Chromosomes
This lesson covers:
- What chromosomes and chromatids are
- What homologous chromosomes are
- The structure of chromosomes after replication
- The terms haploid and diploid
DNA is stored as chromosomes Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. As we saw in the lesson on the genetic code, they consist of DNA tightly coiled around proteins called histones. 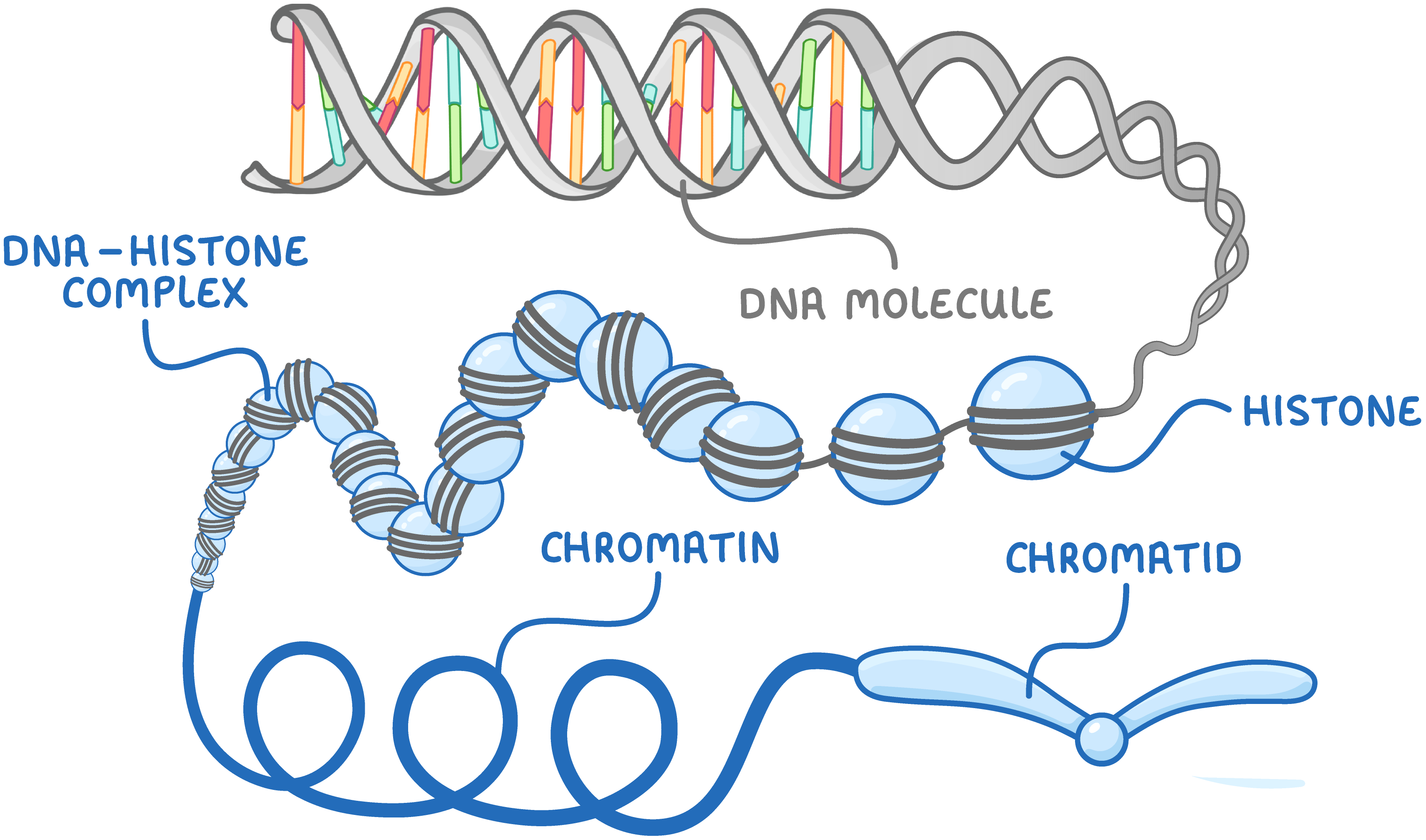 |
The human genome Humans have a total of 46 chromosomes, divided into 23 pairs, within each cell. The first 22 pairs are called autosomes, which are identical in both males and females. The 23rd pair, known as the sex chromosomes, differs between males and females. Males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY), whereas females have two X chromosomes (XX). We can see this in the photograph below, which shows the chromosomes in a typical human male cell. 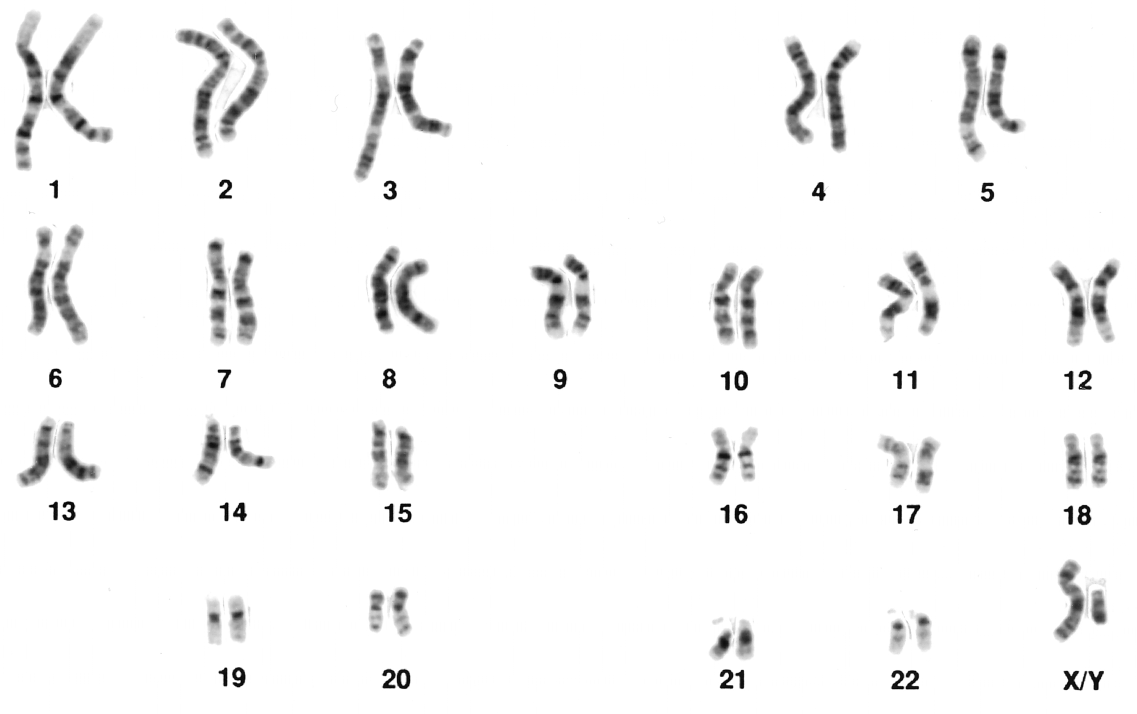 |
Homologous pairs As you can see in the image above, each pair of chromosomes consists of two homologous chromosomes. These are referred to as homologous pairs. One chromosome in the pair is a paternal chromosome inherited from the individual's father, and the other is the maternal chromosome inherited from the mother. Although the chromosomes are identical in terms of the genes they carry, they may contain different alleles.  |
Chromosomes may contain one or two chromatids Chromosomes may contain one or two chromatids depending on the stage in the cell cycle. During interphase, DNA is replicated, which means that each chromosome goes from having one chromatid to having two. 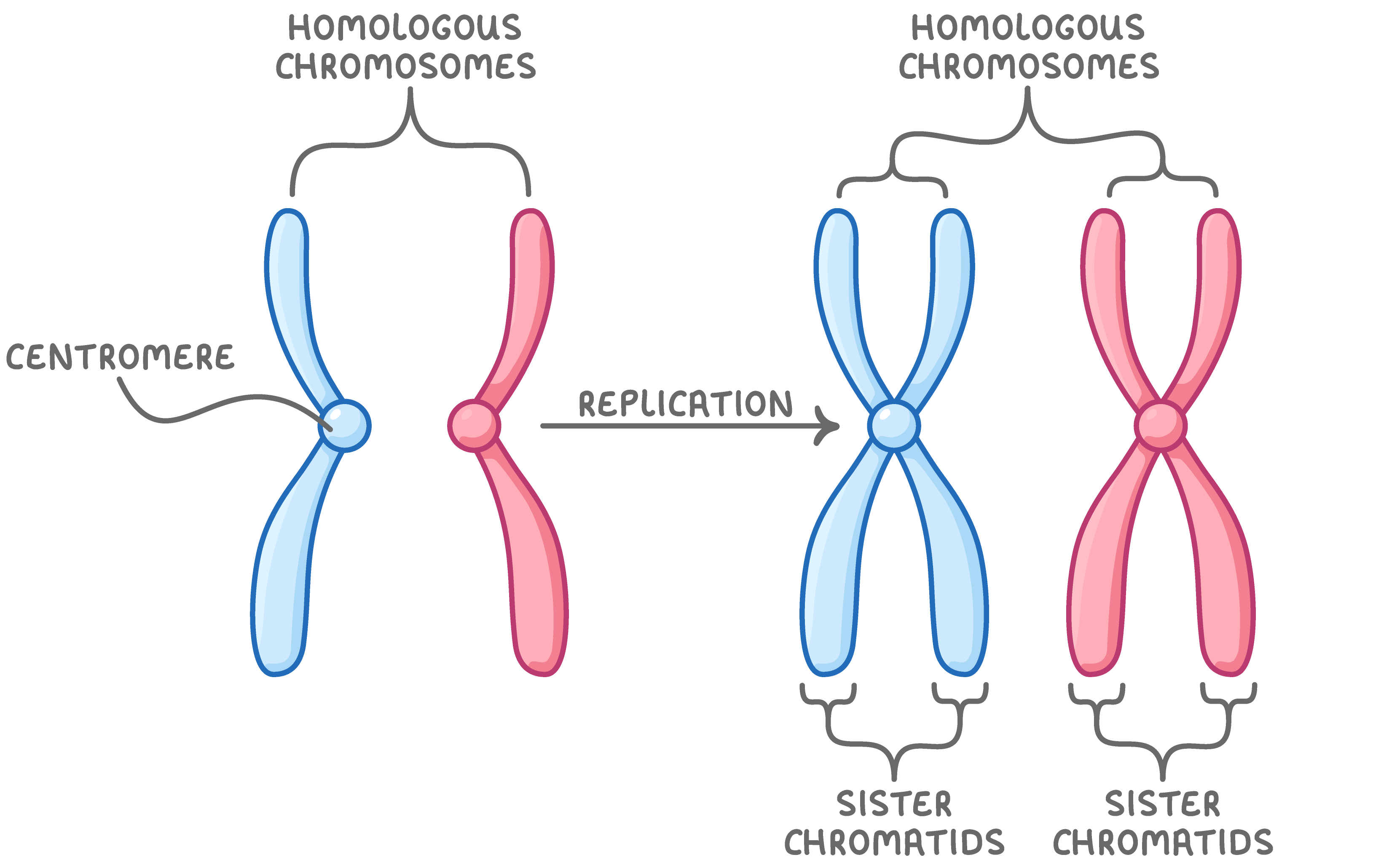 |
The two chromatids in each chromosome are held together by the centromere. The two chromatids within a chromosome are known as sister chromatids because they are genetically identical. |
Diploid and haploid cells In most organisms the body cells are diploid and the sex cells (or gametes) are haploid. |
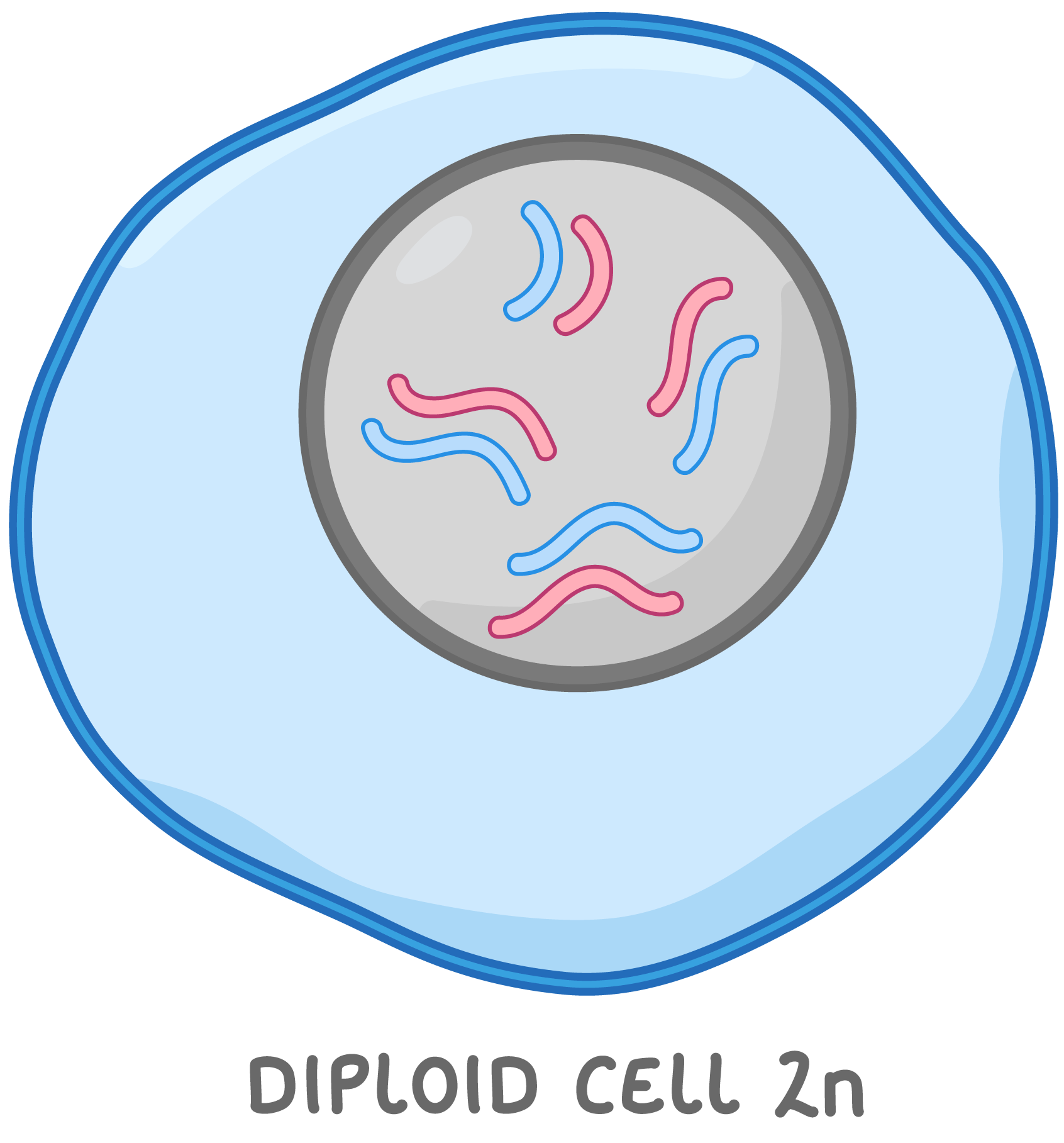 Diploid cells Diploid cells contain two copies of each chromosome, one copy from each parent. The total number of chromosomes in diploid cells is described as '2n' with 'n' representing one set of chromosomes. For example, humans have 46 chromosomes in each body cell. 23 are maternal chromosomes (from the mother) and 23 are paternal chromosomes (from the father). The diploid number for human cells is 2n = 46. Note that the diagram on the right shows only 8 chromosomes rather than the 46 chromosomes found in human diploid cells. |
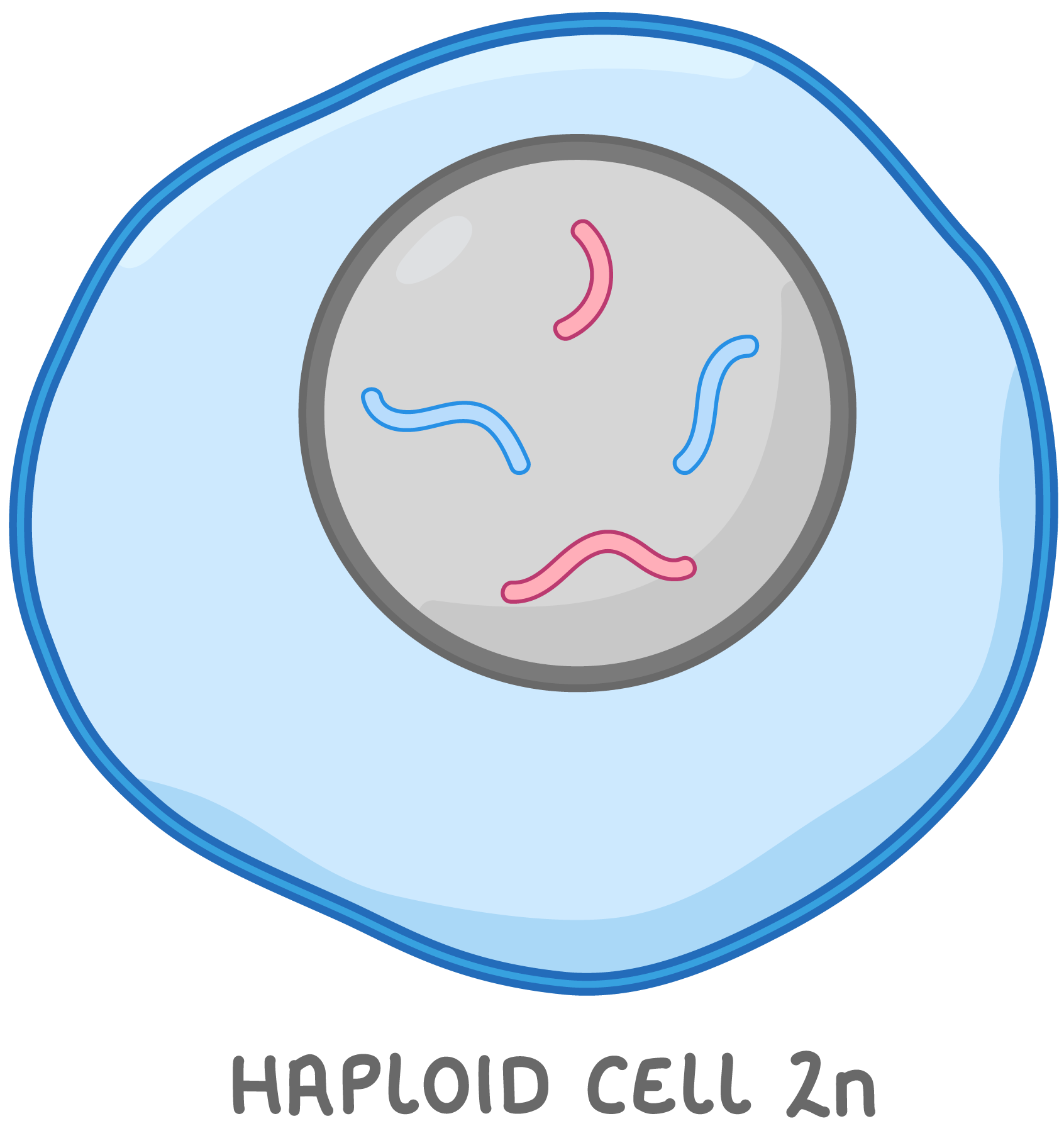 Haploid cells Haploid cells only contain one copy of each chromosome. The total number of chromosomes in haploid cells is described as 'n'. For example, human sex cells have 23 chromosomes, so n = 23. Note that the diagram on the right shows only 4 chromosomes rather than the 23 chromosomes found in human haploid cells. |