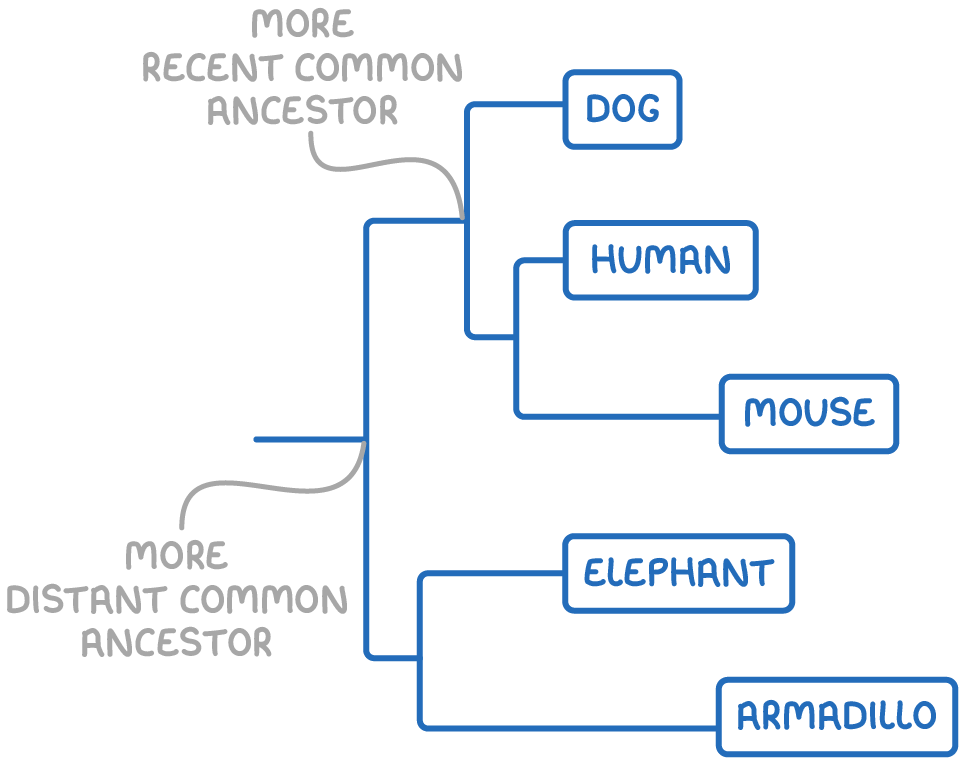
How family trees represent evolutionary relationships
A family tree of different species represents the evolutionary relationships between species. It shows which species had a common ancestor and how they are related to each other.