Stem Cells
This lesson covers:
- What 'stem cells' are
- The different types of stem cells
- Where stem cells are found in living organisms
- How stem cells can be used in research and medicine
Stem cells Multicellular organisms are made up of many different types of cells, each specialised for a particular function. However, all of these cells begin as unspecialised cells known as stem cells. 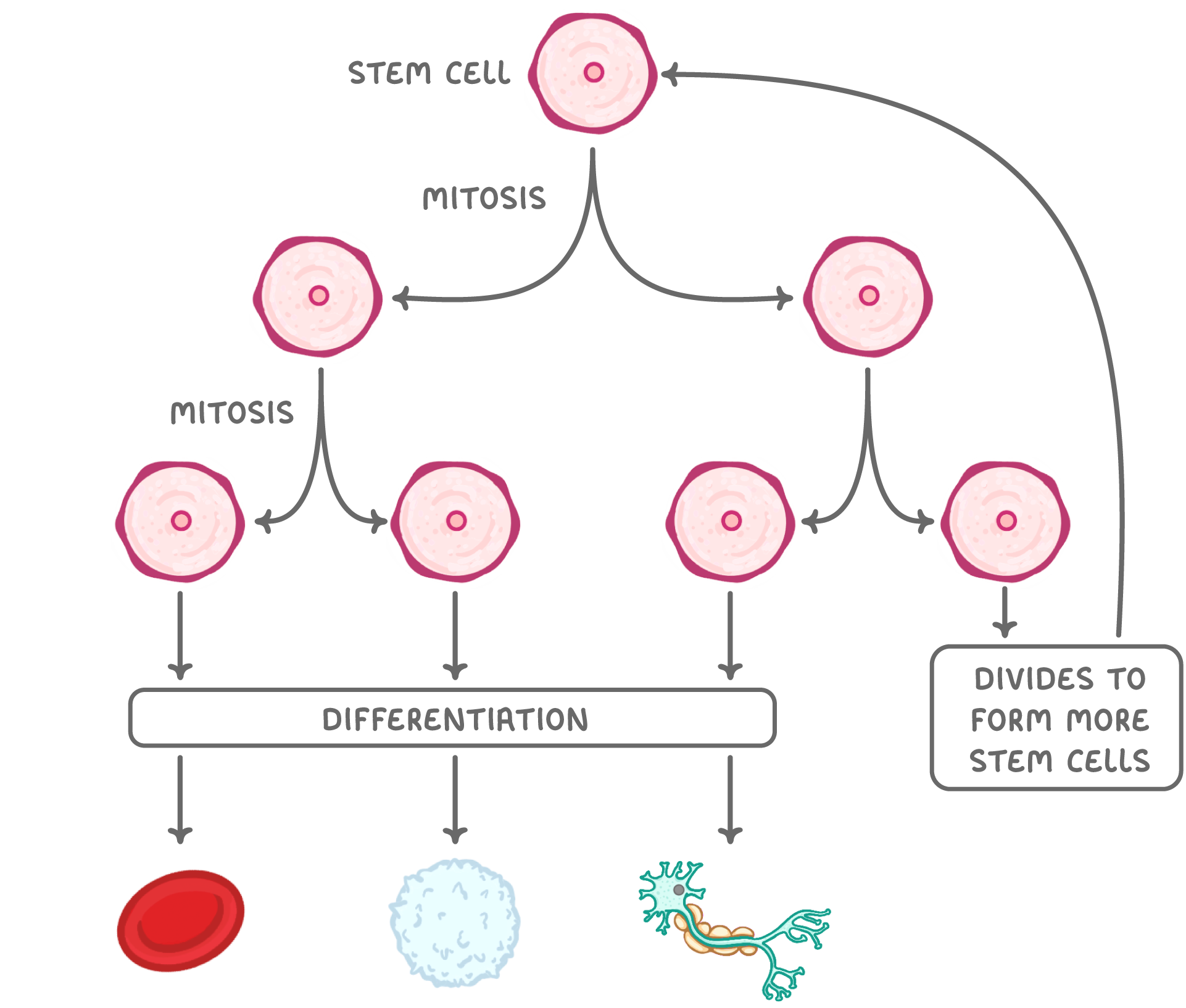 |
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can develop into other types of cell. They are used by organisms for growth, development and tissue repair. Stem cells have two key features:
|
Types of stem cells Stem cells can be grouped into different types based on their ability to differentiate into different cell types, or their potency. The more cell types a stem cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. There are four key types of stem cell:
|
Locations of stem cells Stem cells are found in early embryos, adults, and plants. Embryonic stem cells
Adult stem cells
Plant stem cells
|
Stem cells in research and medicine Since stem cells have the ability to differentiate into specialised cells, they have the potential to treat certain diseases. This works by using stem cells to replace faulty cells or tissues. Parkinson's and Alzheimer's are both neurological disorders caused by a loss of nerve cells in the brain. Transplanted stem cells could help to regenerate nerve cells and reduce symptoms of these conditions. Stem cells can also be used for the following purposes:
|