DNA 1 - Chromosomes, Genome & Migration
This lesson covers:
- What 'DNA' is
- What 'chromosomes' are
- What we mean by the term 'genome', and why understanding the concept is important
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxynuclear acid
Ribonucleic acid
|
DNA has a double helix structure. How many strands is the helix made up of?
1
2
3
|
The DNA in typical human cell is found in tight coils known as .
|
How many chromosomes are there in a typical human cell?
|
Chromosomes exist in pairs. The chromosomes in the 23rd pair are known as the _____________
Sex chromosomes
Determinant chromosomes
Last chromosomes
|
Do women have XX or XY sex chromosomes?
XX
XY
|
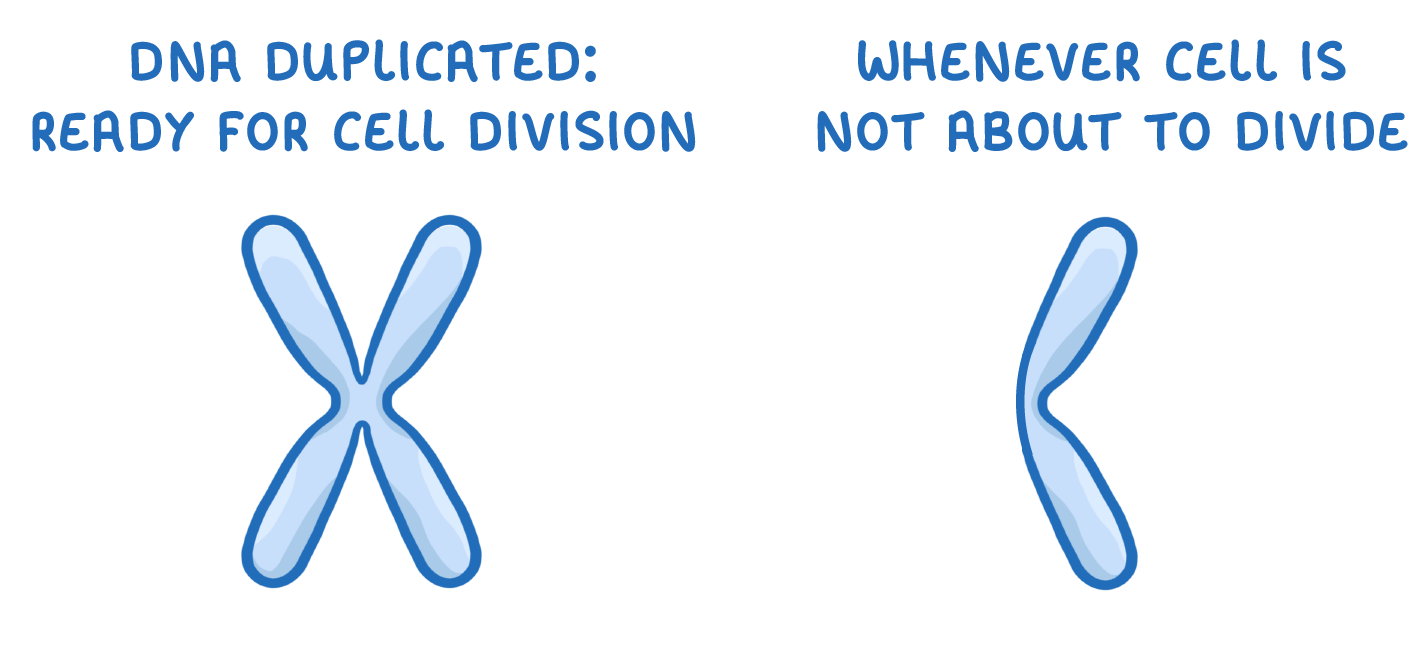
Remember that chromosomes only have an 'X' shape when the DNA has been duplicated ready for cell division. The rest of the time, they will look more like like an 'l'.
What is being described in the following statement?
"A small section of DNA that codes for a specific protein"
|
DNA can code for proteins by coding for the sequence in which acids are joined together.
|
What does the term 'genome' mean?
The entire set of genetic material in an organism
The observable characteristics of an organism
The sequence of amino acids in a protein
|
Some genes can cause specific diseases. We call these _________ diseases.
spontaneous
inherited
communicable
|
True or false? Understanding the genomes of different people around the world can tell us about the migration patterns of our ancestors.
True
False
|