Human Impact on Biodiversity
This lesson covers:
- How human population growth reduces biodiversity
- How agricultural practices can decrease biodiversity
- The effects of climate change on global biodiversity
Human population growth and biodiversity
The human population has increased rapidly, which has negatively impacted global biodiversity.
Some impacts of the growing human population on biodiversity include:
- Deforestation for development destroys habitats and reduces ecosystem diversity.
- Overuse of resources causes certain species to decline or go extinct, reducing genetic and species diversity.
- Urban sprawl isolates wildlife populations, limiting breeding and decreasing genetic diversity.
- Pollution kills species directly and harms habitats long term.
Agricultural practices that reduce biodiversity
Farming methods aimed at maximising crop yields, such as creating monocultures, often decrease biodiversity. These practices decrease habitat, plant, and animal diversity. Populations decline as species lose food, shelter, and breeding sites.
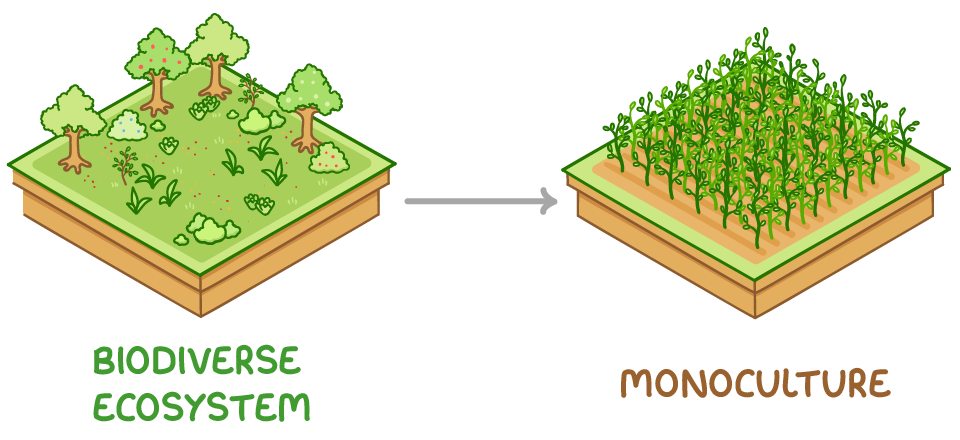
Some of these methods include:
- Monocultures - This involves growing single crops over large areas, typically without crop rotation, directly decreasing the diversity of plants and of species that depend on them for food or a habitat. Monocultures also deplete the nutrients from soil.
- Converting woodland and hedgerows into fields - This decreases numbers of trees and other species, and destroys habitats relied on by many species.
- Filling in ponds, draining marshes, over-grazing of land - This directly destroys habitats and reduces species diversity.
- Removing weeds with herbicides - This may harm other species or those that depend on target species.
- Using pesticides to kill crop pests - This may harm other species or those that depend on target species.
- Using inorganic fertilisers - These may runoff into water courses, causing issues for aquatic species.
Balancing conservation and agriculture
Some methods can help balance conservation and agriculture.
Some of these methods include:
- Maintaining hedgerows.
- Reducing pesticide and herbicide use.
- Using organic fertilisers.
- Using crop rotation.
The impacts of climate change on biodiversity
Burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, causing global warming. Climate change alters regional climates around the world. This can cause shifts in the biodiversity in various habitats.
Effects of climate change on biodiversity:
- Different regions experience changes in temperature and rainfall, and most species are adapted to specific climates.
- Changed conditions will make certain areas more or less habitable in general.
- Suitable habitats for some species will expand or contract e.g. melting polar ice caps removes a habitat for all polar animals.
- Changing climate conditions may influence species distribution and migration.
- Slow-moving species may become extinct if change is too rapid or severe.
- If conditions in general become warmer, tropical diseases will be more likely to spread.
- Rising sea levels may lead to more frequent flooding of terrestrial habitats in low-lying land.