Introduction to Biological Molecules
This lesson covers:
- The different types of biological molecules
- The difference between monomers and polymers
- The difference between condensation and hydrolysis reactions
Types of biological molecules The cells of all living organisms primarily consist of four types of molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These biological molecules are organic, meaning they contain the element carbon. These molecules also contain additional elements:
|
Monomers and polymers Most carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are polymers made up of small units known as monomers.
|
The process by which monomers join to form a polymer is known as polymerisation. 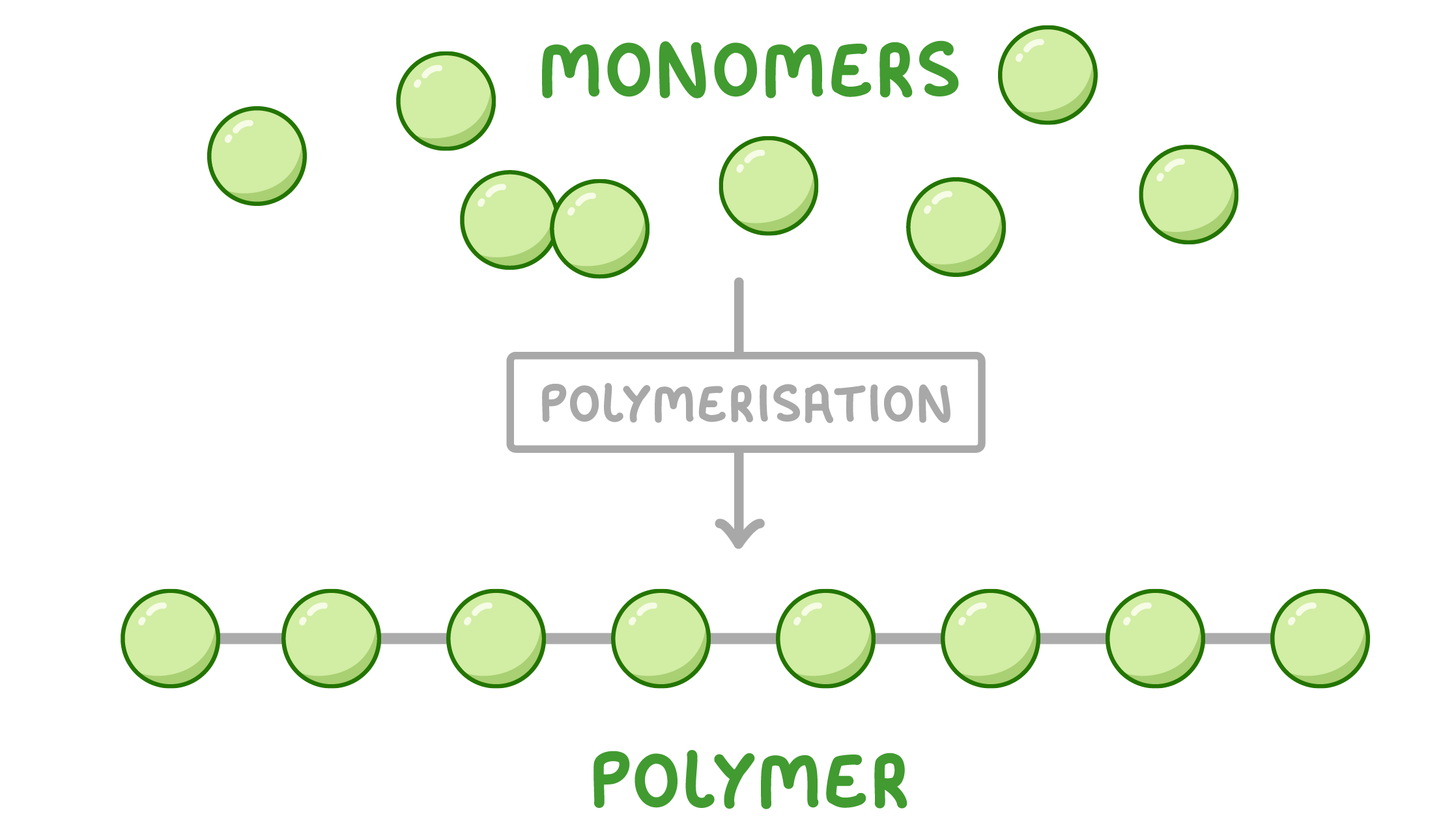 |
 |
Condensation and hydrolysis reactions Most polymers are synthesised via a condensation reaction and broken down via a hydrolysis reaction. |
 Condensation - The removal of water to form a chemical bond between two molecules. |
 Hydrolysis - The addition of water to break a chemical bond between two molecules. |