HIV
This lesson covers:
- The structure of HIV
- The stages of HIV replication
- How HIV causes the symptoms of AIDS
HIV structure The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a virus that weakens the immune system. The structure of this virus is shown in the diagram below. 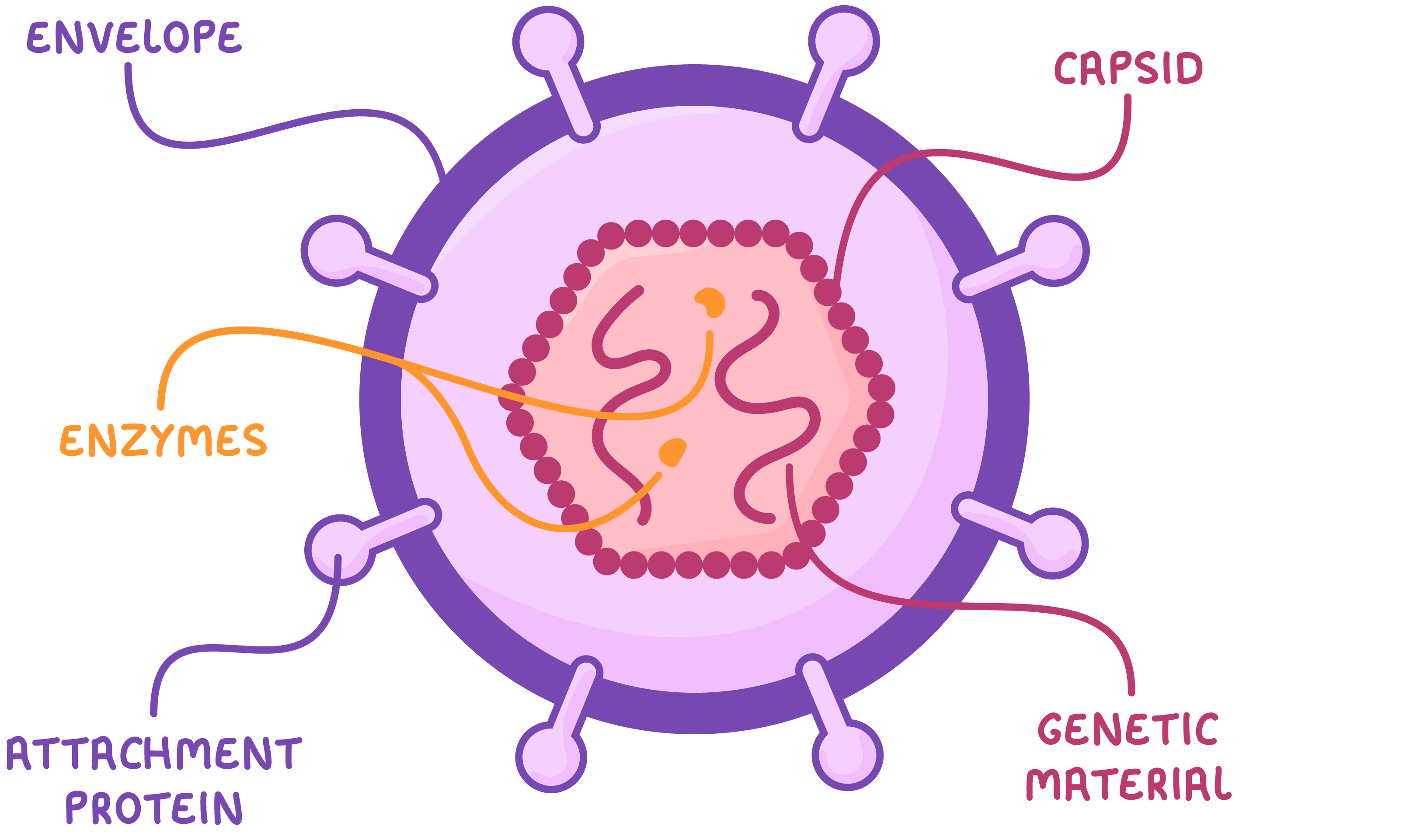 |
The virus contains the following components:
|
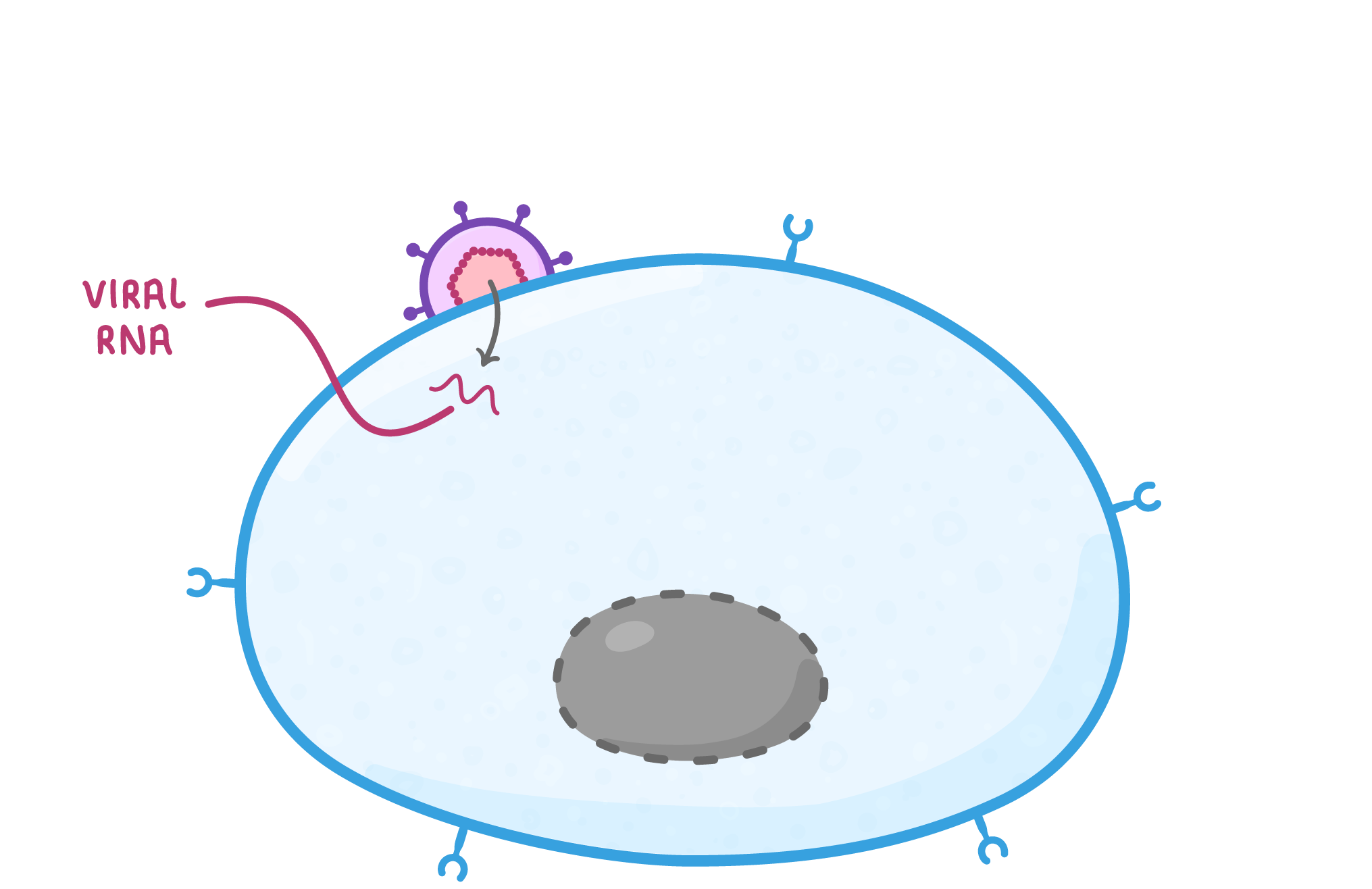
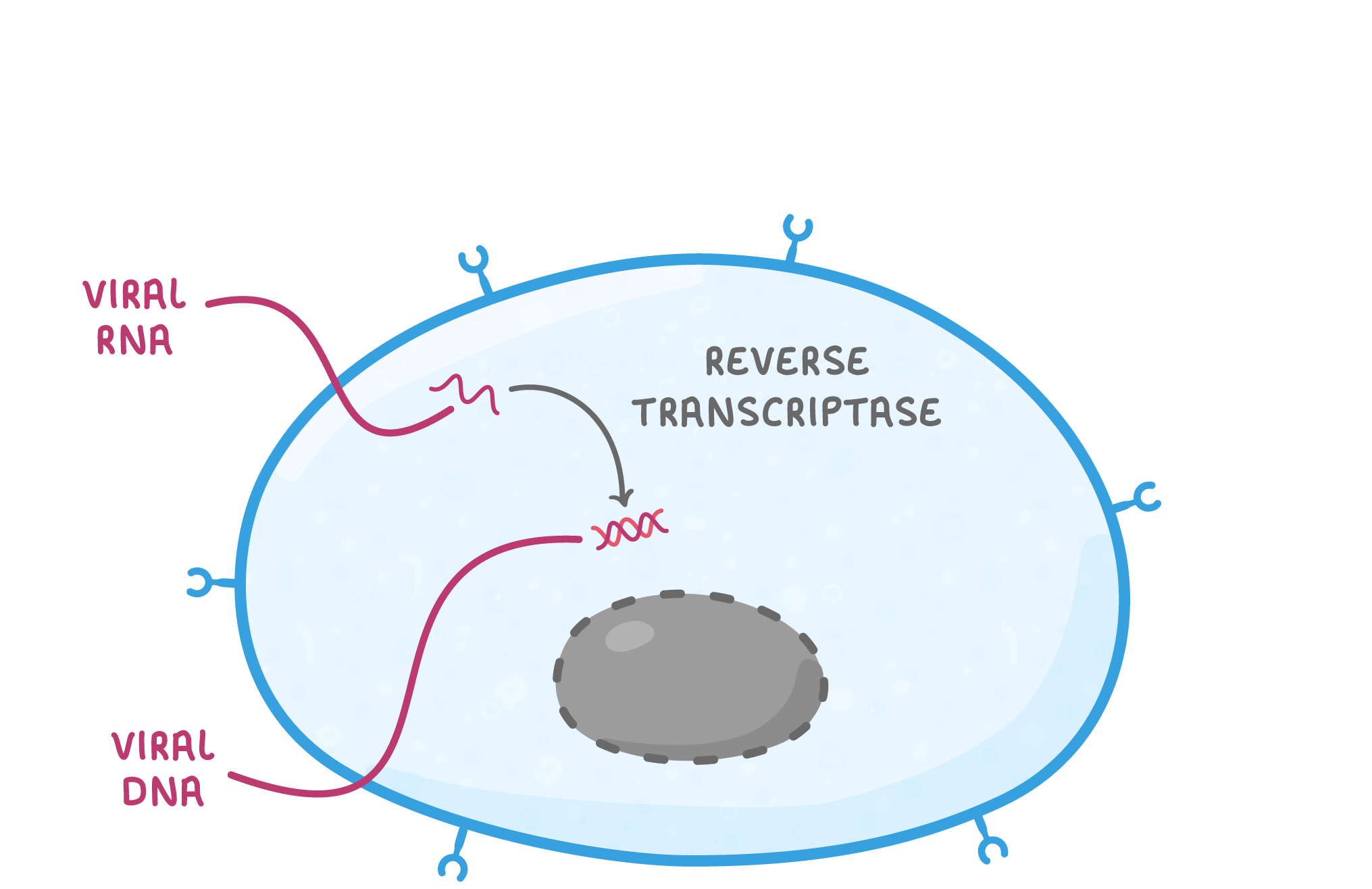
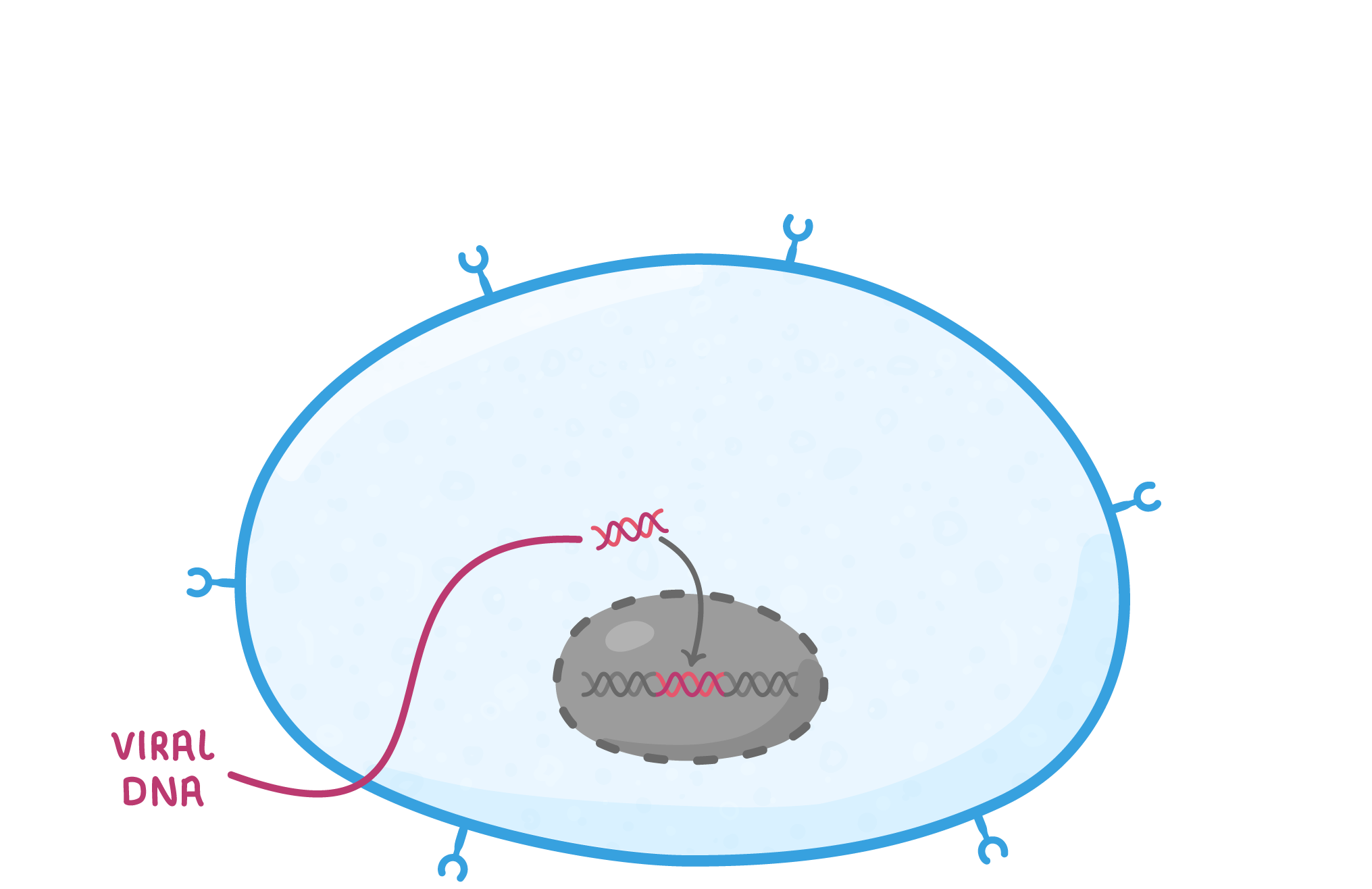
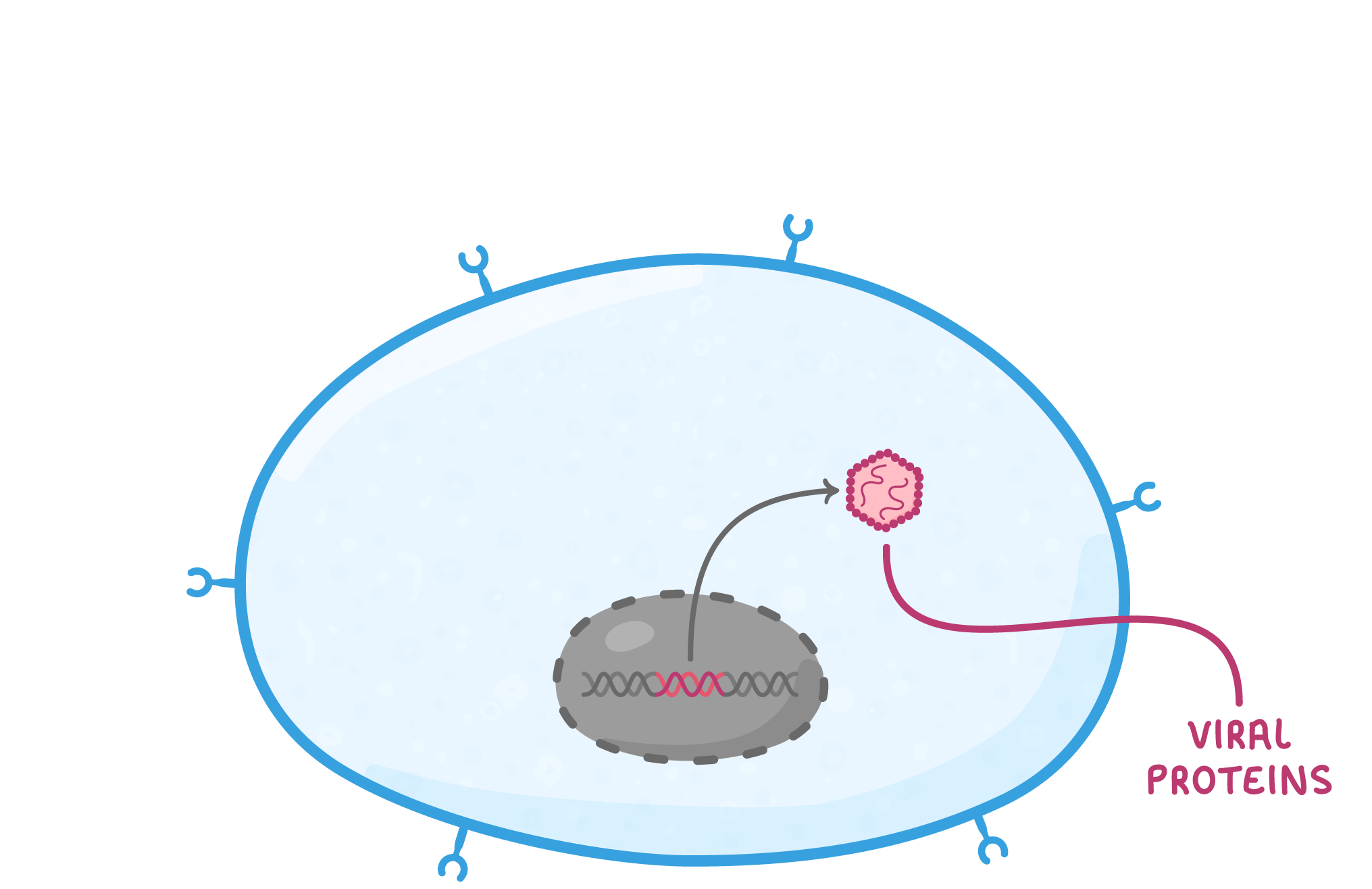
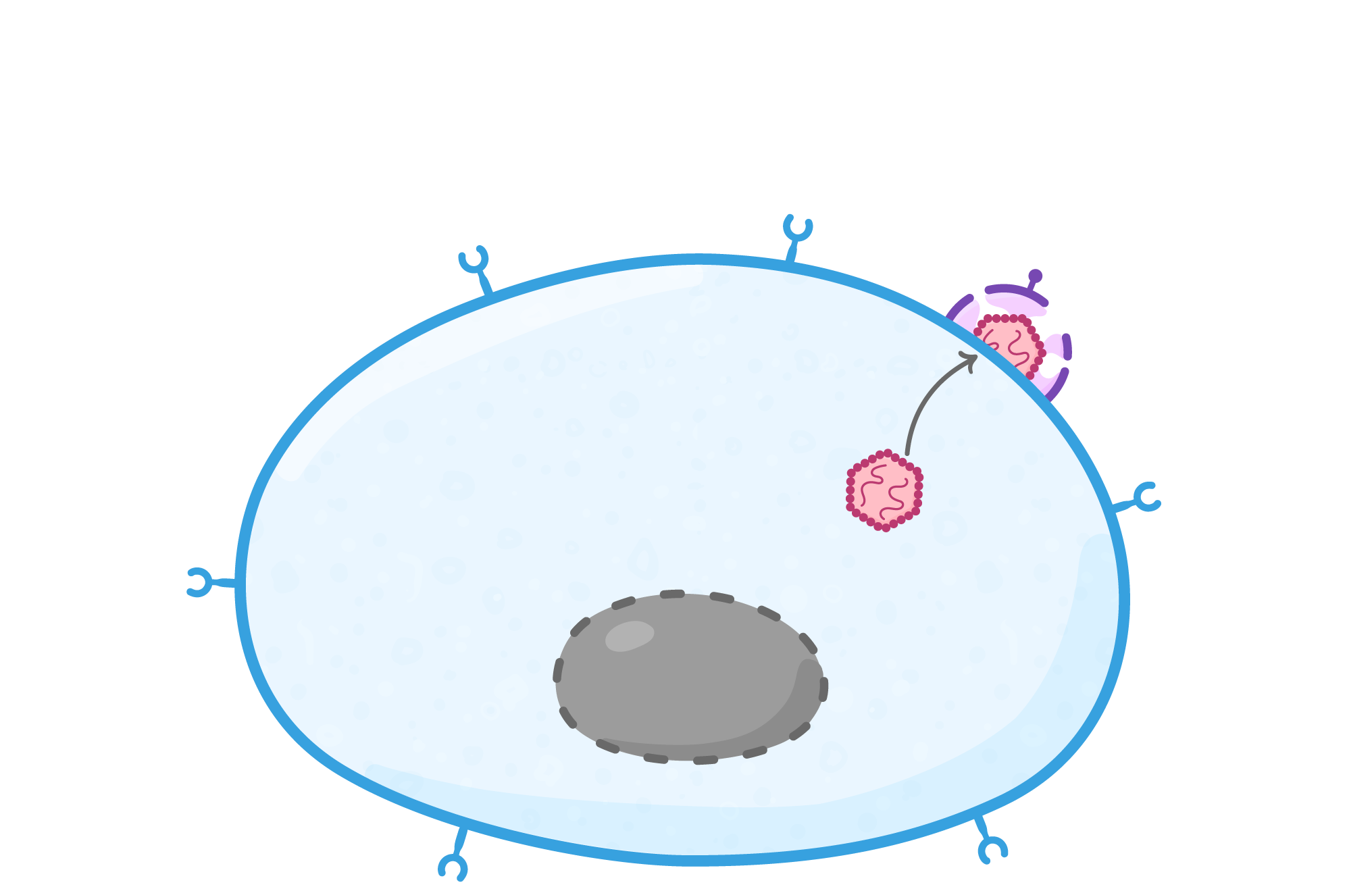
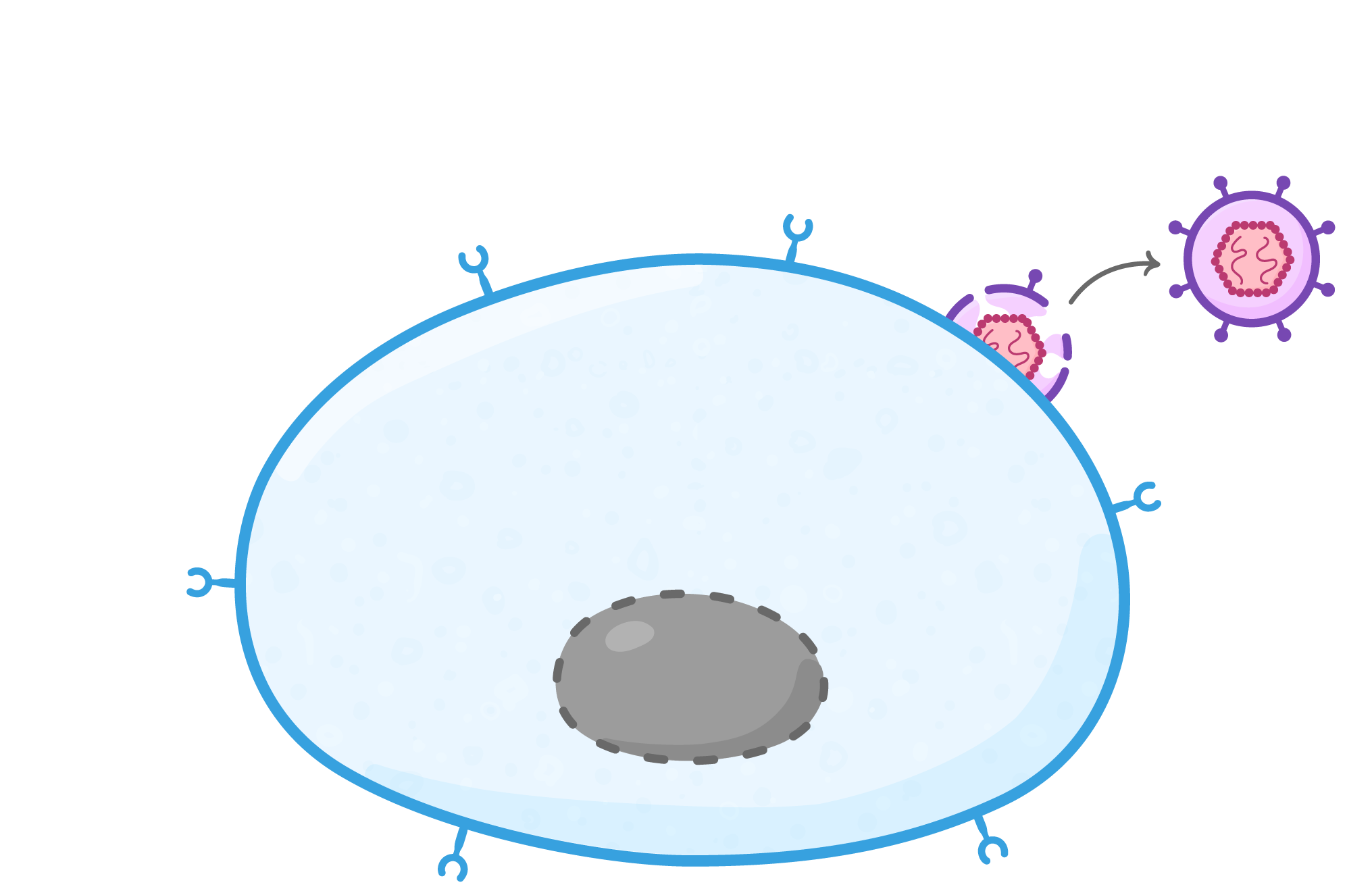
HIV replication As HIV is a virus, it cannot replicate itself and instead must use a host cell to produce new virus particles. HIV uses helper T cells as host cells, damaging the immune system of the infected individual. Their replication process is outlined below: |
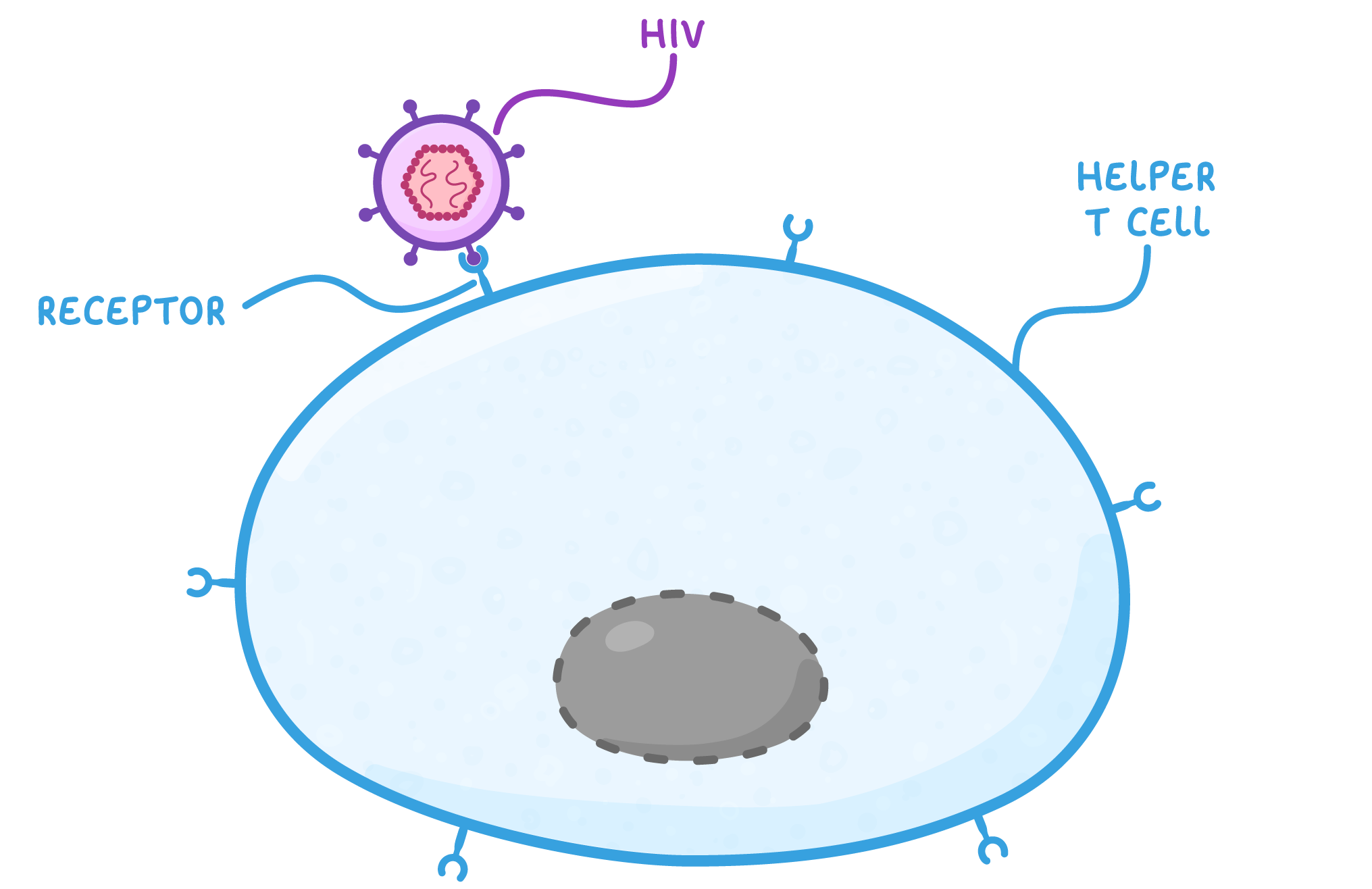 Attachment proteins on the HIV attach to receptors on a helper T cell. |
HIV and AIDS HIV infection progresses through multiple stages that may ultimately lead to the development of AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Stage 1 - Transmission
Stage 2 - Acute infection
Stage 3 - Latency period
Stage 4 - AIDS Development
Individuals with AIDS have a higher likelihood of developing various serious infections, and eventually, an opportunistic infection (e.g., pneumonia) can lead to death. AIDS also increases the risk of developing cancers. Treatment:
|