Human Gas Exchange System
This lesson covers:
- An introduction to the gas exchange system
- The structure and function of the ciliated epithelium
- The structure and adaptations of the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles
- The structure and adaptations of the alveoli
Introduction to the gas exchange system The human gas exchange system consists of the lungs and air passages. This system allows oxygen to enter the blood and carbon dioxide to leave the blood through gas exchange surfaces called alveoli. The lungs are located inside the chest in the thoracic cavity (thorax), protected by the ribcage. The gas exchange system is located inside the body because:
|
Pathway of air Air travels through several structures as it passes through the respiratory system. 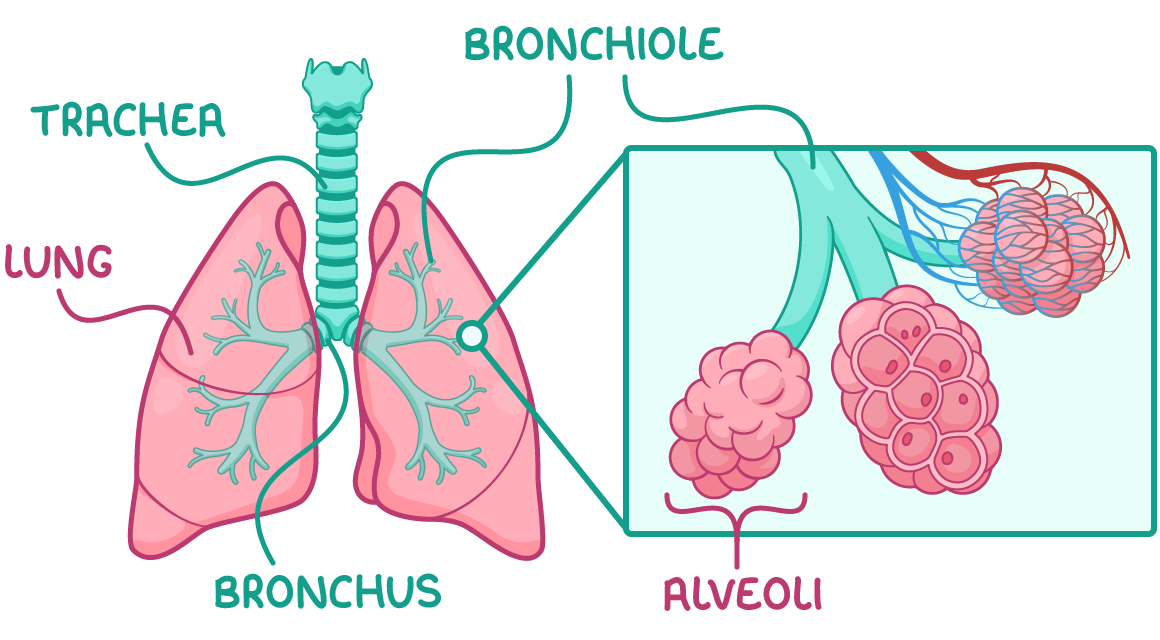 It does this in the following stages:
|
Ciliated epithelium A tissue called the ciliated epithelium is located throughout most of the airways. 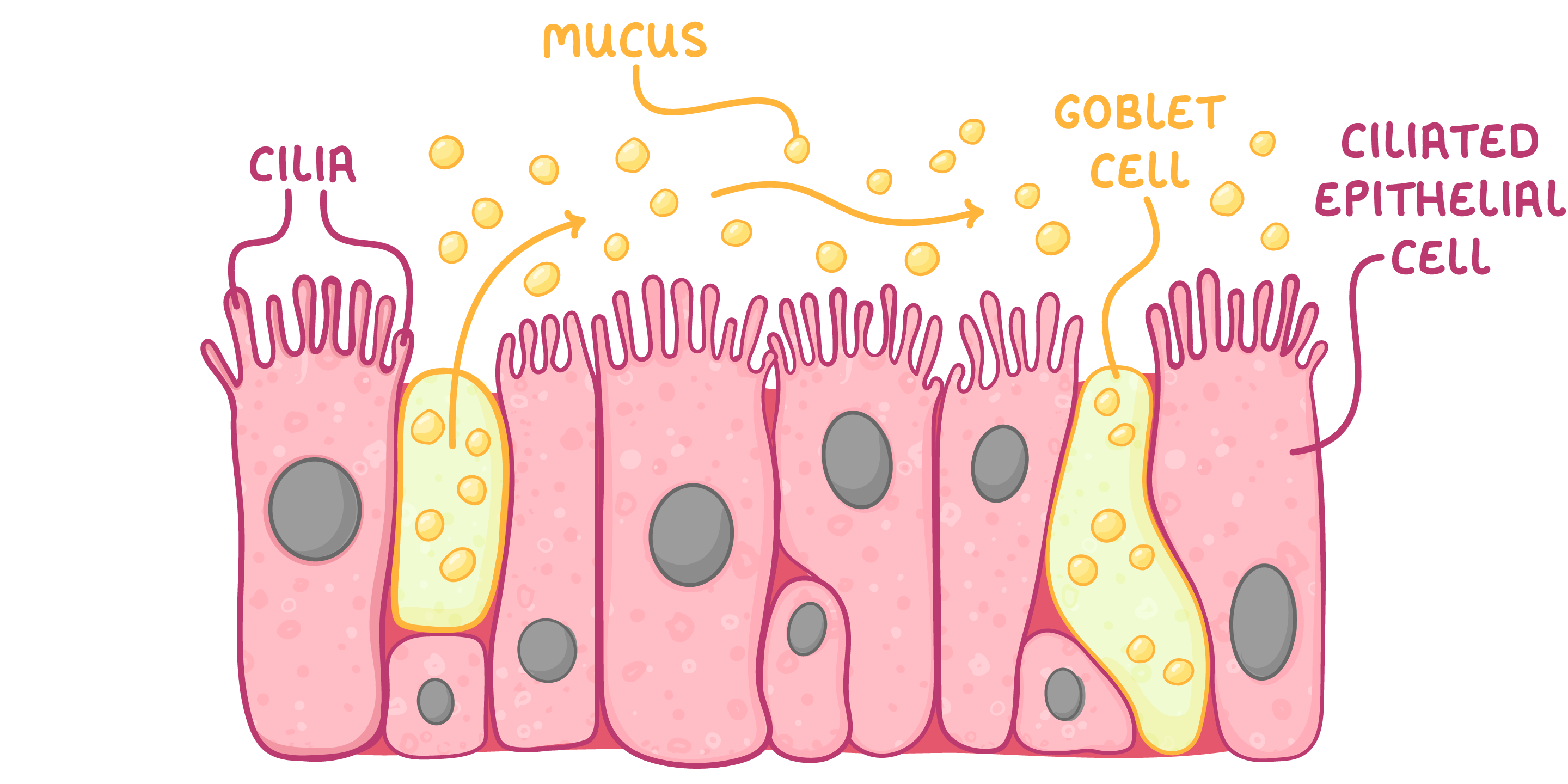 The ciliated epithelium contains mainly goblet cells and ciliated epithelial cells:
|
Structure and adaptations of airways You need to know about the structure of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, and how these structures help them carry out their functions. |
Trachea The trachea is the large tube that carries air from the throat down to the lungs. Adaptations:
|
Bronchi The bronchi are two main branches extending from the trachea that carry air into each lung. Adaptations:
|
Bronchioles The bronchioles are smaller airways branching from the bronchi that carry air to the alveoli. Adaptations:
|
Alveoli and blood vessels Alveoli are tiny air sacs clustered at the ends of the bronchioles. They are surrounded by a network of capillaries so gases can be exchanged between the air in the alveoli and the blood. Gas exchange occurs across the alveolar membrane of alveoli. This is how the alveoli carry out gas exchange:
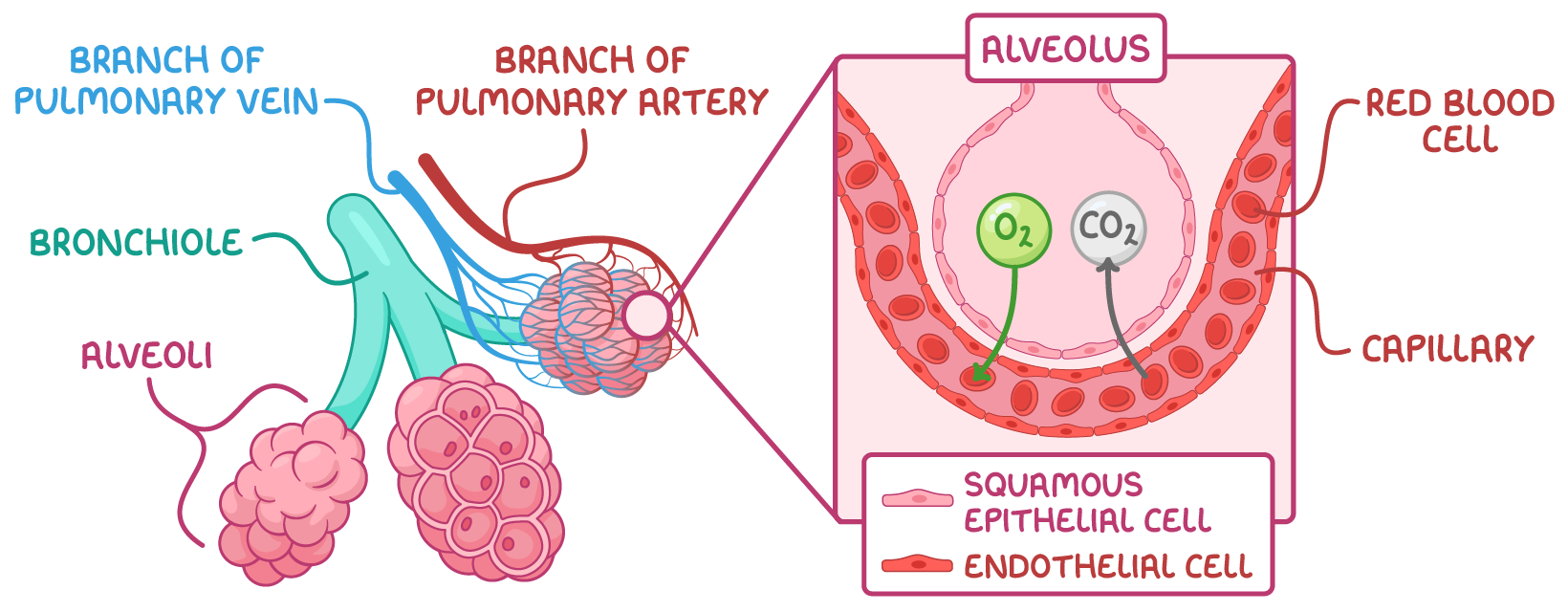 |
Adaptations of the alveoli for gas exchange:
|
Pulmonary blood vessels The pulmonary blood vessels are those involved in circulation of the lungs. They include:
|
Adaptations of the pulmonary capillaries for gas exchange:
|