Cohesion-tension Theory
This lesson covers:
- How water enters the root
- How water moves through the xylem
- The mechanisms driving water upwards
Water movement through a plant
Water enters plants through their roots.
Water then moves through a plant as follows:
- Water enters a plant's root hair cells via osmosis.
- It moves through the cell cytoplasm or cell walls towards the xylem.
- The xylem transports water from the roots up to the leaves.
The cohesion-tension theory
The cohesion-tension theory explains how water moves upwards through the xylem against gravity.
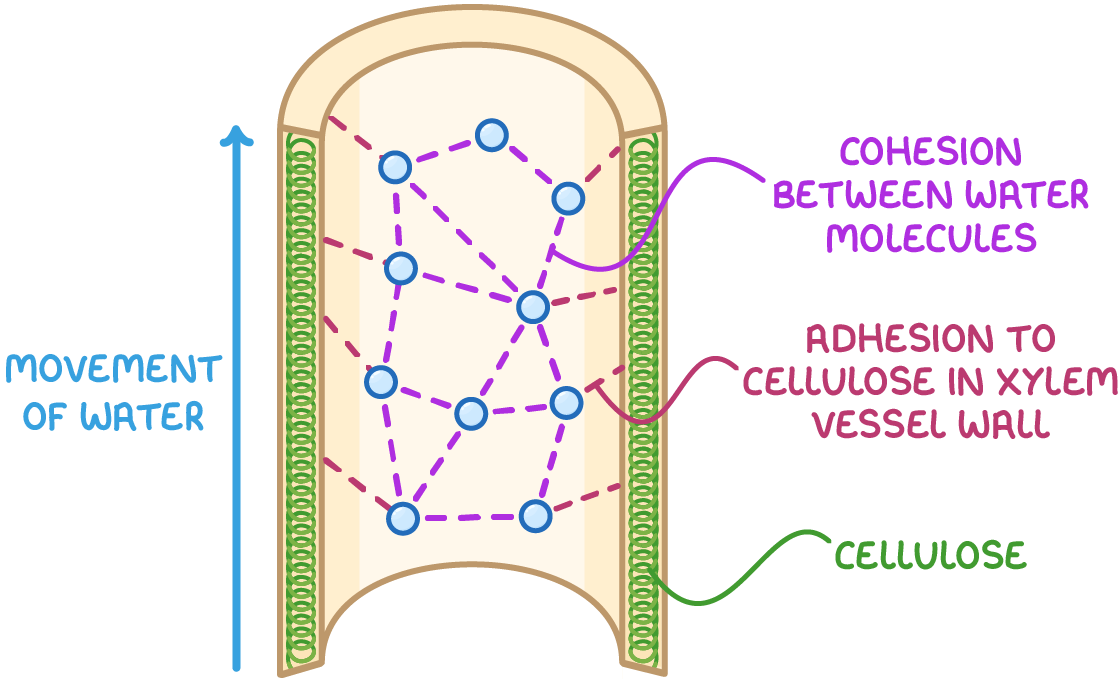
This occurs due to various factors:
- Cohesion - Hydrogen bonding causes water molecules to stick together and move as one continuous column.
- Adhesion - Hydrogen bonding between polar water molecules and non-polar cellulose in xylem vessel walls pulls water upwards through the xylem.
- Transpiration pull - Evaporation of water at leaves creates the transpiration pull, and this tension is transmitted down the whole water column due to cohesion.
This causes water to be pulled up through the xylem vessels.