Plant Cell Organisation
This lesson covers:
- The structure of a plant leaf
- The levels of organisation in plants
The four levels of plant organisation are:
➔ tissues ➔ ➔ organ systems
|
The leaf is an example of an:
Organ system
Cell
Tissue
Organ
|
The root, stem, and leaves, together make up an:
Organ system
Tissue
Cell
Organ
|
A guard cell is an example of a:
Organ system
Organ
Tissue
Cell
|
The palisade mesophyll layer is an example of a:
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Cell
|
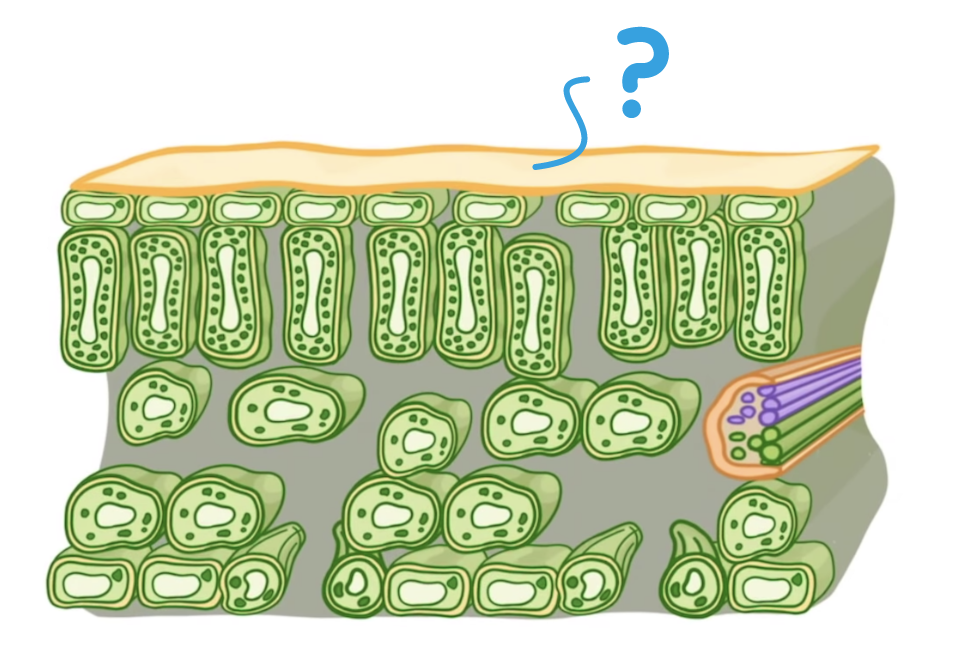
Which part of the leaf is indicated on the diagram above?
|
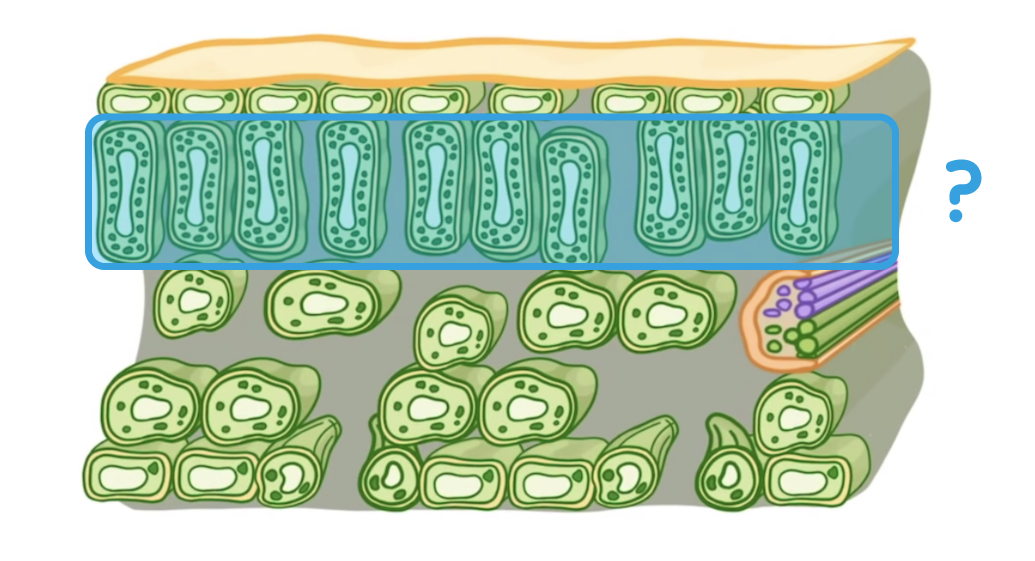
Which structure is highlighted on the diagram above?
Lower epidermis
Upper epidermis
Palisade mesophyll layer
Spongy mesophyll layer
|
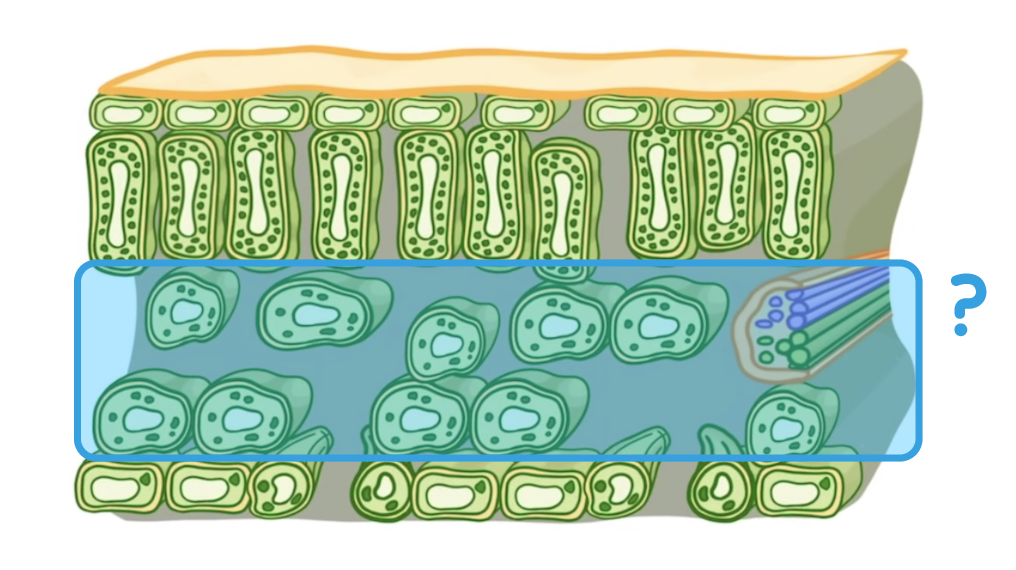
Which structure is highlighted on the diagram above?
Lower epidermis
Palisade mesophyll layer
Upper epidermis
Spongy mesophyll layer
|
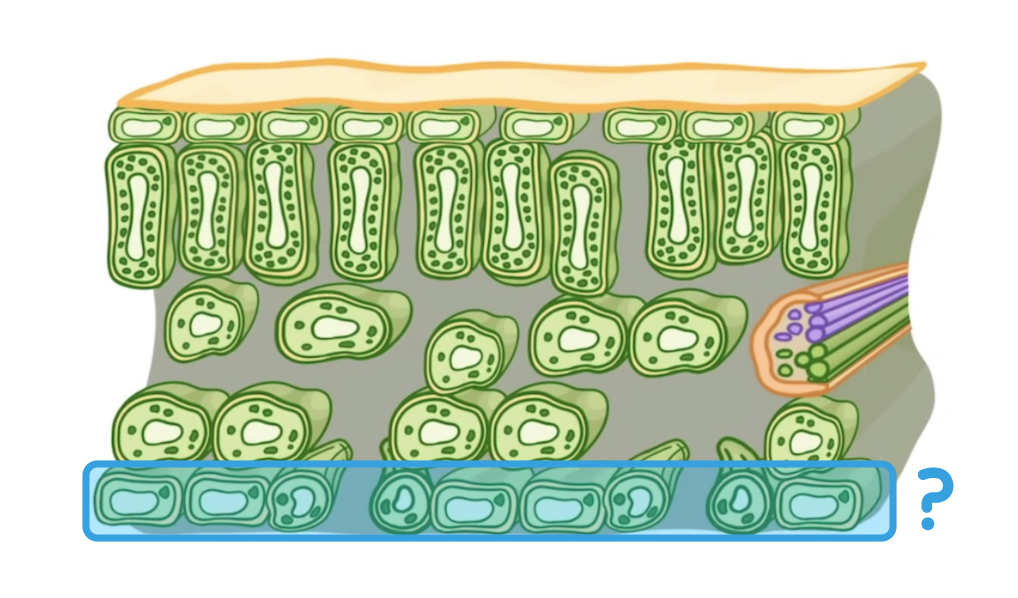
Which structure is highlighted on the diagram above?
Spongy mesophyll layer
Upper epidermis
Palisade mesophyll layer
Lower epidermis
|
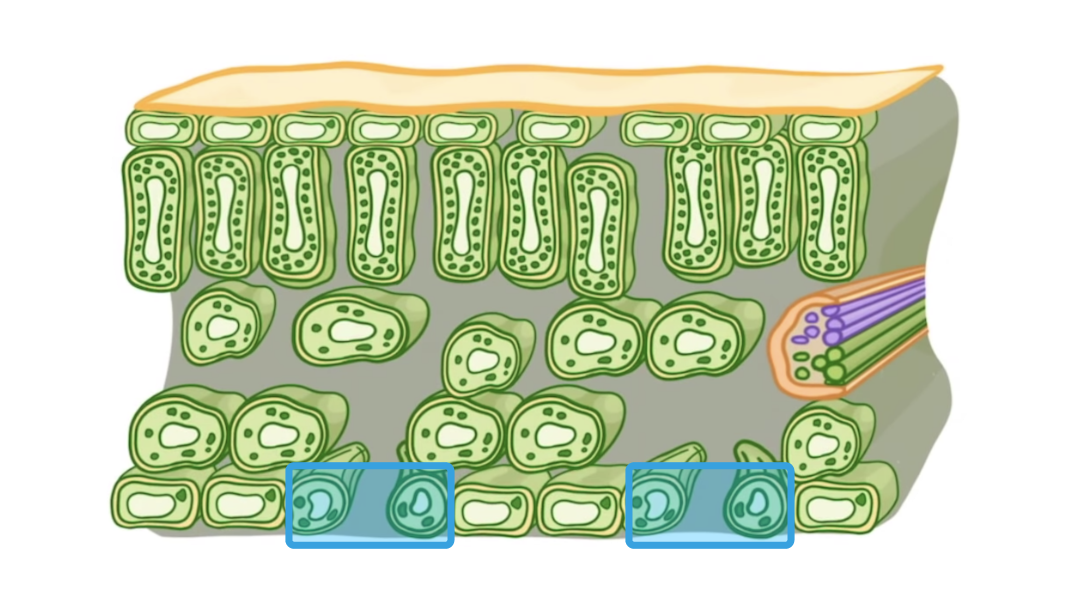
What name is given to the cells highlighted on the diagram above?
|
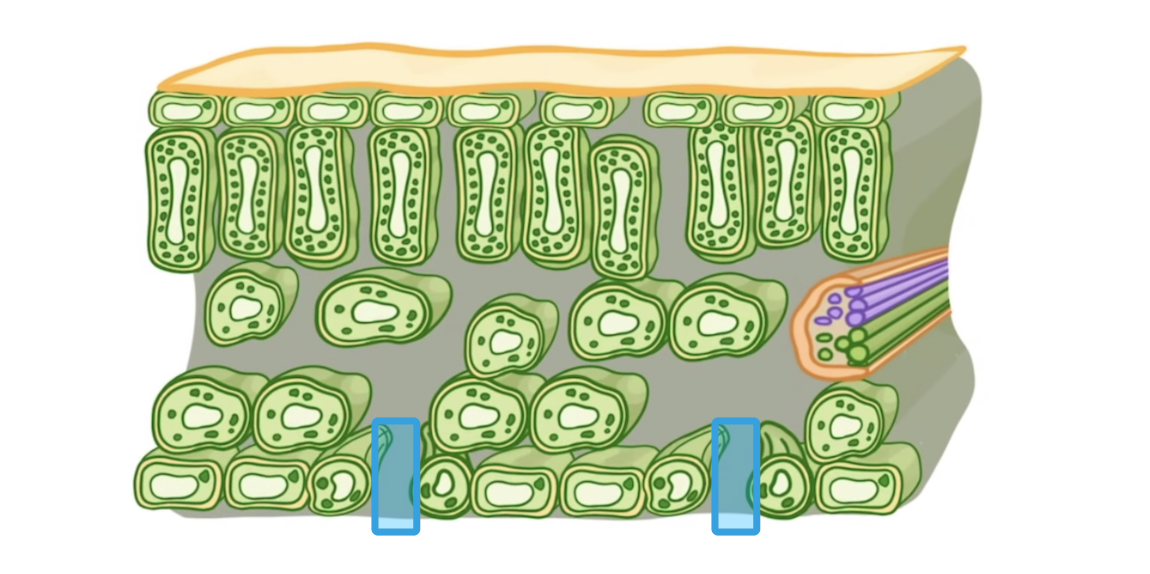
What name is given to the openings indicated on the diagram above?
|
opaque / transparent / smooth / palisade / mesophyll / guard
The upper epidermis is so that light can pass through it. This means that as much light as possible can reach the mesophyll cells below, and be used in photosynthesis.
|
Which structures help to minimise water loss?
(Select all that apply)
Transparent upper epidermis
Guard cells which can close stomata
Waxy cuticle
Lots of spongy mesophyll cells
|
flaccid / turgid / opens / closes / enter / leave
If there is plenty of water in the leaf, guard cells become , which the stomata. This allows carbon dioxide to the leaf, but also allows water to escape.
|
At night time, when photosynthesis can't take place, are the stomata normally open or closed?
Open
Closed
|
What is meristem tissue and where is it found?
|