Eyes 1 - Structure & Iris Reflex
This lesson covers:
- The different structures in the eye
- How the eye responds to light in the iris reflex
- The roles of the circular and radial muscles in the iris
What is the cornea?
A transparent layer at the front of the eye which refracts light
The coloured part of the eye
The gap through which light passes to reach the lens
|
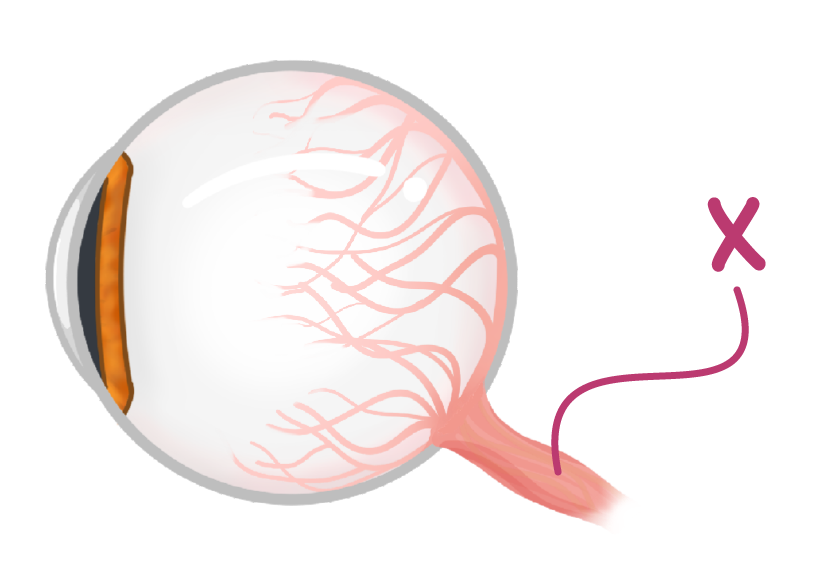
The diagram above shows the labelled as 'X'.
|
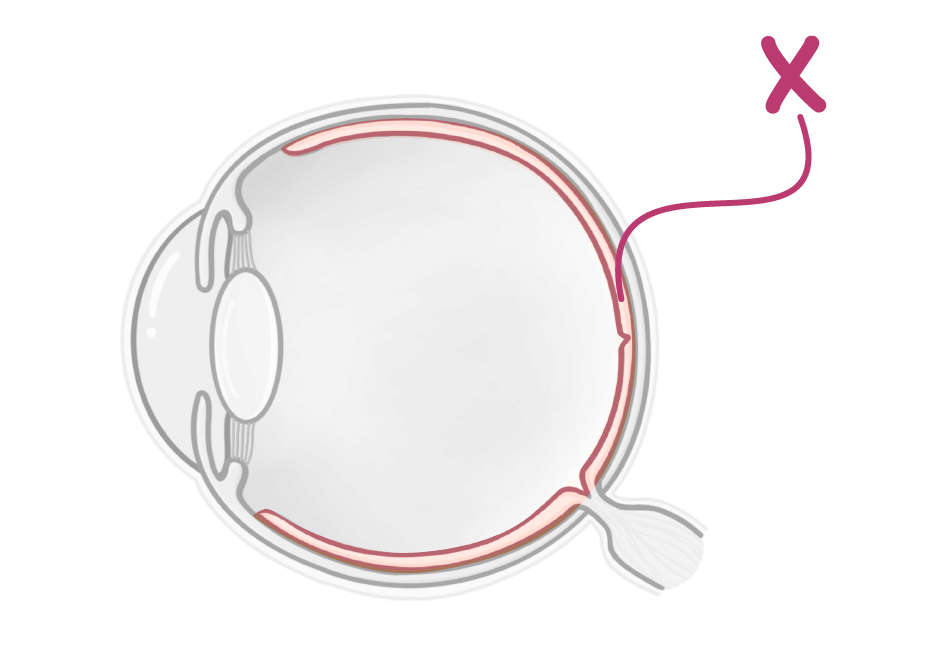
What is the structure labelled X in the image above?
Cornea
Ciliary muscle
Retina
Iris
|
What is the pupil?
A transparent layer at the front of the eye which refracts light
The coloured part of the eye
The gap through which light passes to reach the lens
|
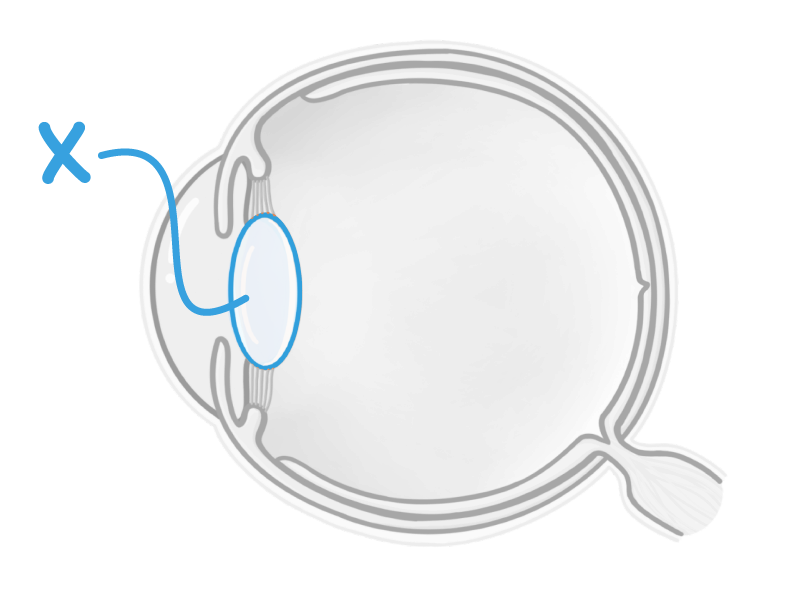
What is the structure labelled X in the image above?
Optic nerve
Ciliary muscle
Suspensory ligament
Lens
|
What are the names of the two types of receptor cells in the retina?
Prism cells
Cone cells
Rod cells
Cube cells
|
Which light-sensitive cells in the retina enable you to see in colour?
Rod cells
Cone cells
|
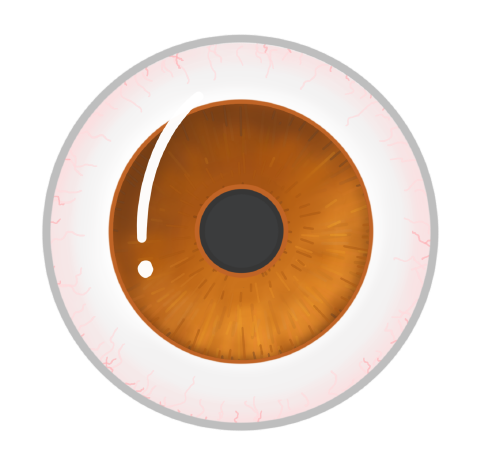

The eye is a sense organ. Which two stimuli are the receptor cells of the eye sensitive to?
Temperature
Light intensity
Colour
Vibration
|
Which light sensitive cells in the retina enable you to see in the dark?
Cone cells
Rod cells
|
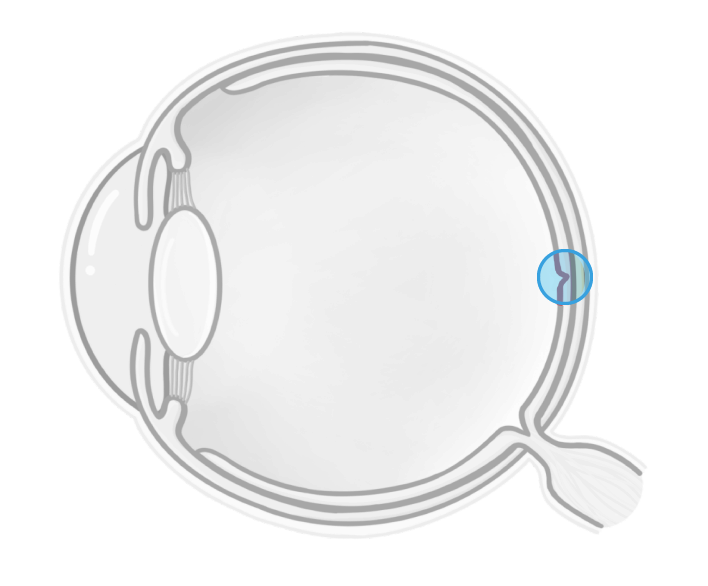
The point where light focuses on the retina is called the . This region contains the highest concentration of cone cells and gives the sharpest image.
|
What is the purpose of the iris reflex?
To prevent dust from entering the eye
To ensure the optimum amount of light enters the eye
To focus on light from different distances
|
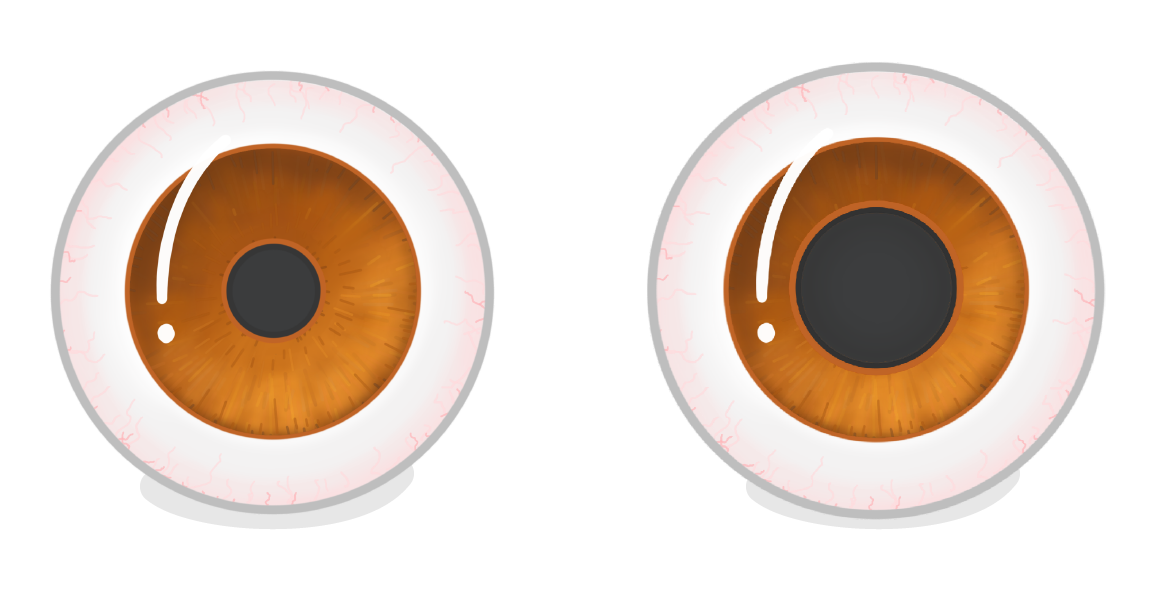

When the pupil is very large, do we describe it as 'constricted' or 'dilated'?
Constricted
Dilated
|
Which two muscles make up the iris?
Linear muscles
Round muscles
Radial muscles
Circular muscles
|
When the eye is exposed to bright light, will the pupil constrict or dilate?
Constrict
Dilate
|
What happens to the circular and radial muscles when the pupil constricts?
(Select all that apply)
The circular muscle relaxes
The radial muscle relaxes
The circular muscle contracts
The radial muscle contracts
|