DNA Replication
This lesson covers:
- The process of DNA replication
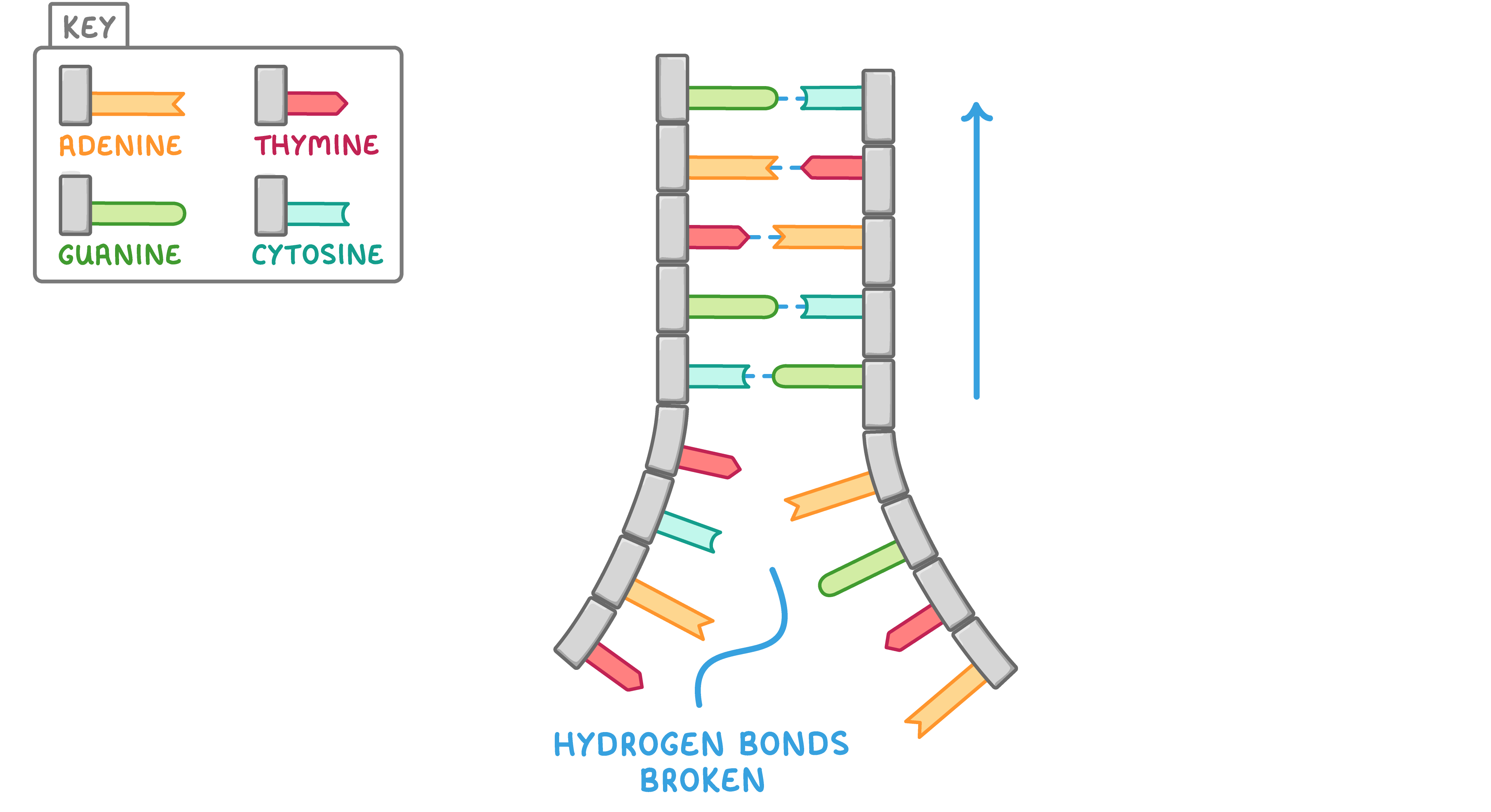
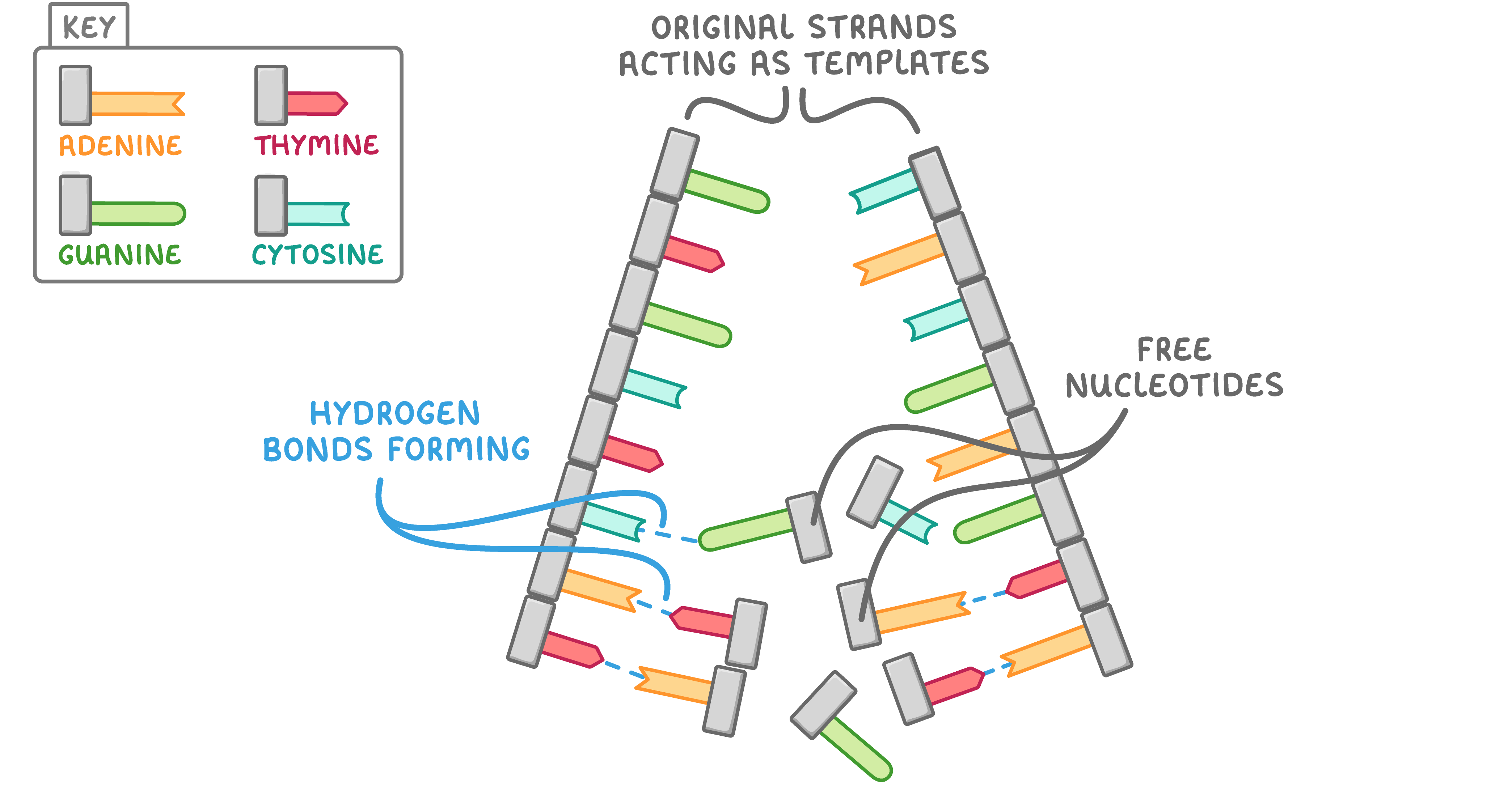
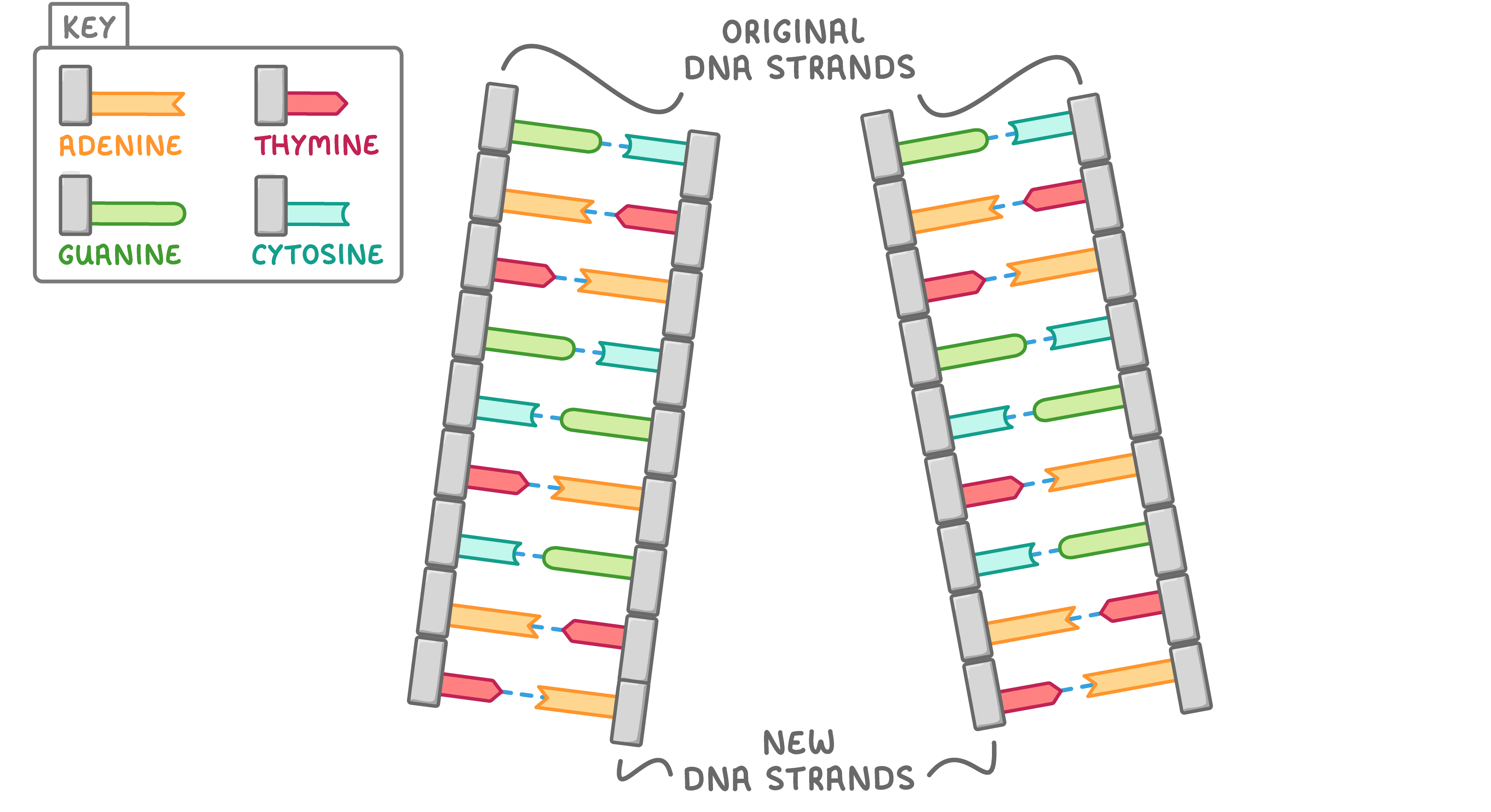
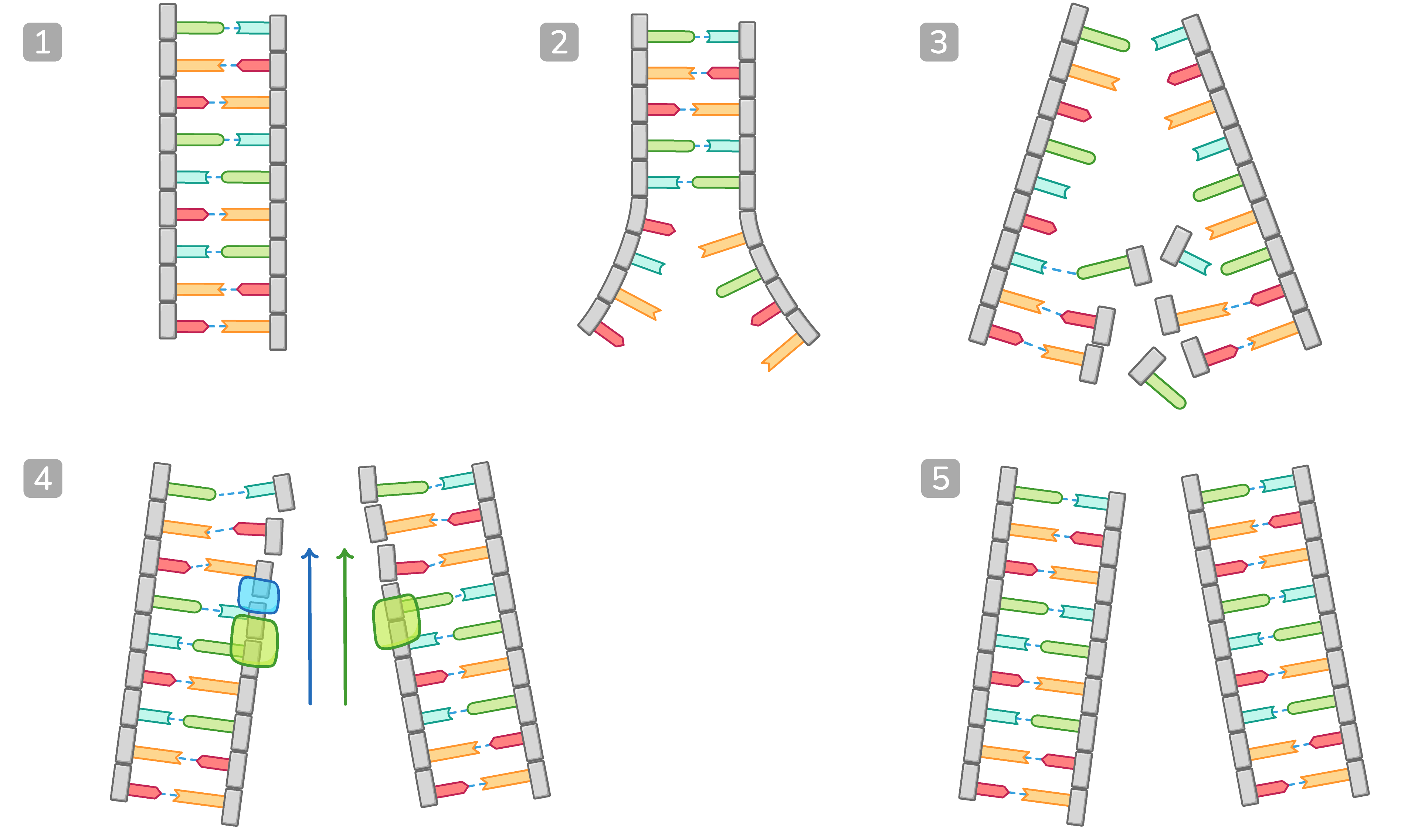
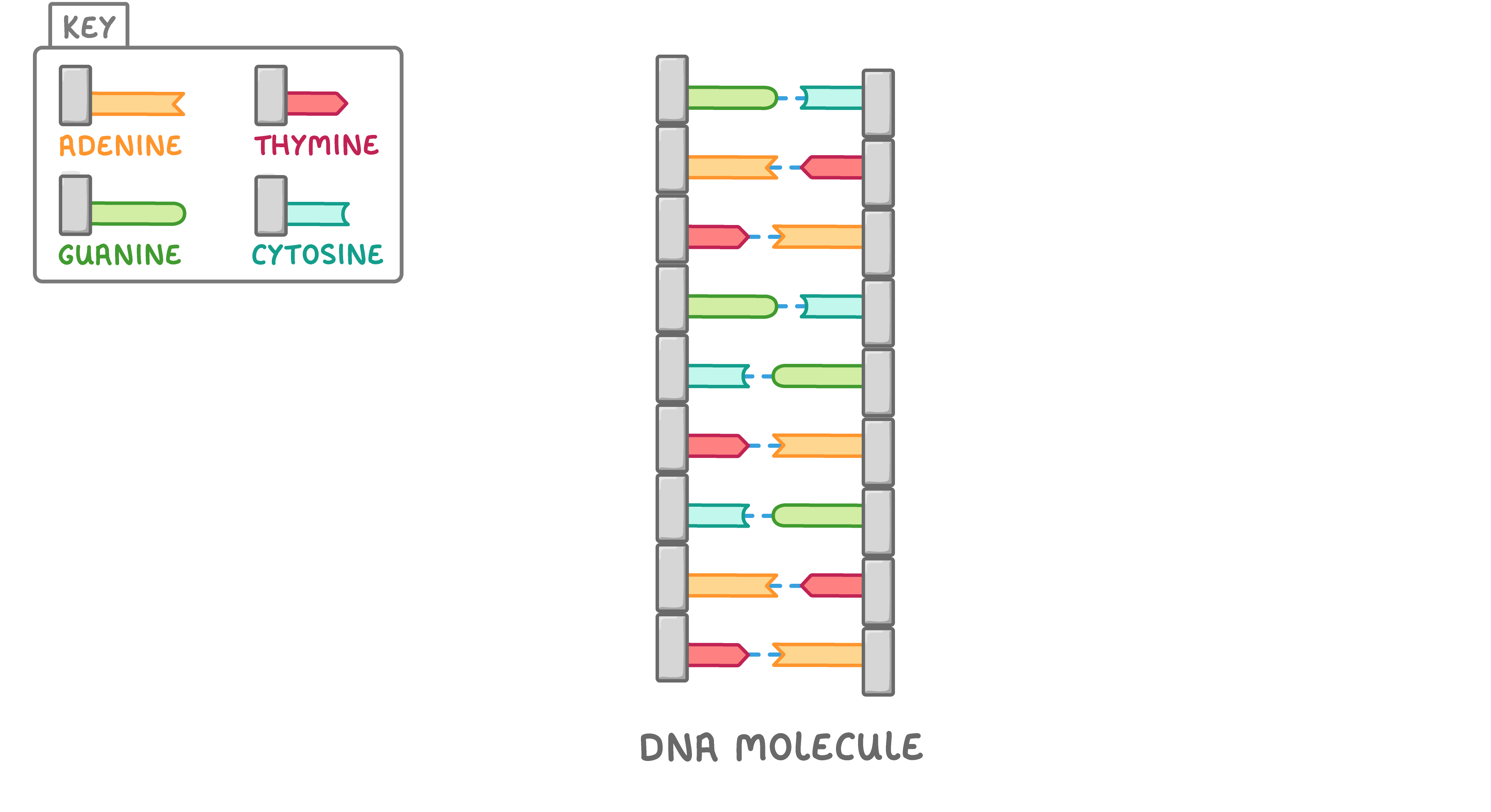
DNA replication DNA is copied via a process known as semi-conservative replication. This produces DNA molecules consisting of one original DNA strand and one newly synthesised DNA strand. |
|
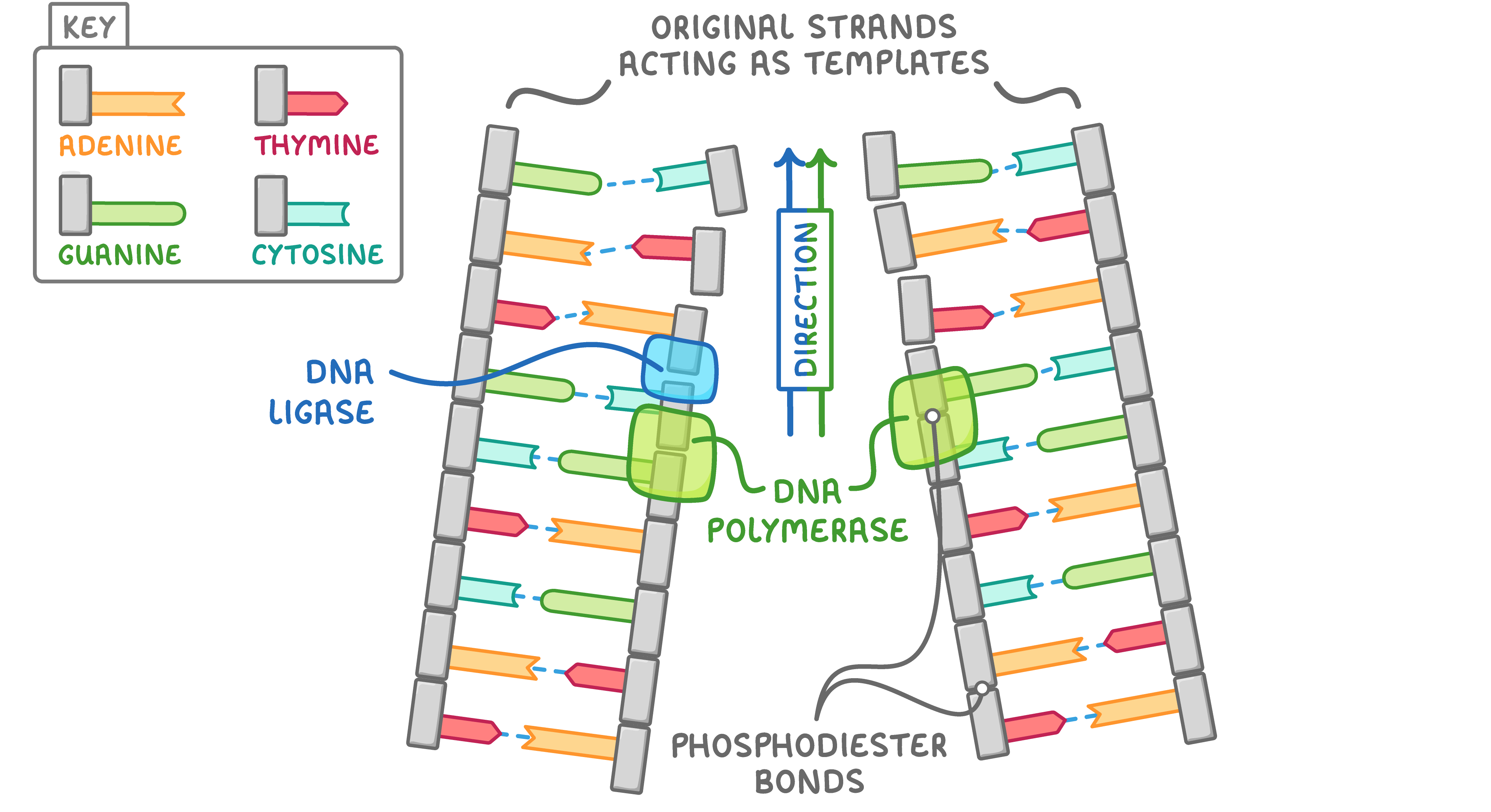
Leading and lagging strands DNA polymerase can only build new DNA strands in the 5' to 3' direction. This affects the process by which each new DNA strand is made. We call the two newly synthesised strands the leading strand and the lagging strand. Leading strand:
Lagging strand:
|