Factors Affecting the Cell Membrane
This lesson covers:
- How temperature affects membrane structure and permeability
- How solvents affect membrane structure and permeability
Different factors affect the permeability of membranes Cell membranes control the movement of substances into and out of cells (or organelles). However, changes to the structure of cell membranes can increase their permeability, allowing more substances to pass through. You need to be able to describe and explain how the following two factors affect the permeability of membranes:
|
Temperature Changes in temperature affect the movement of phospholipids and the structure of proteins in the cell membrane. 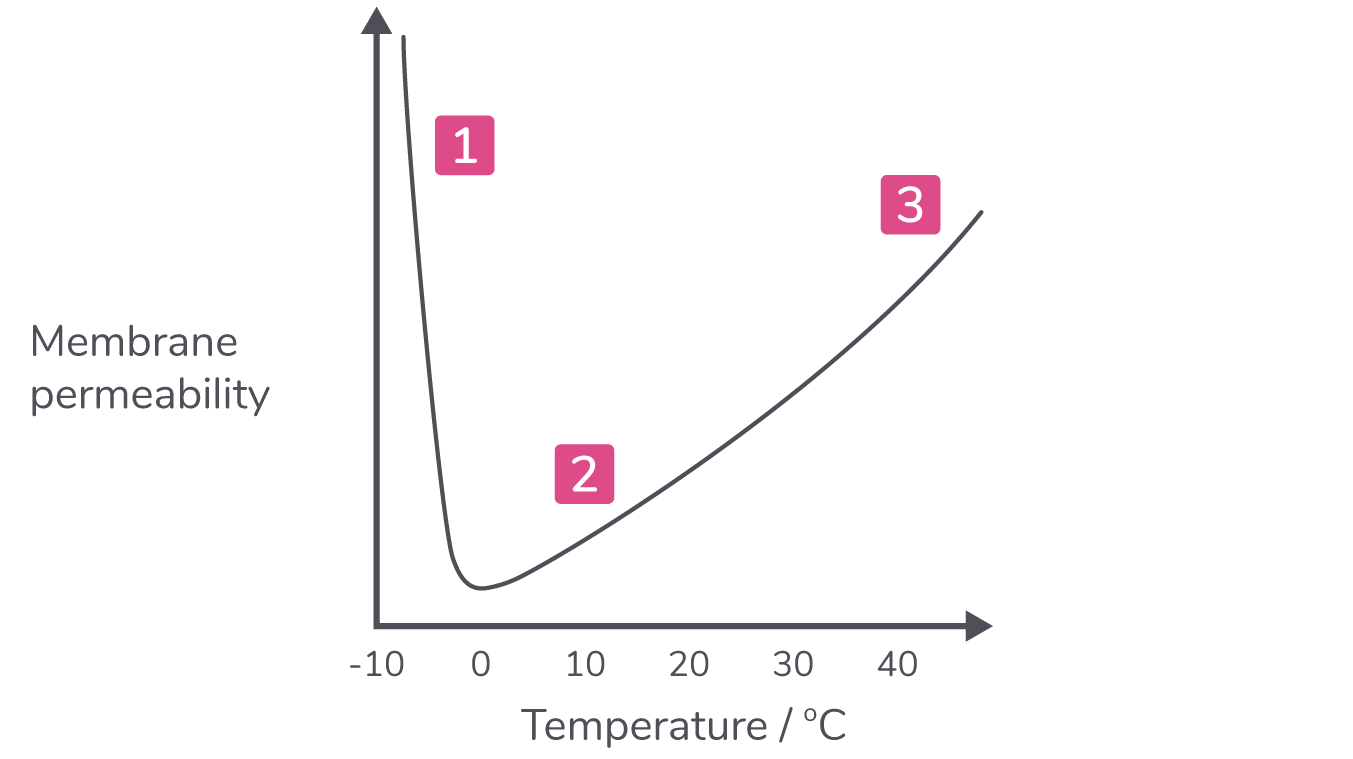 |
How temperature affects cell membranes:
|
Solvents Solvents are liquids that have the ability to dissolve substances. When cells are placed in a solvent such as ethanol, the phospholipids dissolve, causing the membrane to become more fluid. This disrupts the structure of the cell membrane to make it more permeable. Increasing the concentration of the solvent will further increase the permeability of the cell membrane. |