Introduction to Photosynthesis
This lesson covers:
- The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration
- The adaptations of plant leaves for photosynthesis
- The key stages of photosynthesis
The relationship between photosynthesis and respiration
The products of photosynthesis, glucose and oxygen, can be used as reactants in respiration to synthesise ATP.
The products of respiration, carbon dioxide and water, can then be used as reactants in photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis captures light energy to make glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
Overall photosynthesis equation:
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Respiration
Cellular respiration breaks down respiratory substrates like glucose, releasing energy that is temporarily stored in the form of ATP.
Overall respiration equation:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Adaptations of plant leaves for photosynthesis
Many plant leaves have adaptations that allow them to carry out photosynthesis efficiently.
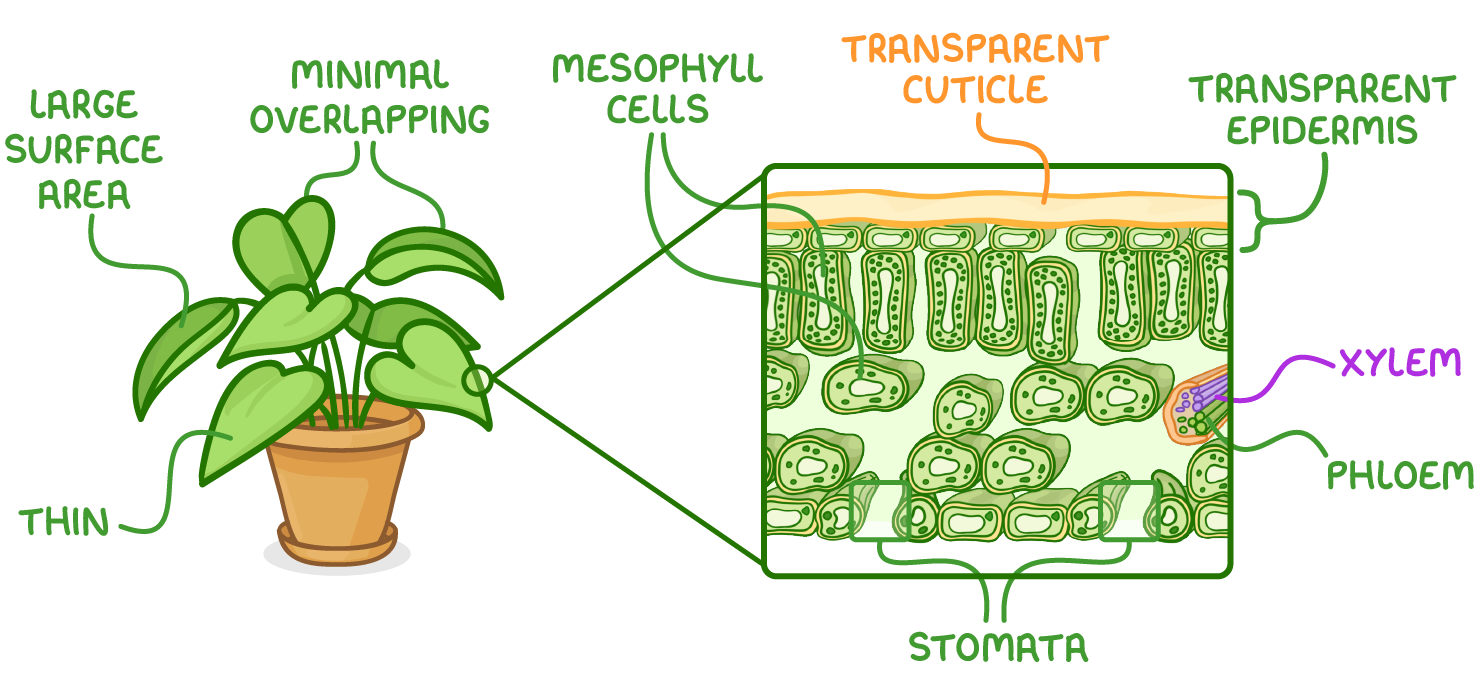
Some adaptations of leaves for photosynthesis include:
- A large surface area - To absorb sunlight.
- Minimal overlapping - To avoid shadowing.
- Being thin - To keep the diffusion distance short.
- A transparent cuticle and epidermis - To allow light to enter the leaves.
- Chloroplast-packed mesophyll cells - To carry out photosynthesis.
- Stomata - For gas exchange, like taking in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
- Xylem and phloem - To transport reactants and products of photosynthesis between the leaves and the rest of the plant.
Key stages of photosynthesis
There are three main stages in photosynthesis:
- Capturing of light energy - This is done by pigments such as chlorophyll.
- The light-dependent reaction - This is when light energy is converted into chemical energy.
- The light-independent reaction - This is when sugars and other organic molecules are produced.