Structure of mRNA & tRNA
This lesson covers:
- The structure of mRNA
- The structure of tRNA
- The similarities and differences between mRNA and tRNA
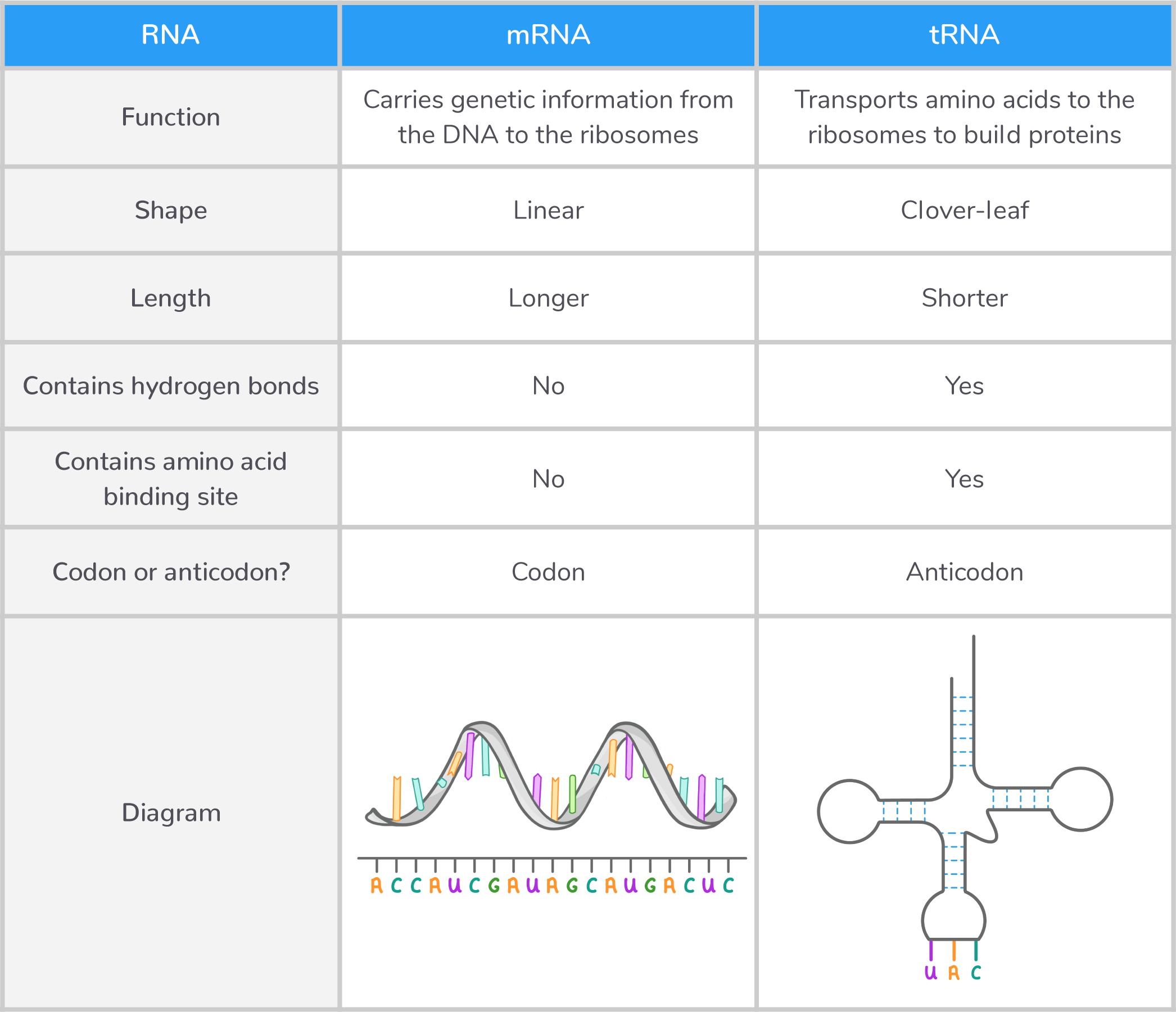
mRNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a type of RNA synthesised during the process of transcription. Its role is to carry genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes (where proteins are made). |
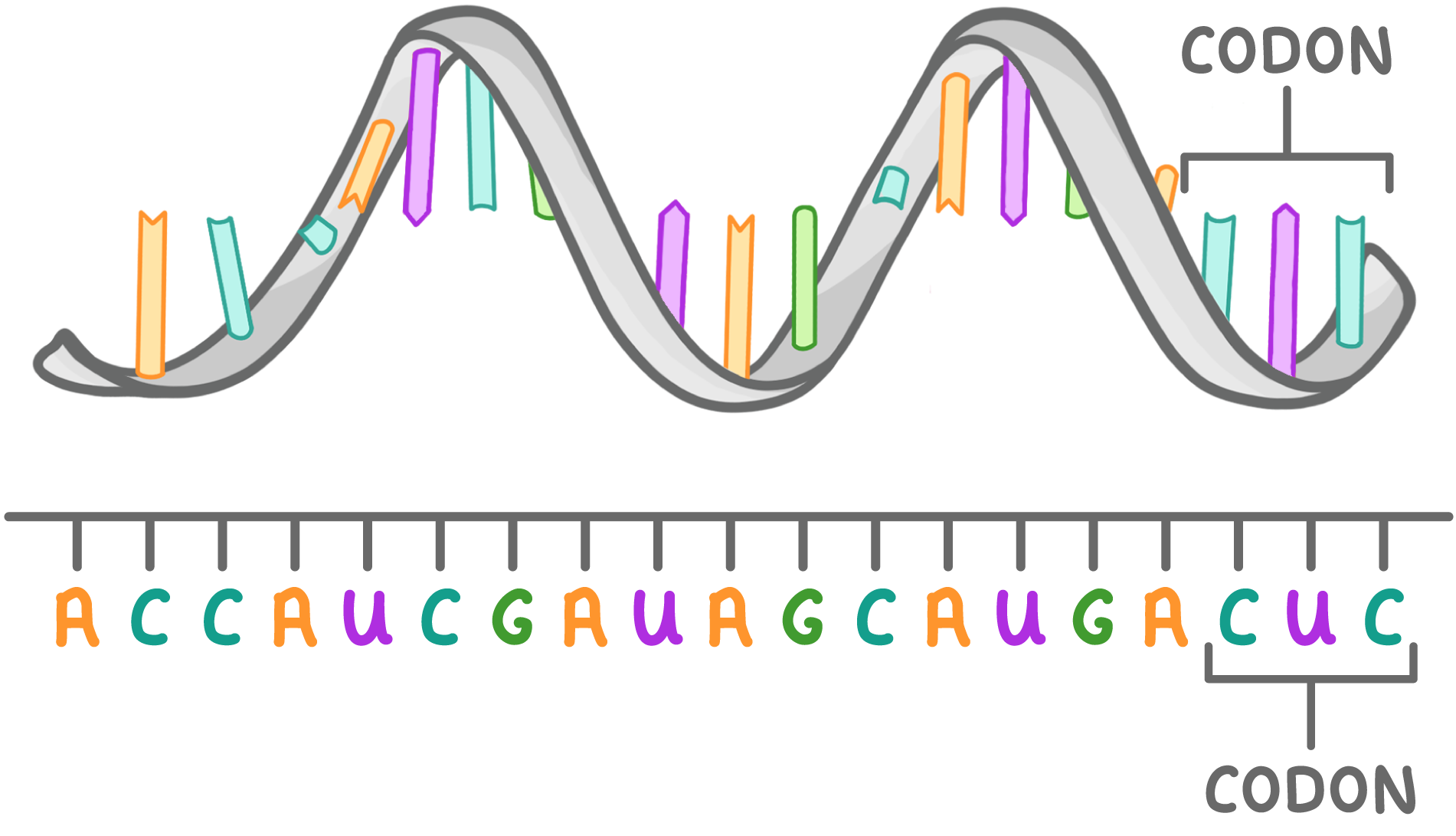 Features of mRNA:
|
tRNA Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a type of RNA used in the process of translation. Its role is to transport amino acids to ribosomes to build up a polypeptide chain. |
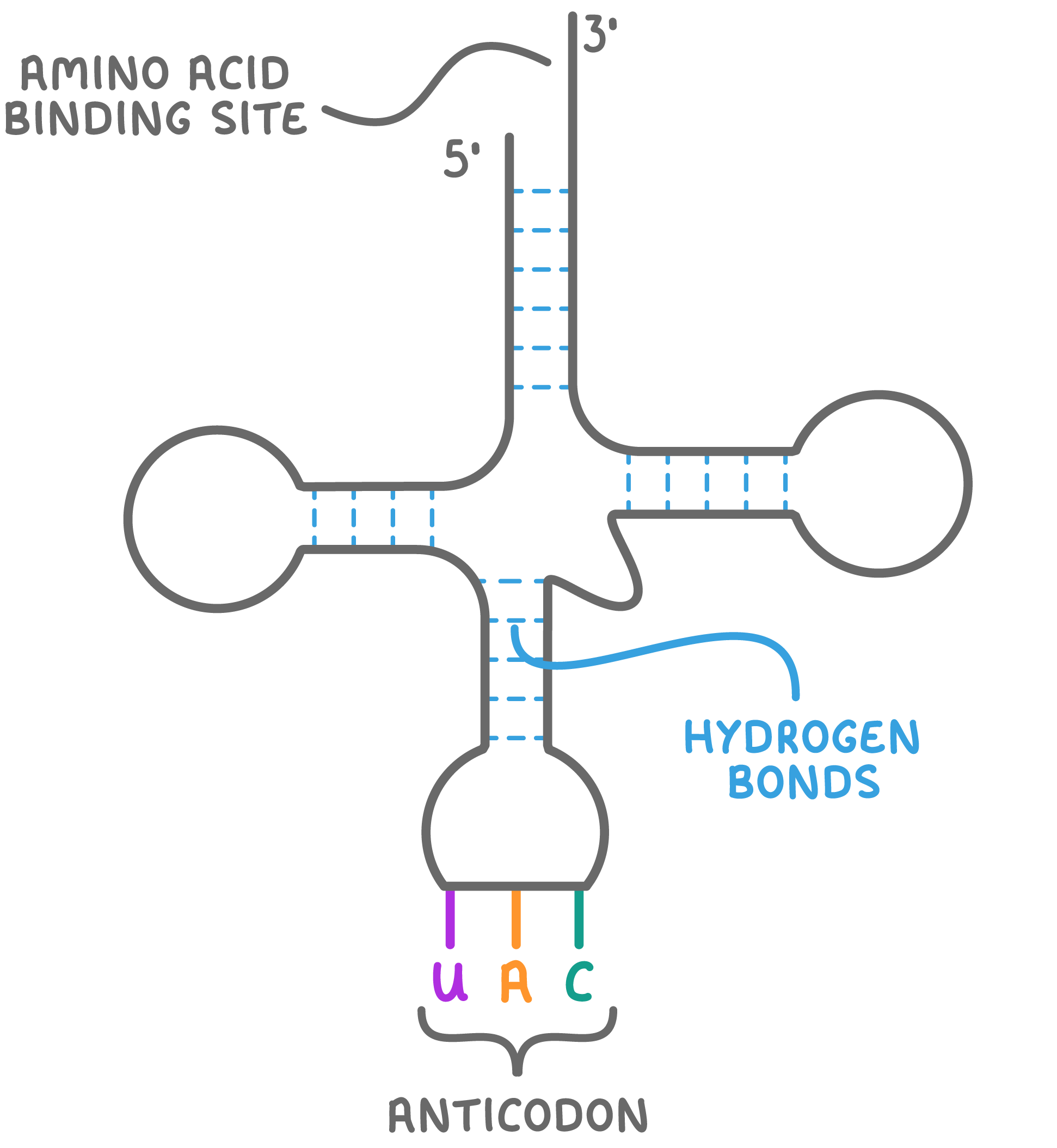 Features of tRNA:
|
Comparing mRNA and tRNA