Light-dependent Reaction
This lesson covers:
- Adaptations of thylakoids for the light-dependent reaction
- Stages of the light-dependent reaction
Adaptations of thylakoids for the light-dependent reaction
The light-dependent reaction occurs in the thylakoid membranes inside chloroplasts.
Thylakoids have several key adaptations for this reaction:
- Large surface area - So they can contain more chlorophyll and electron carriers.
- ATP synthase channels - This allows the synthesis of ATP.
- Selectively permeable - This allows a proton gradient to be set up.
Stages of the light-dependent reaction
The light-independent reaction uses water and light energy. It produces ATP, reduced NADP, and oxygen as a by-product. It is sometimes called photophosphorylation, as it is the process by which ATP is formed using light energy.
The light-dependent reaction involves the following key stages:
- Absorption of light energy and photoionisation.
- Electron transfer along the electron transport chain.
- Photolysis of water.
- Chemiosmosis.
Let’s look at these stages in more detail.
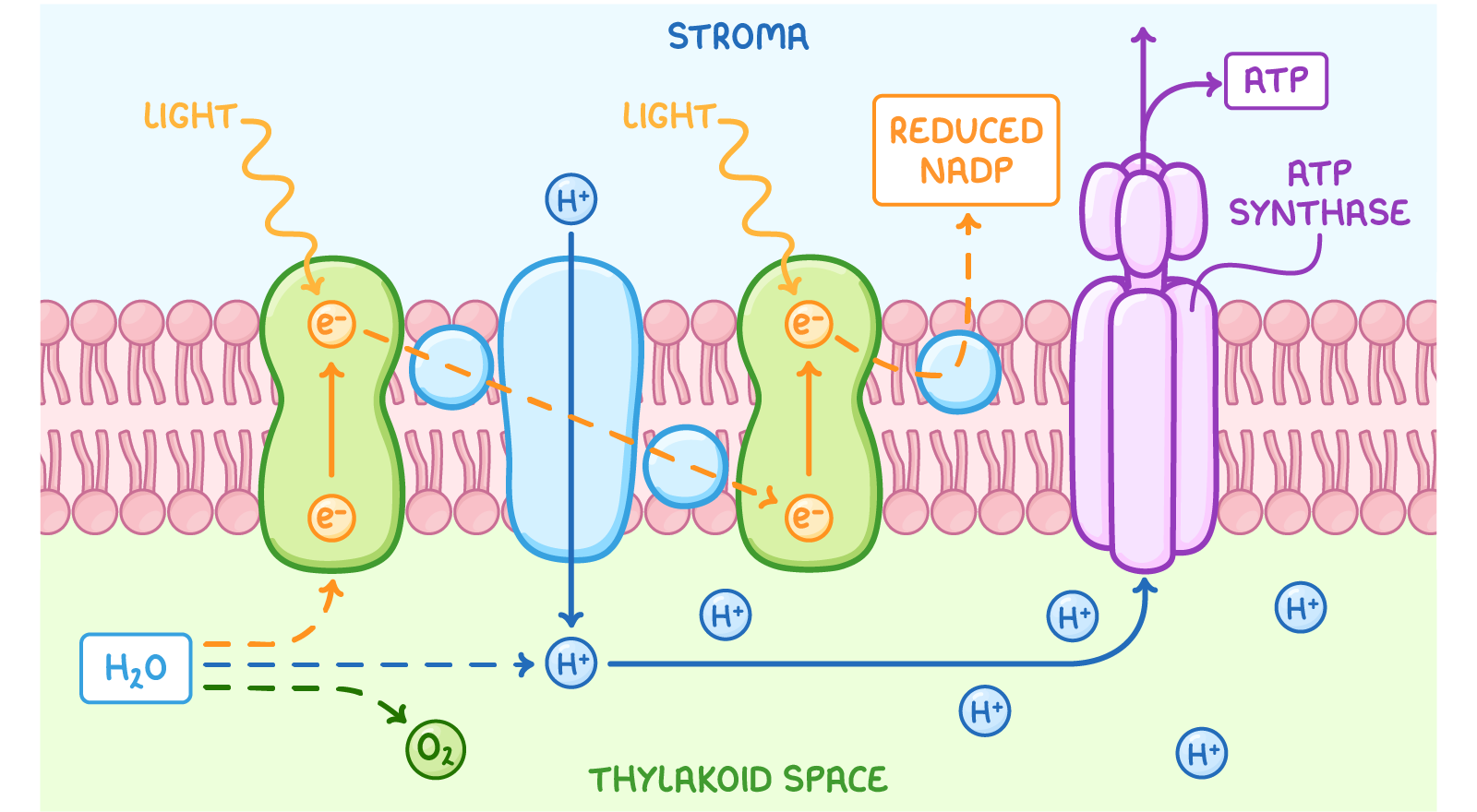
Absorption, photoionisation, and the electron transport chain
- Light energy is absorbed by pigments.
- Photoionisation occurs, which is when these electrons are excited and lost from the pigments (the pigments are oxidised).
- Electrons are transferred to an electron carrier molecule (the electron carrier is reduced).
- Electrons are passed along the electron transport chain, releasing energy as they go.
Photolysis of water
- Light is used to split water into electrons, protons, and oxygen: 2H2O → 4H+ + 4e- + O2.
- The electrons replace those lost from pigments during photoionisation.
- The protons are used for ATP production and combine with electrons to reduce NADP.
- Oxygen gas is released as a by-product.
Chemiosmosis generating ATP and reduced NADP
- The energy lost by electrons along the electron transport chain is used to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane into the thylakoid space.
- This produces a proton gradient, where protons are in a higher concentration in the thylakoid space.
- The protons then diffuse through ATP synthase into the stroma.
- This movement powers ATP synthase to produce ATP from ADP and an inorganic phosphate.
- NADP takes up protons and electrons in the stroma and is reduced.
- Reduced NADP is carried into the light-independent reaction.